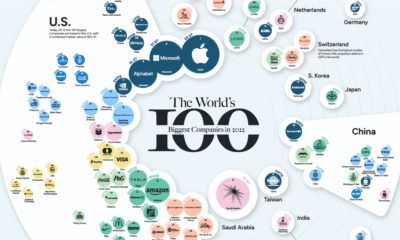
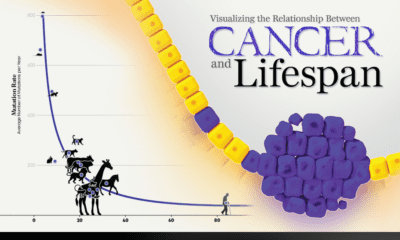
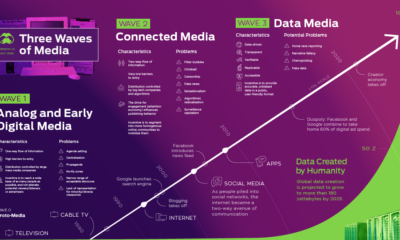
Ruthless Efficiency
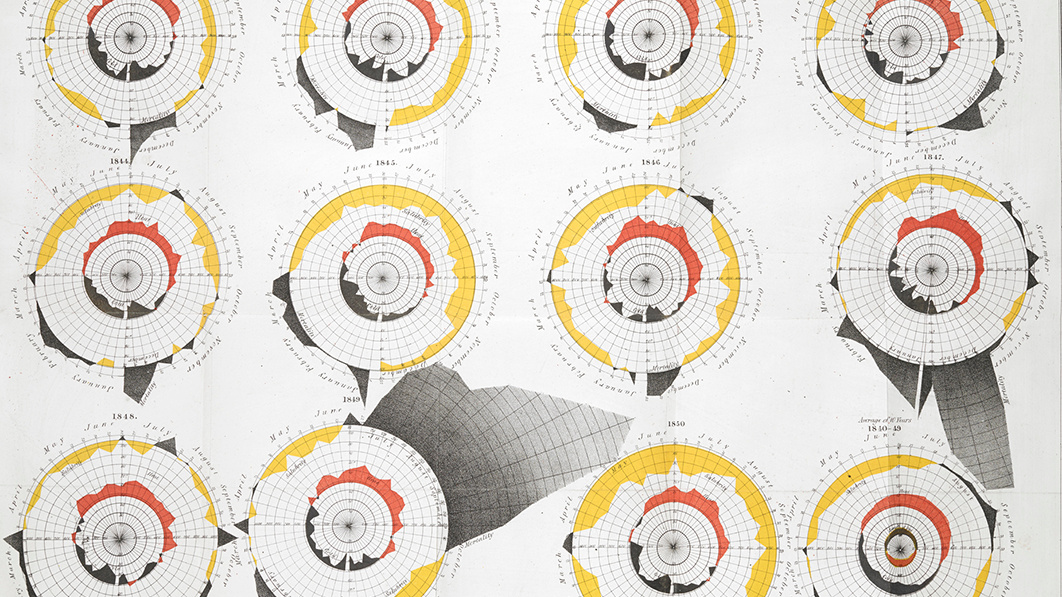
Cholera was a ruthlessly efficient killer, with both rapid onset and severe symptoms. By the time the disease made its way to London and New York in the early 1830s, hundreds of thousands of people had died across Europe, Africa, and Asia. – Thomas Whiteside Hime Needless to say, the human race was concerned. Thanks to high-speed printing press technology, daily newspaper circulations were rising dramatically, and this allowed journalists to experiment with new reporting techniques, including charting data.
