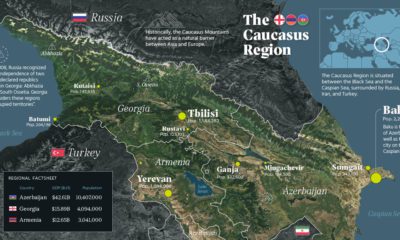
202 Drought Maps of California Show How Dry It Is
If there is one thing we are tuned in here to at Visual Capitalist, it is the value of all natural resources: from metals and energy to fresh water. With population, money, and economic growth all happening at exponential rates, and only a limited amount of underlying resources, there are problems abound. We had a previous post discussing the possibility of Peak Water as well, and it is something we are also addressing in our editorial calendar with an upcoming original infographic series on overpopulation. California has been the victim of years of drought now, and it has cost the state dearly. It’s expected to cost , with the loss of 17,000 jobs as farmers must fallow their regular cash crops. The Week published an interesting excerpt about the impact of the drought on California aquifers and infrastructure: Nearly 75% of all California fresh water comes from the Sierra Nevada snowpack, and right now it is reduced to only about 20% of its usual size. Sadly, we expect fresh water problems to be more common in the future as aquifers get depleted and climate changes happen. Original graphic from: The LA Times
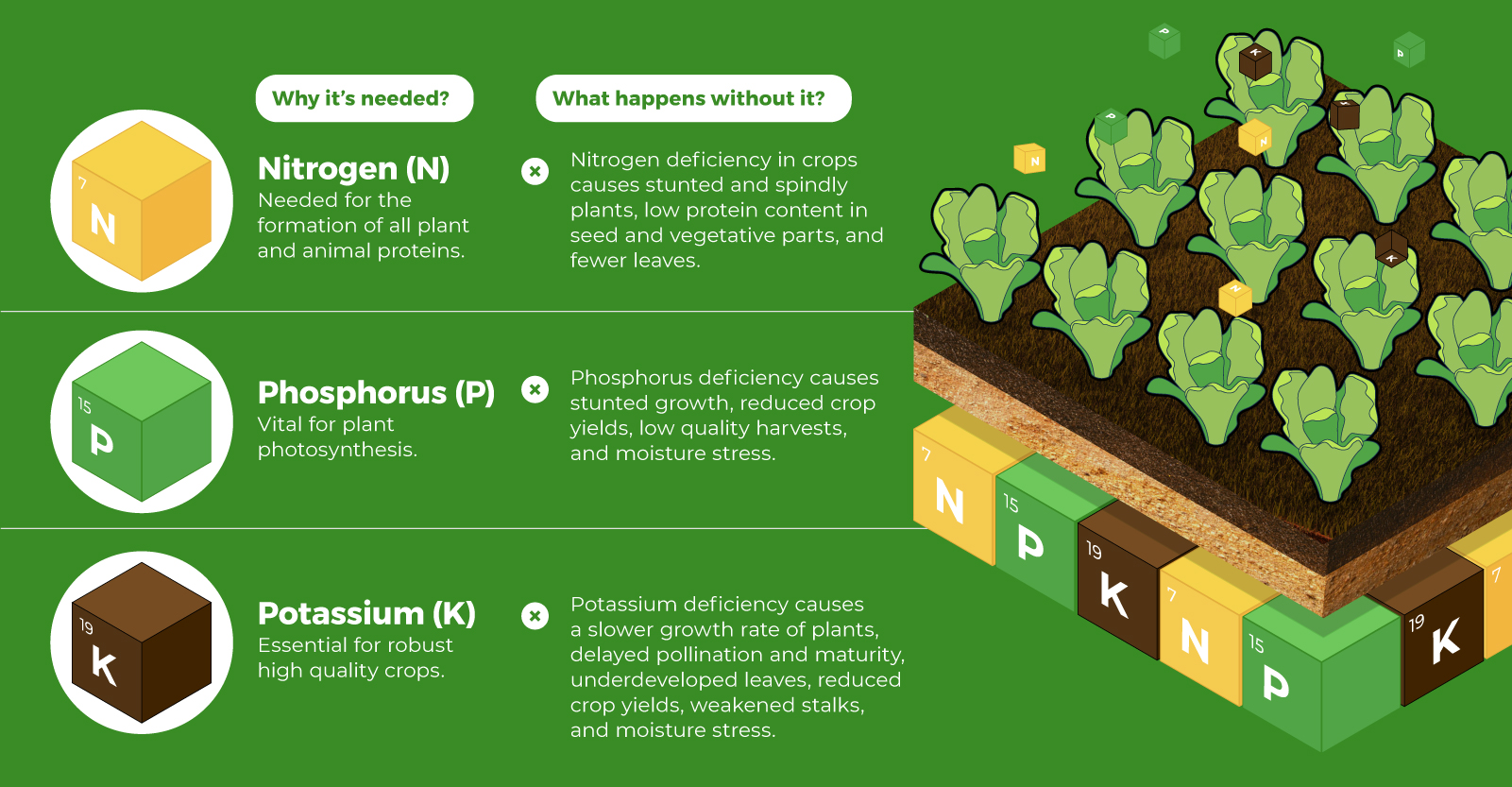
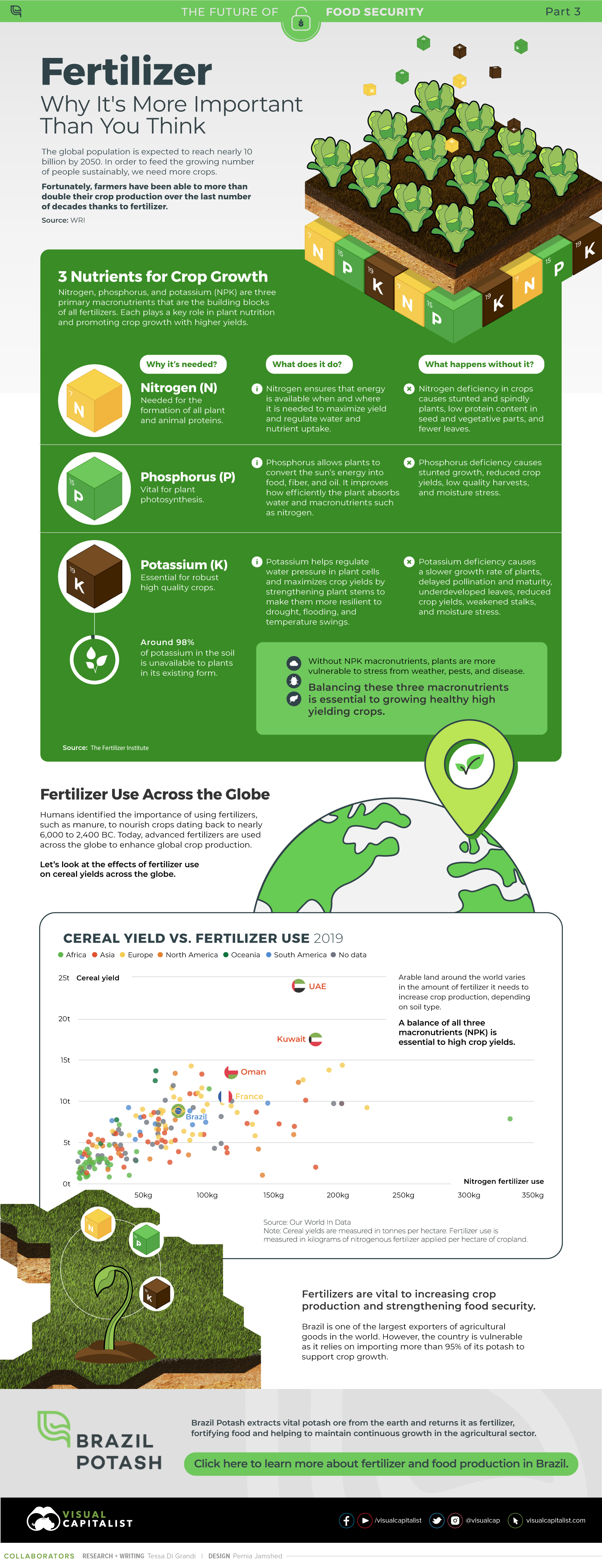
on Over recent decades, farmers have been able to more than double their production of crops thanks to fertilizers and the vital nutrients they contain. When crops are harvested, the essential nutrients are taken away with them to the dining table, resulting in the depletion of these nutrients in the soil. To replenish these nutrients, fertilizers are needed, and the cycle continues. The above infographic by Brazil Potash shows the role that each macronutrient plays in growing healthy, high-yielding crops.
Food for Growth
