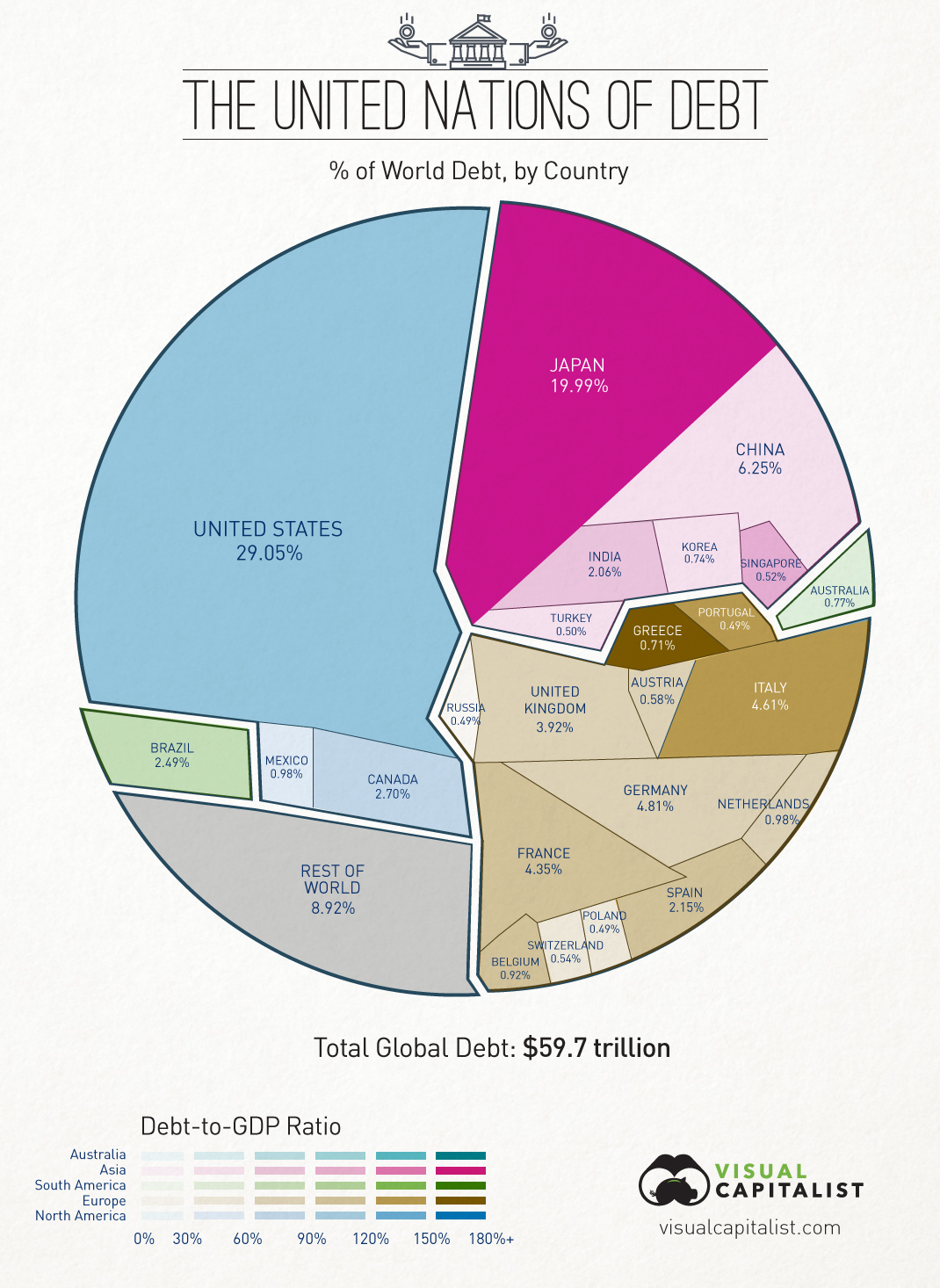
$60 Trillion of World Debt in One Visualization
Two weeks ago, we published a post showing the world economy in one visualization. In the corresponding comments section, a user asked us if we could put together a similar visualization but instead honing in on world debt. Today’s visualization breaks down $59.7 trillion of world debt by country, as well as highlighting each country’s debt-to-GDP ratio using colour. The data comes from the IMF and only covers public government debt. It excludes the debt of country’s citizens and businesses, as well as unfunded liabilities which are not yet technically incurred yet. All figures are based on USD. The numbers that stand out the most, especially when comparing to the previous world economy graphic:
The United States constitutes 23.3% of the world economy but 29.1% of world debt. It’s debt-to-GDP ratio is 103.4% using IMF figures. Japan makes up only 6.18% of total economic production, but has amounted 19.99% of global debt. China, the world’s second largest economy (and largest by other measures), accounts for 13.9% of production. They only have 6.25% of world debt and a debt-to-GDP ratio of 39.4%. 7 of the 15 countries with the most total debt are European. Together, excluding Russia, the European continent holds over 26% of total world debt.
