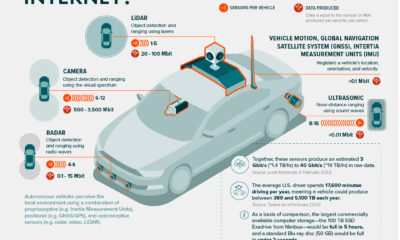
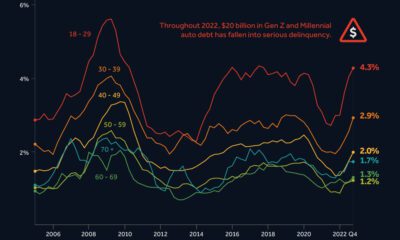
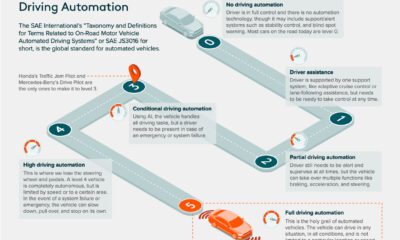
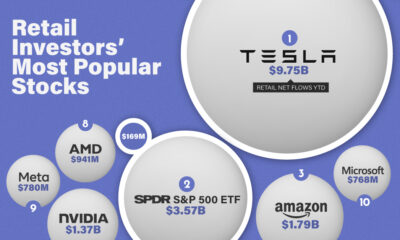
Keeping track of which companies have adopted these technologies can be difficult. Thankfully, the EPA’s 2022 Automotive Trends Report includes data that shows which automakers have adopted what technologies.
Understanding the Data
The percentages in this infographic show how 14 major automakers have adopted various fuel-saving technologies into their lineups. The report did not specify if this data is for North American models only. There are several geographical trends hidden within this dataset. To make them more obvious, we color-coded the 14 automakers by their nationality.
Asian Automakers
Starting from the top of the graphic, we can see that Japanese automakers are big proponents of gasoline direct injection (GDI) engines, as well as continuously variable transmissions (CVT). With a GDI engine, fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber at high pressure. This is more precise than the traditional method known as port injection, which results in greater fuel efficiency and lower emissions. CVT transmissions use pulleys instead of gears to improve fuel efficiency. CVTs are best paired with smaller, lower output engines, which may explain why Japanese automakers (who have a history of building smaller cars) have adopted them so widely. Note that Toyota is listed as having 0% adoption of direct injection, but this isn’t exactly true. The automaker uses its D4-S system, which is a combination of both port and direct fuel injection. South Korean automakers, on the other hand, have a more balanced technology profile, adopting a wider number of technologies, but each to a lesser degree.
German Automakers
German automakers are well-known for their expertise in building combustion engines, so it’s no surprise they use turbocharging and direct injection in nearly every model. They’ve also heavily adopted high gear-count transmissions (7 or more gears), which can not only enable better fuel efficiency, but also faster acceleration. The downside to these transmissions is that they can be very heavy and complex. Furthermore, German automakers utilize the auto start-stop feature in many of their vehicles, and are tied with Toyota in terms of hybrid adoption.
American & Other Automakers
Ford and GM’s technology profile is similar to the Germans, using turbocharging and direct injection combined with 7+ gear transmissions. GM uses turbocharging less frequently, but stands out with its high usage of cylinder deactivation technology, at 54% of models. Referred to by GM as Active Fuel Management (AFM), this feature shuts down half of the engine’s cylinders during light driving. GM is known for its small-block V8 engines, which can be had in many of the company’s models. Given the high cylinder count of a V8, AFM is a clever trick for improving fuel efficiency. Stellantis, which is a merger between Italian-American Fiat Chrysler and French Peugeot, has not widely adopted many technologies except for the 7+ gear transmission. Finally there’s Tesla, which does not use any of the aforementioned technologies due to it being a pure electric automaker.
Going The Way of the Dinosaur
The technologies shown in this infographic have helped to bring the average mpg of a new car to record highs in recent years. Many of these innovations could become obsolete as automakers slowly phase out gasoline engines. In 2021, six major automakers including Ford, Mercedes-Benz, and GM pledged to phase out the sale of new gasoline and diesel-powered cars by 2040. Other companies such as Porsche believe that the combustion engine still has a future, pointing to synthetic fuels as a means of significantly reducing CO2 emissions. on These faulty airbags, installed by 19 different automakers including BMW and Toyota from 2002 to 2015, can explode when deployed and have led to numerous tragic accidents. Their recall affected 67 million airbags (including Honda’s vehicles above) and has been known as the largest safety recall in U.S. history. Over the past four decades, there have been over 22,000 automobile recalls in the United States. In this interactive piece, Chimdi Nwosu uses data from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration to visualize the types of automobile recalls over the past 40 years, the companies with the most recalls, the components that were recalled the most, and, most importantly, their impacts on people.
