Electric semi trucks are coming, and they could help to decarbonize the shipping and logistics industry. However, range remains a major limitation. This presents challenges for long-hauling, where the average diesel-powered semi can travel up to 2,000 miles before refueling. Compare this to the longest range electric model, the Tesla Semi, which promises up to 500 miles. A key word here is “promises”—the Semi is still in development, and nothing has been proven yet. In this infographic, we’ve listed all of the upcoming electric semi trucks, complete with range and charge time estimates. Further in the article, we’ll explore the potential commercial use cases of this first generation of trucks.
Model Overview
The following table includes all of the models included in the above infographic. Source: US News, CNBC, InsideEVs With the exception of Tesla’s Semi, all of these trucks are currently in operation or expected to begin delivering this year. You may want to take this with a grain of salt, as the electric vehicle industry has become notorious for delays. In terms of range, Tesla and Nikola are promising the highest figures (300+ miles), while the rest of the competition is targeting between 150 to 275 miles. It’s reasonable to assume that the Tesla and Nikola semis will be the most expensive. Charge times are difficult to compare because of the variables involved. This includes the amount of charge and the type of charger used. Nikola, for example, claims it will take 2 hours to charge its Tre BEV from 10% to 80% when using a 240kW charger. Charger technology is also improving quickly. Tesla is believed to be rolling out a 1 MW (1,000 kW) charger that could add 400 miles of range in just 30 minutes.
Use Cases of Electric Semi Trucks
Given their relatively lower ranges, electric semis are unlikely to be used for long hauls. Instead, they’re expected to be deployed on regional and urban routes, where the total distance traveled between destinations is much lower. There are many reasons why electric semis are suited for these routes, as listed below:
Smaller batteries can be installed, which keeps the cost of the truck lower Urban routes provide greater opportunities to use regenerative braking Quieter and cleaner operation in densely populated areas
An example of a regional route would be delivering containers from the Port of Los Angeles to the Los Angeles Transportation Center Intermodal Facility (LATC). The LATC is where containers are loaded onto trains, and is located roughly 28 miles away. With a round trip totaling nearly 60 miles, an electric semi with a range of 200 miles could feasibly complete this route three times before needing a charge. The truck could be charged overnight, as well as during off hours in the middle of the day.
Hydrogen for Long Hauls?
We’ve covered the differences between battery and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles in the past, but this was from a passenger car perspective. The conclusion, in that case, was that battery electric has become the dominant technology. In terms of long-haul trucking, however, hydrogen may have an edge. There are several reasons for why hydrogen could be beneficial for delivering heavy cargo over long distances. These are listed below:
Refueling a hydrogen fuel cell takes less time than recharging a battery. Note, however, that charge times are still improving. A fuel cell configuration is typically lighter than an equivalent battery pack. Less drivetrain weight translates to a higher cargo capacity. Hydrogen-powered trucks could achieve a much higher range.
This last point hasn’t been proven yet, but we can reference Nikola, which is developing hydrogen-powered semi trucks. The company has two models in the works, which are the Tre FCEV with a range of 500 miles, and the Two FCEV with a range of 900 miles. Keep in mind that these numbers are once again estimates and that Nikola has been accused of fraud in the past.
Who’s Using Electric Semi Trucks Today?
Although there are very few models available, electric semi trucks are indeed being used today. In January 2020, Anheuser-Busch announced that it had received its 100th 8TT. The 8TT is produced by China’s BYD Motors and was one of the first electric semis to see real-world application. The brewing company uses its 8TTs to deliver products to retail destinations across California (e.g. grocery stores). Another U.S. company using electric semis is Walmart. The retailer is trialing both the eCascadia from Freightliner and the Tre BEV from Nikola. The trucks are being used to pick up cargo from suppliers and then deliver it to regional consolidation centers. on
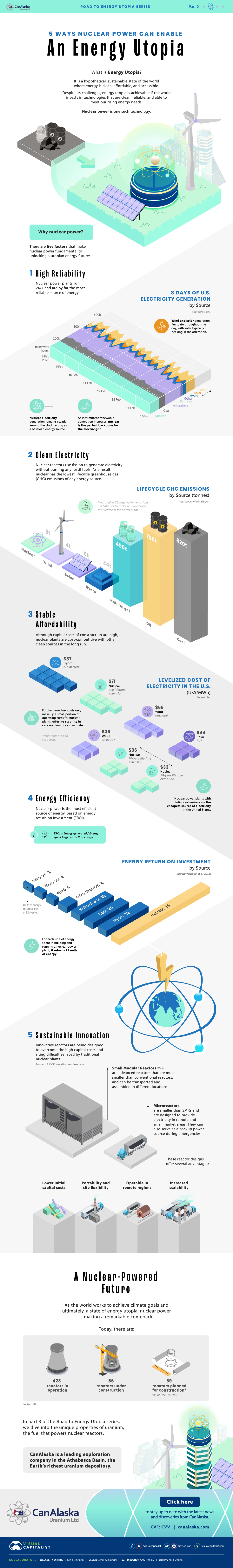
#1: High Reliability
Nuclear power plants run 24/7 and are the most reliable source of sustainable energy. Nuclear electricity generation remains steady around the clock throughout the day, week, and year. Meanwhile, daily solar generation peaks in the afternoon when electricity demand is usually lower, and wind generation depends on wind speeds.As the use of variable solar and wind power increases globally, nuclear offers a stable and reliable backbone for a clean electricity grid.
