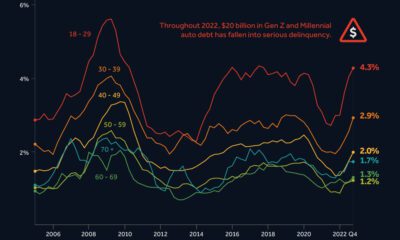
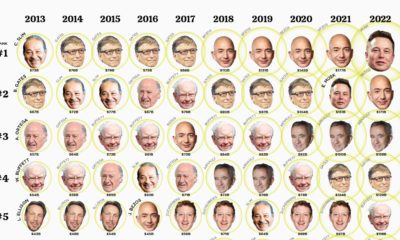
In this motion graphic video, we break down the full story behind Donald Trump’s wealth. Not only do we examine his major business successes and failures, but we even look back at real estate’s prominent role in the history of the Trump family. To conclude, the video breaks down Trump’s net worth and financial history, while highlighting some of the help he has gotten along the way in building his fortune.
Family Matters
The story started well over a century ago with Donald’s grandfather, Frederick Trump. Real estate runs deep in the blood of the Trump family, and Frederick was actually the first Trump to own a hotel. During the famous Klondike gold rush in Canada, Frederick owned an inn and restaurant that served gold miners. When he passed away, he left an estate worth just under $500,000 in today’s dollars to his heirs. His eldest son, Fred Trump, carried on the Trump legacy by going into business with his mother, using the nest egg for seed money. Fred became a very successful builder in New York City’s outer boroughs. He built single family houses in Queens in the 1920s, helped pioneer the supermarket with the “Trump Market” during the Great Depression, and even built barracks for the Navy during World War 2. But Fred’s real cash cow came in 1949, when he got a government loan to build Shore Haven Apartments in Brooklyn. The Federal Housing Administration paid him $10.3 million, but he was able to build the apartments for significantly less. The government kept overpaying for houses in Brooklyn and Queens, and Fred kept building them. According to Donald, his father became “one of the biggest landlords in New York’s outer boroughs”. By the time of Fred’s death in 1999, it’s said that Fred Trump was worth between $250 and $300 million.
Donald’s Vision
Born in Queens, Donald J. Trump would join his father’s company early on in his career. His father’s cash cow was now gone, but Donald had a different vision for the Trump name anyways. He envisioned the “Trump” brand as being synonymous with luxury worldwide. To do this, in the mid-1970s, Donald went into real estate in Manhattan. Relying on the business connections and creditworthiness of his old man, he borrowed a “small sum” of 1 million dollars to get started.
Trump’s Biggest Successes
Trump’s top three business successes include the Grand Hyatt, 40 Wall Street, and the Apprentice.
- Grand Hyatt In 1976, Donald Trump and Hyatt partnered to buy the rundown Commodore Hotel near Grand Central Station. At the time, the whole neighborhood was in disarray with many nearby buildings on the verge of foreclosure. Trump negotiated contracts with banks and the city in an effort to fund the hotel and rejuvenate the area. The end result was the Grand Hyatt, a 25-story hotel, which Trump sold his share of for $142 million in 1996.
- 40 Wall Street Another big win for Trump was with 40 Wall Street, once the tallest building in the world. He bought it for $1 million after years of vacancy. Today, it’s prime real estate in the financial district, worth more than $500 million – a huge return.
- The Apprentice The Apprentice was also a financial home run for Trump. As the show’s host and executive producer, he raked in $1 million per episode for a whopping 185 episodes.
Trump’s Biggest Failures
Like many businessmen, Donald Trump’s career has also had his share of failures.
- Atlantic City Donald’s biggest failure may be his ill-fated venture into casinos in Atlantic City. The bleeding started in 1988 when he acquired the Taj Mahal Casino. Funded primarily by junk bonds, the massive casino would be $3 billion in debt within just a year of opening. Trump, who racked up $900 million in personal liabilities, had the business declare bankruptcy. To stay afloat, he ditched many personal assets such as half of his stake in the company, a 282-foot megayacht, and his airline. Things were dire, and Trump’s dad chipped in by providing a $3.5 million loan in the form of casino chips to help make a loan payment. Trump’s casino holding company would enter bankruptcy two additional times: in 2004, after accruing $1.8 billion in debt, and in 2009, after missing a bond payment during the Financial Crisis. Each time, Trump’s stake in the company fell.