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK) are three primary macronutrients that are the building blocks of the global fertilizer industry. Each plays a key role in plant nutrition and promoting crop growth with higher yields. Let’s take a look at how each macronutrient affects plant growth. If crops lack NPK macronutrients, they become vulnerable to various stresses caused by weather conditions, pests, and diseases. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain a balance of all three macronutrients for the production of healthy, high-yielding crops.
The Importance of Fertilizers
Humans identified the importance of using fertilizers, such as manure, to nourish crops dating back to nearly 6,000 to 2,400 BC. As agriculture became more intensive and large-scale, farmers began to experiment with different types of fertilizers. Today advanced chemical fertilizers are used across the globe to enhance global crop production. There are a myriad of factors that affect soil type, and so the farmable land must have a healthy balance of all three macronutrients to support high-yielding, healthy crops. Consequently, arable land around the world varies in the amount and type of fertilizer it needs. Fertilizers play an integral role in strengthening food security, and a supply of locally available fertilizer is needed in supporting global food systems in an ever-growing world. Brazil is one of the largest exporters of agricultural goods in the world. However, the country is vulnerable as it relies on importing more than 95% of its potash to support crop growth. Brazil Potash is developing a new potash project in Brazil to ensure a stable domestic source of this nutrient-rich fertilizer critical for global food security. Click here to learn more about fertilizer and food production in Brazil.