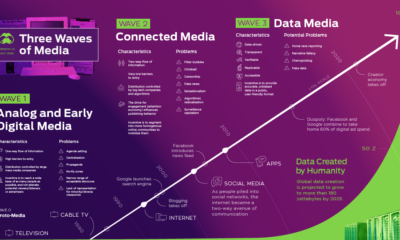
While “data is the new oil” has almost become a cliché, the impact that data abundance is having on the world is undeniable. All of the world’s most valuable companies are heavily reliant on data for their continued success. Even oil giant Saudi Aramco, the world’s most valuable company, runs a 6,000 m² data center, and is partnering with Google Cloud. In a world where nearly everything is quantified, communicating insights from that data becomes a massive opportunity. This is where data storytelling comes in. In simple terms, it’s the difference between simply making a chart, and actually explaining what it means, why it’s important, and how it fits into the broader context. This style of data-driven communication is cropping up everywhere, from newsrooms to corporate communications. Here, we examine five megatrends fueling the rise of data storytelling.
① Information Overload
It’s estimated that between 2015 and 2025, the world will see a 16-fold increase in data.
The bad news: The rising tide of information is growing faster than our ability to harness it The good news: This growing universe of data holds the promise of more insight, if properly utilized
Thankfully, data storytelling is an emerging field that thrives on information abundance. As our society and economy grow more complex, more high-quality, actionable information is critical for today’s decision makers.
② Declining Trust in Media
Trust in news media has been declining for decades, and in many countries around the world, the majority of people don’t feel that media is a trustworthy source of information. Trust in social media is similarly shaky. Only one-third of people surveyed around the world believe that social media is a trustworthy source of information. As well, a recent poll found that 75% of U.S. adults felt that political views were likely being censored by social media platforms. The mass media ecosystem as it currently exists is facing a crisis of confidence. When a system is no longer adequately serving the needs of its users, that system is ripe for disruption.
③ Winner-Take-All Dynamics
This information abundance should be propelling humankind forward, but more often than not, valuable insights are lost in the noise—either poorly presented or pushed to the margins by clickbait and other distractions. Today, most of us rely on algorithms and aggregators to deliver information to us. Over time, those systems become very good at feeding us information that is generally what we’re looking for. The downside, however, is that engagement-driven algorithms reward only the most compelling narratives. The handful of stories you see are the result of fierce, darwinistic competition on platforms like Twitter or Medium. This hyper-competitive environment is part of the reason there are so many problems with media today—clickbait and tabloidization being two prominent examples. Data storytelling takes potentially dry, complex topics and makes them more accessible, compelling, and more likely to win the battle for people’s attention.
④ Moving Beyond Text
Many of our existing systems look the way they do in part because of past technological limitations. Search engines, for example, are still largely driven by text-based considerations. This makes sense as the early internet was essentially a collection of pages with text and hyperlinks. Today, search engines are much better taking other forms of information into consideration, and technological advancements are breaking new ground in analyzing video and data visualizations. Advancements in AI could soon allow users to search for visualizations in ways that don’t even involve text keywords. In a future where searching for information in a visual format is as intuitive as a Google search today, the utility and reach of data storytelling will increase dramatically.
⑤ Democratization of Data Storytelling
Even as the number of people with professional credentials in data analytics, data science, and other similar professions is on the rise, it’s never been easier for laypersons to create and publish high quality visualizations. Free tools which are usable on almost any device have broken down barriers of access for millions of people around the world. There is now a universe of resources for people and organizations looking to convert data into a compelling visual format. Below is a shortlist of data storytelling resources ranging from the intuitive design tools to powerful coding language libraries: Of course there are many more resources out there, and we’ll be covering this more comprehensively in the future.
The Last Mile
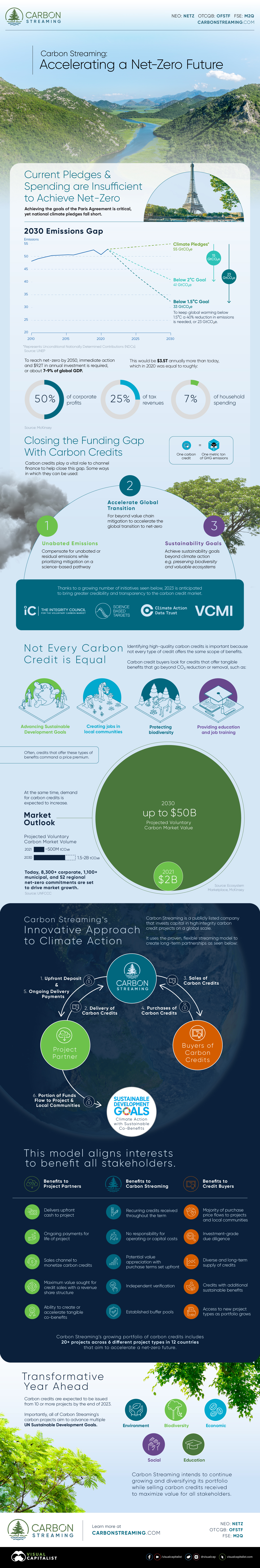
This last mile analogy lends itself to communication as well. Analytics and datasets can be polished and made publicly accessible, but the real world is messy. Humans are unpredictable, each with their own style of learning and varying levels of data literacy. Also, unlike e-commerce—which begins with a defined request—insight comes in unexpected flashes. Those moments of serendipity need the right conditions to occur, and the fact of the matter is, most sources of high quality information (databases, white papers, reports, etc.) are only accessed by the small number of people who conduct research for a living. This is the great opportunity presented by data storytelling. High quality information is distilled into a form that is more digestible, memorable, and sharable, allowing more people to benefit from this era of information abundance. Put simply: data storytelling bridges the gap between under-utilized knowledge and the growing number of people who are striving to separate the signal from the noise. on To reach net-zero by 2050, immediate action and $9.2 trillion in annual investment is required, or about 7-9% of global GDP. This would be $3.5 trillion annually more than today, which in 2020 was equal to roughly:
50% of corporate profits25% of tax revenues7% of household spending
This infographic sponsored by Carbon Streaming Corporation shows how carbon credits can help accelerate a net-zero future by funding climate action.