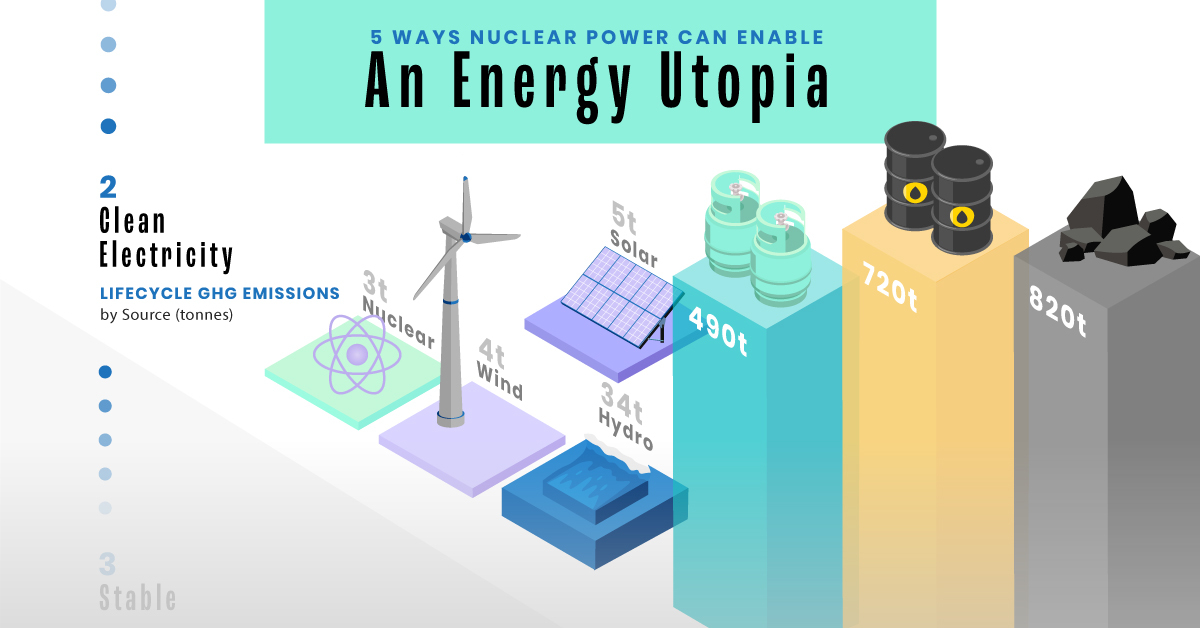
#2: Clean Electricity
Nuclear reactors use fission to generate electricity without any greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.Consequently, nuclear power is the cleanest energy source on a lifecycle basis, measured in CO2-equivalent emissions per gigawatt-hour (GWh) of electricity produced by a power plant over its lifetime. The lifecycle emissions from a typical nuclear power plant are 273 times lower than coal and 163 times lower than natural gas. Furthermore, nuclear is relatively less resource-intensive, allowing for lower supply chain emissions than wind and solar plants.
#3: Stable Affordability
Although nuclear plants can be expensive to build, they are cost-competitive in the long run. Most nuclear plants have an initial lifetime of around 40 years, after which they can continue operating with approved lifetime extensions. Nuclear plants with lifetime extensions are the cheapest sources of electricity in the United States, and 88 of the country’s 92 reactors have received approvals for 20-year extensions. Additionally, according to the World Nuclear Association, nuclear plants are relatively less susceptible to fuel price volatility than natural gas plants, allowing for stable costs of electricity generation.
#4: Energy Efficiency
Nuclear’s high energy return on investment (EROI) exemplifies its exceptional efficiency. EROI measures how many units of energy are returned for every unit invested in building and running a power plant, over its lifetime. According to a 2018 study by Weissbach et al., nuclear’s EROI is 75 units, making it the most efficient energy source by some distance, with hydropower ranking second at 35 units.
#5: Sustainable Innovation
New, advanced reactor designs are bypassing many of the difficulties faced by traditional nuclear plants, making nuclear power more accessible.
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are much smaller than conventional reactors and are modular—meaning that their components can be transported and assembled in different locations. Microreactors are smaller than SMRs and are designed to provide electricity in remote and small market areas. They can also serve as backup power sources during emergencies.
These reactor designs offer several advantages, including lower initial capital costs, portability, and increased scalability.
A Nuclear-Powered Future
Nuclear power is making a remarkable comeback as countries work to achieve climate goals and ultimately, a state of energy utopia. Besides the 423 reactors in operation worldwide, another 56 reactors are under construction, and at least 69 more are planned for construction. Some nations, like Japan, have also reversed their attitudes toward nuclear power, embracing it as a clean and reliable energy source for the future. CanAlaska is a leading exploration company in the Athabasca Basin, the Earth’s richest uranium depository. Click here to learn more now. In part 3 of the Road to Energy Utopia series, we explore the unique properties of uranium, the fuel that powers nuclear reactors.