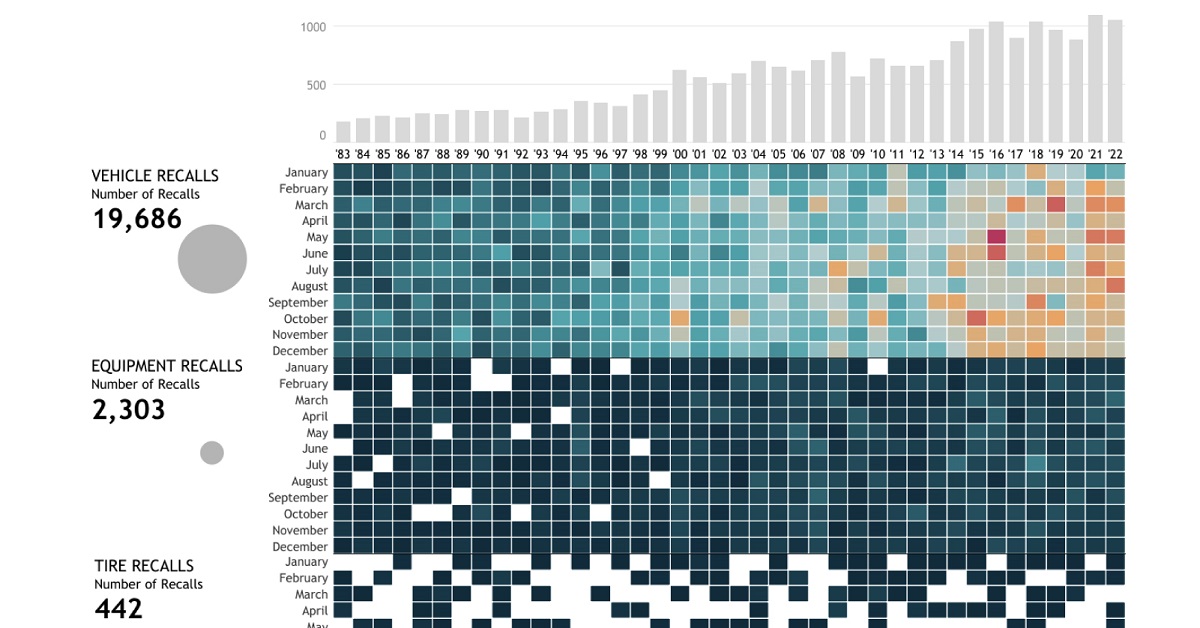
Breaking Down U.S. Automobile Recalls
Whether a recall affects specific vehicle components, equipment, or vehicles as a whole, it affects the lives of millions of automobile users. When combined, these numbers ramp up exponentially. The U.S. alone has seen a total of 22,651 recalls over the past 40 years, impacting more than one billion people. Almost 72% of these people were affected by nearly 20,000 vehicle recalls, while around 19% were impacted by over 2,000 equipment recalls during this period. Comparatively, the 442 tire recalls and 220 child seat recalls affected significantly less, but still a total of 96.9 million people. While an inconvenience to many, the recall of these faulty vehicle parts saves many more from unfortunate incidents that may have occurred if left unchecked.
Minor and Major Recalls
One of the largest recalls in history took place in 2014 when General Motors—the manufacturer with the highest total of recalls in four decades—recalled millions of vehicles including the 2005-2007 Chevrolet Cobalt, 2007 Pontiac G5, and 2006-2007 Chevrolet HHR, amongst others. The reason for this recall was a faulty ignition switch that caused the vehicle’s engine to shut down while driving, disabling safety systems including airbags. This fault led to the death of hundreds of people. However, not all recalls are this severe. BMW, for example, recalled just four vehicles in December last year because one of the four bolts in the driver’s backrest was not attached properly. Similarly in 2020, Ford recalled some of its vehicles due to a faulty door latch. While this recall inconvenienced over two million users, it was less likely to lead to severe consequences if left unchecked.
A Safer Future?
The number of automobile recalls over the past four decades has seen a steep rise. As have car safety standards. While recalls could hint at the risks involved in taking your car out for a drive, they also indicate manufacturers taking responsibility for their faulty commodities, and affect a very small percentage of vehicles on the road. To improve automobile safety, the NHTSA proposed a New Car Assessment Program in 2022, which provides vehicle users with safety ratings for every new vehicle. This five-star safety rating program rates the vehicles’ safety features, crashworthiness, and resistance to rollover. With self-driving cars now also entering the mix, we need to stay informed about vehicle safety to keep our vehicles, our streets, and ourselves safe in the future.