- Other Businesses While three of Trump’s four bankruptcies involved Atlantic City casinos, he has also struggled in other ventures outside of real estate: Trump airlines, Trump Vodka, Trump: The Game, Trump Magazine, Trump Steaks, and Trump University were all destined for failure. Trump Mortgages was launched in 2006 right before the real estate crash, and it also imploded.
Trump’s Net Worth
According to Trump’s campaign, he is worth “in excess of TEN BILLION DOLLARS”. However, he has also been accused in the past of artificially inflating his net worth. Forbes and Bloomberg News both have drastically different estimates of his wealth at $4.5 billion and $2.9 billion respectively. Using the middle of the road figure from Forbes, here is how Trump’s wealth breaks down:
48% is in New York City real estate 7% is in cash and liquid assets such as investments 8% is in golf courses 4% is in “toys” such as helicopters, penthouse, or his Boeing 757 plane
The remainder includes other real estate assets outside of New York City, as well as the value of the licensing agreements for hotels, real estate, or other Trump products.
Trump as an Investor
So how did Donald Trump do in managing his fortune? See Trump’s performance as an investor compared to other benchmarks in the next video for The Money Project.
About the Money Project
The Money Project aims to use intuitive visualizations to explore ideas around the very concept of money itself. Founded in 2015 by Visual Capitalist and Texas Precious Metals, the Money Project will look at the evolving nature of money, and will try to answer the difficult questions that prevent us from truly understanding the role that money plays in finance, investments, and accumulating wealth. on Even while political regimes across these countries have changed over time, they’ve largely followed a few different types of governance. Today, every country can ultimately be classified into just nine broad forms of government systems. This map by Truman Du uses information from Wikipedia to map the government systems that rule the world today.
Countries By Type of Government
It’s important to note that this map charts government systems according to each country’s legal framework. Many countries have constitutions stating their de jure or legally recognized system of government, but their de facto or realized form of governance may be quite different. Here is a list of the stated government system of UN member states and observers as of January 2023: Let’s take a closer look at some of these systems.
Monarchies
Brought back into the spotlight after the death of Queen Elizabeth II of England in September 2022, this form of government has a single ruler. They carry titles from king and queen to sultan or emperor, and their government systems can be further divided into three modern types: constitutional, semi-constitutional, and absolute. A constitutional monarchy sees the monarch act as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, giving them little to no real power. For example, King Charles III is the head of 15 Commonwealth nations including Canada and Australia. However, each has their own head of government. On the other hand, a semi-constitutional monarchy lets the monarch or ruling royal family retain substantial political powers, as is the case in Jordan and Morocco. However, their monarchs still rule the country according to a democratic constitution and in concert with other institutions. Finally, an absolute monarchy is most like the monarchies of old, where the ruler has full power over governance, with modern examples including Saudi Arabia and Vatican City.
Republics
Unlike monarchies, the people hold the power in a republic government system, directly electing representatives to form government. Again, there are multiple types of modern republic governments: presidential, semi-presidential, and parliamentary. The presidential republic could be considered a direct progression from monarchies. This system has a strong and independent chief executive with extensive powers when it comes to domestic affairs and foreign policy. An example of this is the United States, where the President is both the head of state and the head of government. In a semi-presidential republic, the president is the head of state and has some executive powers that are independent of the legislature. However, the prime minister (or chancellor or equivalent title) is the head of government, responsible to the legislature along with the cabinet. Russia is a classic example of this type of government. The last type of republic system is parliamentary. In this system, the president is a figurehead, while the head of government holds real power and is validated by and accountable to the parliament. This type of system can be seen in Germany, Italy, and India and is akin to constitutional monarchies. It’s also important to point out that some parliamentary republic systems operate slightly differently. For example in South Africa, the president is both the head of state and government, but is elected directly by the legislature. This leaves them (and their ministries) potentially subject to parliamentary confidence.
One-Party State
Many of the systems above involve multiple political parties vying to rule and govern their respective countries. In a one-party state, also called a single-party state or single-party system, only one political party has the right to form government. All other political parties are either outlawed or only allowed limited participation in elections. In this system, a country’s head of state and head of government can be executive or ceremonial but political power is constitutionally linked to a single political movement. China is the most well-known example of this government system, with the General Secretary of the Communist Party of China ruling as the de facto leader since 1989.
Provisional
The final form of government is a provisional government formed as an interim or transitional government. In this system, an emergency governmental body is created to manage political transitions after the collapse of a government, or when a new state is formed. Often these evolve into fully constitutionalized systems, but sometimes they hold power for longer than expected. Some examples of countries that are considered provisional include Libya, Burkina Faso, and Chad.