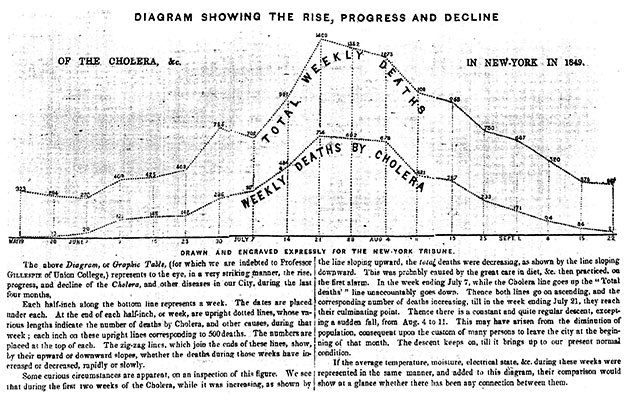
At the time, the chart above was such a novel approach that it required four paragraphs to explain how to read it. People of that era were simply not used to seeing data in a visual form. At a glance though, the chart is extremely effective at communicating a grim message: cholera had ravaged New York City over the summer of 1849. Despite the concerted push to eradicate the disease, the medical community was still largely in the dark about how to prevent future outbreaks. Because doctors could treat numerous patients without falling ill, it was assumed that a miasmic environment (i.e. slums, densely-packed housing) was causing the spread.
Data Viz in the Time of Cholera
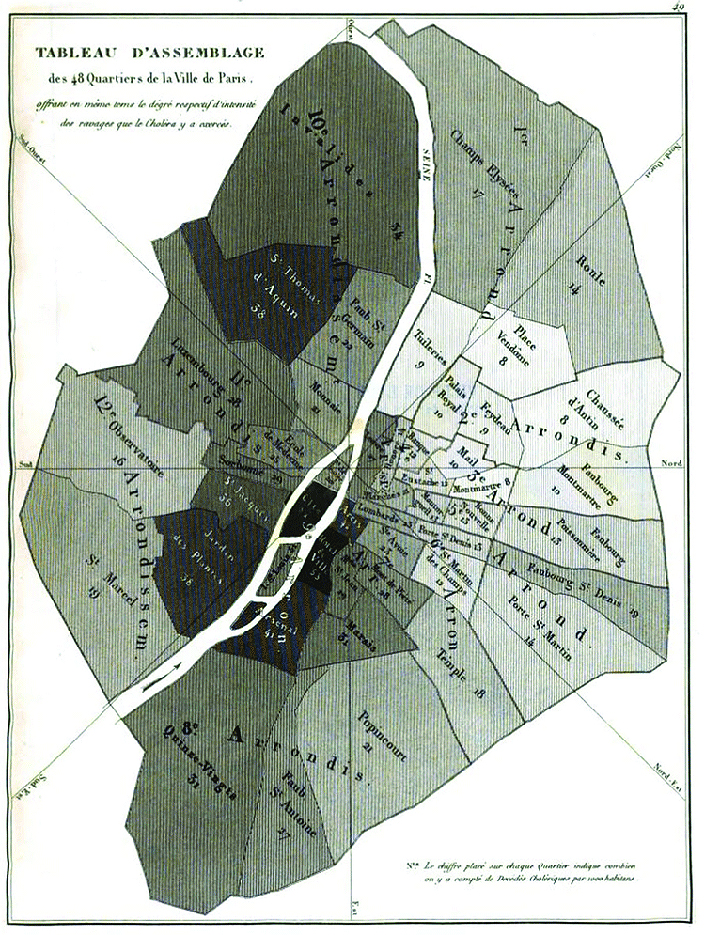
Today, we have tools that allow us to map just about anything, but in the mid-1800s, mapping data was still an innovative concept. As early as the 1830s, geographers began using spatial analysis to study cholera epidemiology. The heat map below shows which sections of Paris were hardest hit by a recent outbreak of cholera.