Combining the debt of the United States, Japan, and Europe together accounts for 75% of total global debt.
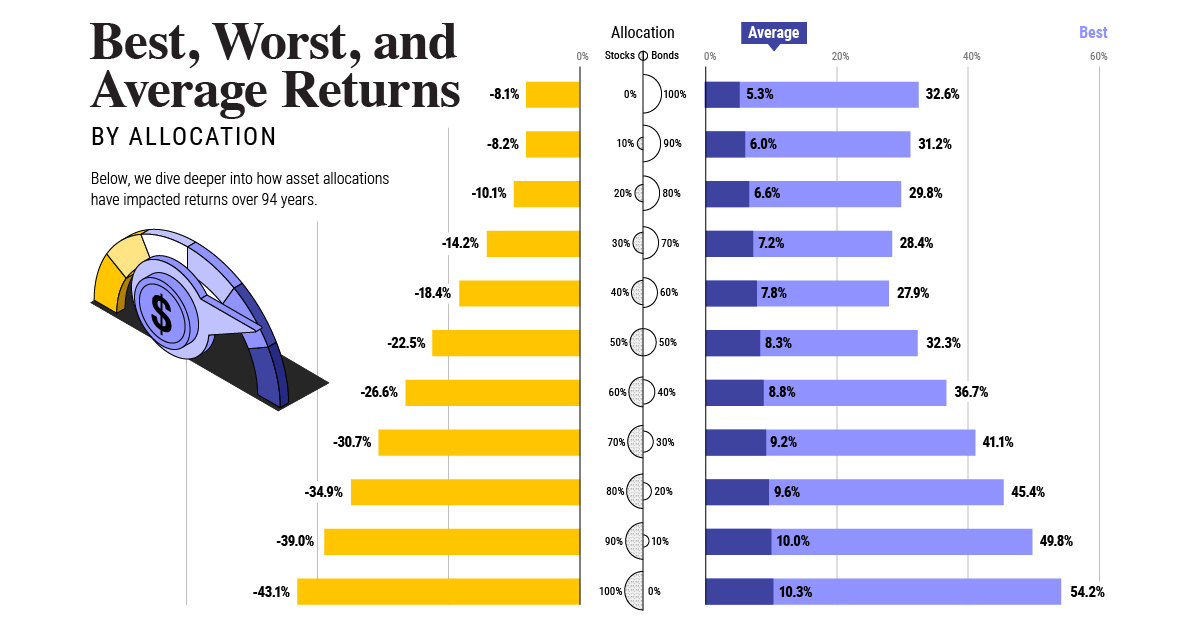
on Last year, stock and bond returns tumbled after the Federal Reserve hiked interest rates at the fastest speed in 40 years. It was the first time in decades that both asset classes posted negative annual investment returns in tandem. Over four decades, this has happened 2.4% of the time across any 12-month rolling period. To look at how various stock and bond asset allocations have performed over history—and their broader correlations—the above graphic charts their best, worst, and average returns, using data from Vanguard.
How Has Asset Allocation Impacted Returns?
Based on data between 1926 and 2019, the table below looks at the spectrum of market returns of different asset allocations:
We can see that a portfolio made entirely of stocks returned 10.3% on average, the highest across all asset allocations. Of course, this came with wider return variance, hitting an annual low of -43% and a high of 54%.
A traditional 60/40 portfolio—which has lost its luster in recent years as low interest rates have led to lower bond returns—saw an average historical return of 8.8%. As interest rates have climbed in recent years, this may widen its appeal once again as bond returns may rise.
Meanwhile, a 100% bond portfolio averaged 5.3% in annual returns over the period. Bonds typically serve as a hedge against portfolio losses thanks to their typically negative historical correlation to stocks.
A Closer Look at Historical Correlations
To understand how 2022 was an outlier in terms of asset correlations we can look at the graphic below:
The last time stocks and bonds moved together in a negative direction was in 1969. At the time, inflation was accelerating and the Fed was hiking interest rates to cool rising costs. In fact, historically, when inflation surges, stocks and bonds have often moved in similar directions. Underscoring this divergence is real interest rate volatility. When real interest rates are a driving force in the market, as we have seen in the last year, it hurts both stock and bond returns. This is because higher interest rates can reduce the future cash flows of these investments. Adding another layer is the level of risk appetite among investors. When the economic outlook is uncertain and interest rate volatility is high, investors are more likely to take risk off their portfolios and demand higher returns for taking on higher risk. This can push down equity and bond prices. On the other hand, if the economic outlook is positive, investors may be willing to take on more risk, in turn potentially boosting equity prices.
Current Investment Returns in Context
Today, financial markets are seeing sharp swings as the ripple effects of higher interest rates are sinking in. For investors, historical data provides insight on long-term asset allocation trends. Over the last century, cycles of high interest rates have come and gone. Both equity and bond investment returns have been resilient for investors who stay the course.