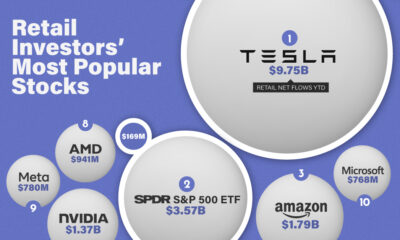
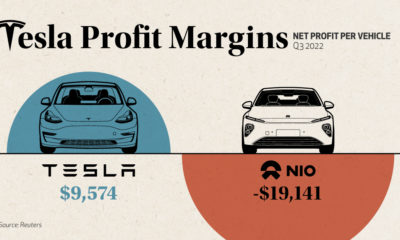
Today’s five-minute-long animation is presented in association with Global Energy Metals, and it tells you everything you need to know about the history of Tesla, including Elon Musk’s vision for the future of the iconic electric car company.
Watch the video:
The video primarily keys in on Tesla’s successes and the setbacks the company has faced along the way – it also shows that Tesla was able to pass Ford in market value just seven years after the company’s IPO.
The Rise of Tesla Series
The above video is the culmination of our Rise of Tesla Series, which also includes three full-length infographics that tell a more in-depth story about the history of Tesla, and what the company aspires to:
- Tesla’s Origin Story (View infographic)
What was the vision behind the founding of Tesla? Early hurdles faced by the company, including its near escape from the brink of bankruptcy Elon Musk’s takeover of the company, and the dramatic actions taken to keep it alive A timeline showing the development of the Roadster, and why this first car matters
- Tesla’s Journey: How it Passed Ford in Value (View Infographic)
The company’s plan to parlay the Roadster’s success into a viable long-term company strategy Introducing the Tesla Model S and Model X How the company would use the Gigafactory concept to bring economies of scale to battery production Other milestones: Powerwall, Autopilot, and Tesla’s growing Supercharger network The announcement of the Model 3
- Elon Musk’s Vision for the Future of Tesla (View Infographic)
Detailing Tesla’s ambitions for the future, including how it plans to productize the factory Other vehicles Tesla plans to release, including the Tesla Semi and a future ultra low cost model How Tesla plans to combine fully autonomous cars with the future sharing economy Exploding demand for lithium-ion batteries, and why Tesla is planning on building additional Gigafactories
on
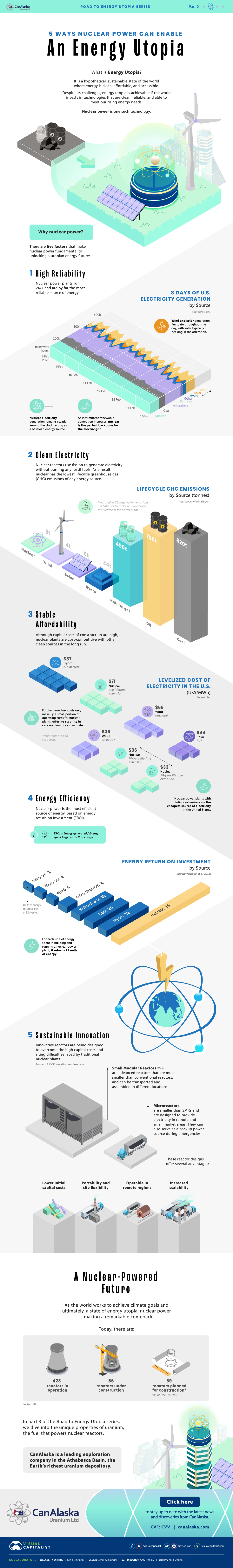
#1: High Reliability
Nuclear power plants run 24/7 and are the most reliable source of sustainable energy. Nuclear electricity generation remains steady around the clock throughout the day, week, and year. Meanwhile, daily solar generation peaks in the afternoon when electricity demand is usually lower, and wind generation depends on wind speeds.As the use of variable solar and wind power increases globally, nuclear offers a stable and reliable backbone for a clean electricity grid.