Closing the Funding Gap With Carbon Credits
Carbon credits play a vital role in channelling finance to help close this funding gap. Here are some ways in which carbon credits can be used: Thanks to a growing number of initiatives listed below, 2023 is anticipated to bring greater credibility and transparency to the carbon credit market.
The Integrity Council for the Voluntary Carbon MarketScience Based Targets initiative (SBTi)Climate Action Data TrustVoluntary Carbon Markets Integrity Initiative
Not Every Carbon Credit is Equal
Identifying high-quality carbon credits is important because not every type of credit offers the same scope of benefits. Carbon credit buyers look for credits that offer tangible benefits that go beyond CO₂ reduction or removal, such as:
Advancing Sustainable Development GoalsCreating jobs in local communitiesProtecting biodiversityProviding education and job training
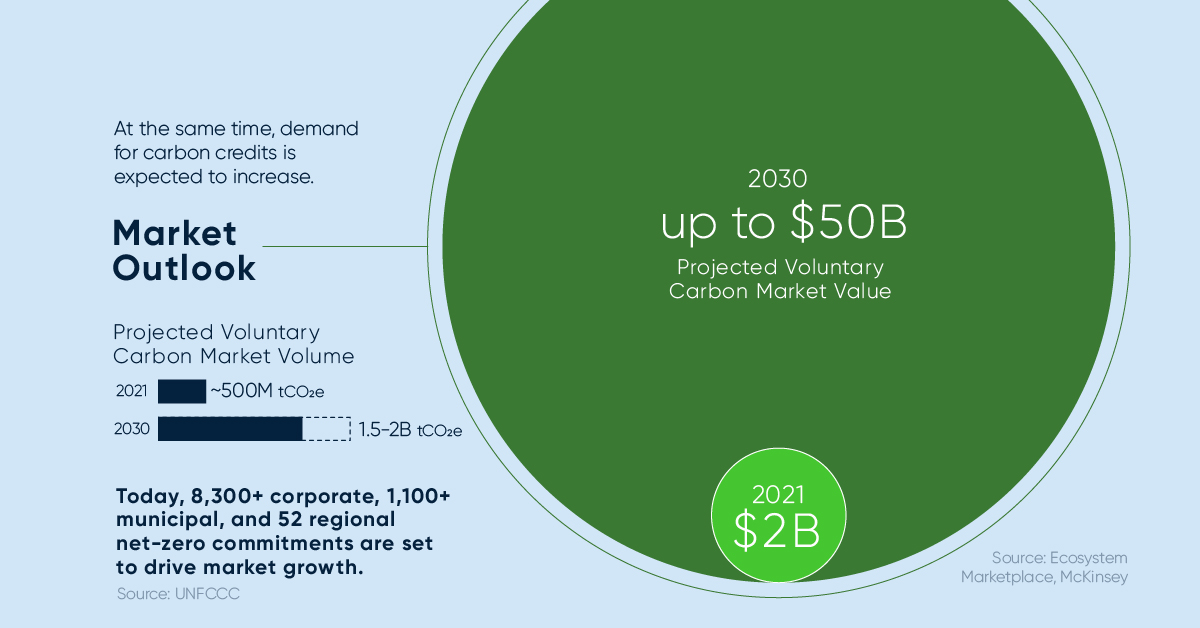
Often, credits that offer these types of benefits command a price premium. At the same time, demand for carbon credits is expected to increase. Within the decade, the value of the voluntary carbon market could grow from $2 billion up to $50 billion. Voluntary carbon markets refer to the transactions in which carbon credits are purchased by corporate and other buyers that voluntarily (not required by a regulatory act) want to compensate for their emissions or advance sustainability goals.
Source: Ecosystem Marketplace, McKinsey, UNFCCC Today, over 8,300 corporate, 1,100 municipal, and 52 regional net-zero commitments are set to drive market growth.
Carbon Streaming’s Innovative Approach to Climate Action
Carbon Streaming is a publicly listed company that invests capital in high integrity carbon credit projects on a global scale. It uses the proven, flexible streaming model to create long-term partnerships. This model aligns interests to benefit all stakeholders. Carbon Streaming’s growing portfolio of carbon credits includes over 20 projects across six different project types in 12 countries that aim to accelerate a net-zero future.
Transformative Year Ahead
By the end of 2023, carbon credits are expected to be issued from 10 or more projects. Importantly, all of Carbon Streaming’s carbon projects aim to advance multiple UN Sustainable Development Goals. Carbon Streaming intends to continue growing and diversifying its portfolio while selling carbon credits received to maximize value for all stakeholders.
Interested in learning more about Carbon Streaming? Click here to learn more.