Many states already have economies that are comparable to some of the world’s largest countries, giving you a sense of what they might be combined. And while every state plays a role in the bigger picture, some states such as New York and California have an outsized impact on fueling the country’s overall economic engine.
The State of State Economies
Today’s animation comes to us from SavingSpot, and it covers the size of state economies by GDP going back all the way to 1963. The video uses inflation-adjusted data from the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, showing how the ranking of top state economies has changed over time as different states have taken advantage of economic booms. Let’s dive into the data to see how things have changed.
Going Back in Time
The earliest data in the animation comes from 1963, when New York led the pack with a $70.6 billion economy in inflation-adjusted terms. State Economies by GDP, Inflation-Adjusted Chained $USD (1963) California ($67.8 billion), Illinois ($39.5 billion), Pennsylvania ($34.5 billion) and Ohio ($33.3 billion) round out the top five, and together they added up to 40.5% of the national GDP.
The Largest State Economies by GDP Today
Looking at the most recent data from 2017, you can see the ranking changes significantly: State Economies by GDP, Inflation-Adjusted Chained $USD (2017) California is the largest economy today – it has a state GDP of $2.6 trillion, which is comparable to the United Kingdom. Meanwhile, Florida and Georgia are two states that did not crack the top 10 back in the 1960s, while Texas jumped up to become the second largest state economy. It’s actually not a coincidence that all of these states are in the southern half of the country, as air conditioning has played a surprisingly pivotal role in shaping modern America. In fact, the share of the nation’s population living in the Sunbelt rose from 28% in 1950 to 40% in 2000, and this increase in population has coincided with economic growth in many of the states that used to be a sweaty mess.
A Final Look
Here is a final animated version of the top 10 largest states by GDP, also provided by SavingSpot:
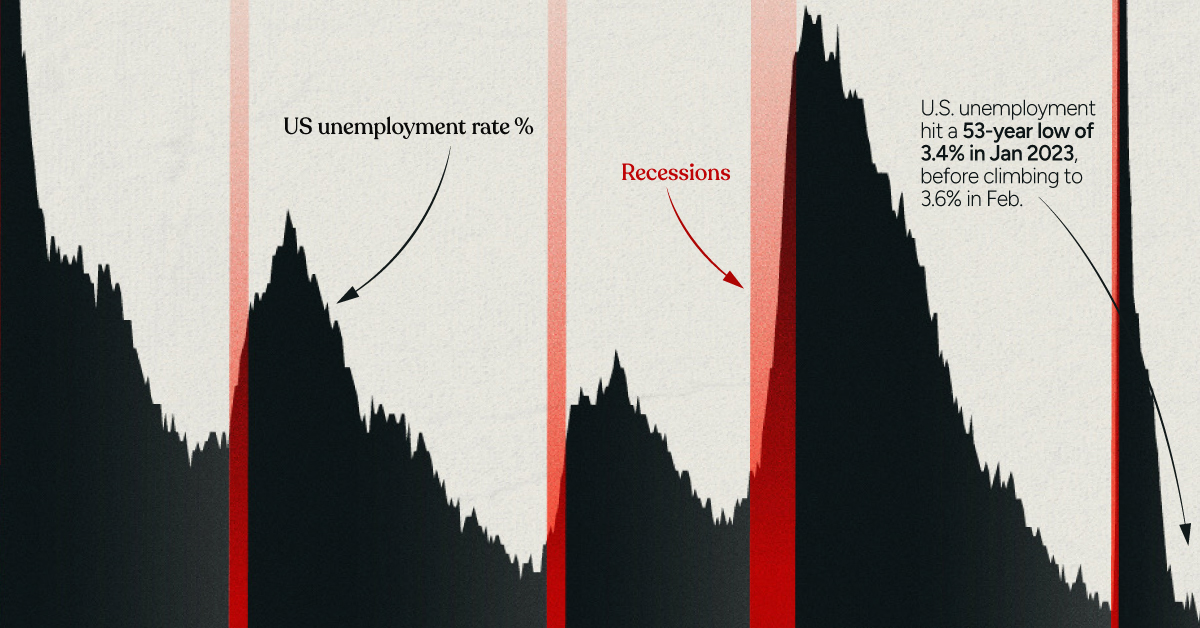
on Both figures surpassed analyst expectations by a wide margin, and in January, the unemployment rate hit a 53-year low of 3.4%. With the recent release of February’s numbers, unemployment is now reported at a slightly higher 3.6%. A low unemployment rate is a classic sign of a strong economy. However, as this visualization shows, unemployment often reaches a cyclical low point right before a recession materializes.
Reasons for the Trend
In an interview regarding the January jobs data, U.S. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen made a bold statement: While there’s nothing wrong with this assessment, the trend we’ve highlighted suggests that Yellen may need to backtrack in the near future. So why do recessions tend to begin after unemployment bottoms out?
The Economic Cycle
The economic cycle refers to the economy’s natural tendency to fluctuate between periods of growth and recession. This can be thought of similarly to the four seasons in a year. An economy expands (spring), reaches a peak (summer), begins to contract (fall), then hits a trough (winter). With this in mind, it’s reasonable to assume that a cyclical low in the unemployment rate (peak employment) is simply a sign that the economy has reached a high point.
Monetary Policy
During periods of low unemployment, employers may have a harder time finding workers. This forces them to offer higher wages, which can contribute to inflation. For context, consider the labor shortage that emerged following the COVID-19 pandemic. We can see that U.S. wage growth (represented by a three-month moving average) has climbed substantially, and has held above 6% since March 2022. The Federal Reserve, whose mandate is to ensure price stability, will take measures to prevent inflation from climbing too far. In practice, this involves raising interest rates, which makes borrowing more expensive and dampens economic activity. Companies are less likely to expand, reducing investment and cutting jobs. Consumers, on the other hand, reduce the amount of large purchases they make. Because of these reactions, some believe that aggressive rate hikes by the Fed can either cause a recession, or make them worse. This is supported by recent research, which found that since 1950, central banks have been unable to slow inflation without a recession occurring shortly after.
Politicians Clash With Economists
The Fed has raised interest rates at an unprecedented pace since March 2022 to combat high inflation. More recently, Fed Chairman Jerome Powell warned that interest rates could be raised even higher than originally expected if inflation continues above target. Senator Elizabeth Warren expressed concern that this would cost Americans their jobs, and ultimately, cause a recession. Powell remains committed to bringing down inflation, but with the recent failures of Silicon Valley Bank and Signature Bank, some analysts believe there could be a pause coming in interest rate hikes. Editor’s note: just after publication of this article, it was confirmed that U.S. interest rates were hiked by 25 basis points (bps) by the Federal Reserve.