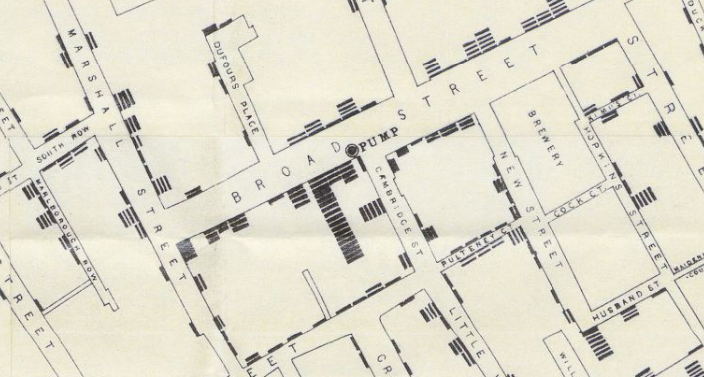
In 1854, Dr. John Snow was convinced that cholera was spreading via tainted water and decided to display neighborhood mortality data directly on a map. This method clearly revealed a cluster of cases around a specific pump. View the full version of the map here The result is one of the most influential maps in modern history. In addition to the real-world utility the map provided in helping physicians understand how cholera was spreading, it also exemplified a seismic shift in thinking that opened up new avenues for data to be analyzed and displayed. Despite the tragic circumstances of the time period, we can be thankful that the urgency of the situation allowed the world’s pioneering researchers, journalists, and physicians to experiment with new data visualization techniques to better understand the world. on Even while political regimes across these countries have changed over time, they’ve largely followed a few different types of governance. Today, every country can ultimately be classified into just nine broad forms of government systems. This map by Truman Du uses information from Wikipedia to map the government systems that rule the world today.
Countries By Type of Government
It’s important to note that this map charts government systems according to each country’s legal framework. Many countries have constitutions stating their de jure or legally recognized system of government, but their de facto or realized form of governance may be quite different. Here is a list of the stated government system of UN member states and observers as of January 2023: Let’s take a closer look at some of these systems.
Monarchies
Brought back into the spotlight after the death of Queen Elizabeth II of England in September 2022, this form of government has a single ruler. They carry titles from king and queen to sultan or emperor, and their government systems can be further divided into three modern types: constitutional, semi-constitutional, and absolute. A constitutional monarchy sees the monarch act as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, giving them little to no real power. For example, King Charles III is the head of 15 Commonwealth nations including Canada and Australia. However, each has their own head of government. On the other hand, a semi-constitutional monarchy lets the monarch or ruling royal family retain substantial political powers, as is the case in Jordan and Morocco. However, their monarchs still rule the country according to a democratic constitution and in concert with other institutions. Finally, an absolute monarchy is most like the monarchies of old, where the ruler has full power over governance, with modern examples including Saudi Arabia and Vatican City.
Republics
Unlike monarchies, the people hold the power in a republic government system, directly electing representatives to form government. Again, there are multiple types of modern republic governments: presidential, semi-presidential, and parliamentary. The presidential republic could be considered a direct progression from monarchies. This system has a strong and independent chief executive with extensive powers when it comes to domestic affairs and foreign policy. An example of this is the United States, where the President is both the head of state and the head of government. In a semi-presidential republic, the president is the head of state and has some executive powers that are independent of the legislature. However, the prime minister (or chancellor or equivalent title) is the head of government, responsible to the legislature along with the cabinet. Russia is a classic example of this type of government. The last type of republic system is parliamentary. In this system, the president is a figurehead, while the head of government holds real power and is validated by and accountable to the parliament. This type of system can be seen in Germany, Italy, and India and is akin to constitutional monarchies. It’s also important to point out that some parliamentary republic systems operate slightly differently. For example in South Africa, the president is both the head of state and government, but is elected directly by the legislature. This leaves them (and their ministries) potentially subject to parliamentary confidence.
One-Party State
Many of the systems above involve multiple political parties vying to rule and govern their respective countries. In a one-party state, also called a single-party state or single-party system, only one political party has the right to form government. All other political parties are either outlawed or only allowed limited participation in elections. In this system, a country’s head of state and head of government can be executive or ceremonial but political power is constitutionally linked to a single political movement. China is the most well-known example of this government system, with the General Secretary of the Communist Party of China ruling as the de facto leader since 1989.
Provisional
The final form of government is a provisional government formed as an interim or transitional government. In this system, an emergency governmental body is created to manage political transitions after the collapse of a government, or when a new state is formed. Often these evolve into fully constitutionalized systems, but sometimes they hold power for longer than expected. Some examples of countries that are considered provisional include Libya, Burkina Faso, and Chad.