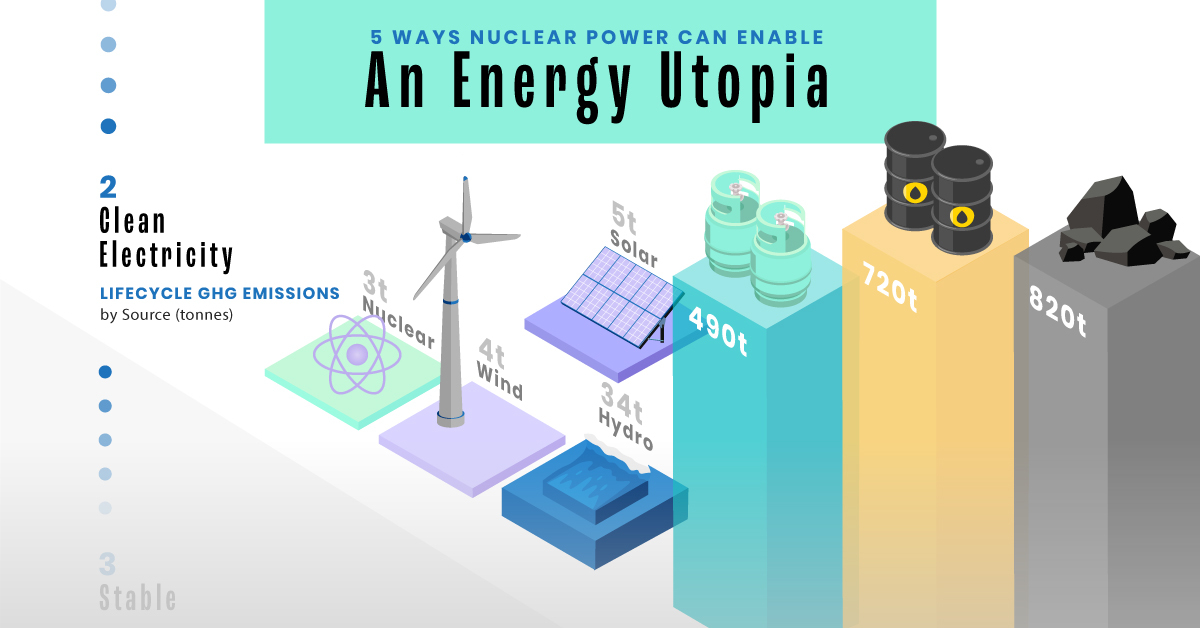
#2: Clean Electricity
Nuclear reactors use fission to generate electricity without any greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.Consequently, nuclear power is the cleanest energy source on a lifecycle basis, measured in CO2-equivalent emissions per gigawatt-hour (GWh) of electricity produced by a power plant over its lifetime. The lifecycle emissions from a typical nuclear power plant are 273 times lower than coal and 163 times lower than natural gas. Furthermore, nuclear is relatively less resource-intensive, allowing for lower supply chain emissions than wind and solar plants.
#3: Stable Affordability
Although nuclear plants can be expensive to build, they are cost-competitive in the long run. Most nuclear plants have an initial lifetime of around 40 years, after which they can continue operating with approved lifetime extensions. Nuclear plants with lifetime extensions are the cheapest sources of electricity in the United States, and 88 of the country’s 92 reactors have received approvals for 20-year extensions. Additionally, according to the World Nuclear Association, nuclear plants are relatively less susceptible to fuel price volatility than natural gas plants, allowing for stable costs of electricity generation.
#4: Energy Efficiency
Nuclear’s high energy return on investment (EROI) exemplifies its exceptional efficiency. EROI measures how many units of energy are returned for every unit invested in building and running a power plant, over its lifetime. According to a 2018 study by Weissbach et al., nuclear’s EROI is 75 units, making it the most efficient energy source by some distance, with hydropower ranking second at 35 units.
#5: Sustainable Innovation
New, advanced reactor designs are bypassing many of the difficulties faced by traditional nuclear plants, making nuclear power more accessible.
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are much smaller than conventional reactors and are modular—meaning that their components can be transported and assembled in different locations. Microreactors are smaller than SMRs and are designed to provide electricity in remote and small market areas. They can also serve as backup power sources during emergencies.
These reactor designs offer several advantages, including lower initial capital costs, portability, and increased scalability.
A Nuclear-Powered Future
Nuclear power is making a remarkable comeback as countries work to achieve climate goals and ultimately, a state of energy utopia. Besides the 423 reactors in operation worldwide, another 56 reactors are under construction, and at least 69 more are planned for construction. Some nations, like Japan, have also reversed their attitudes toward nuclear power, embracing it as a clean and reliable energy source for the future. CanAlaska is a leading exploration company in the Athabasca Basin, the Earth’s richest uranium depository. Click here to learn more now. In part 3 of the Road to Energy Utopia series, we explore the unique properties of uranium, the fuel that powers nuclear reactors.