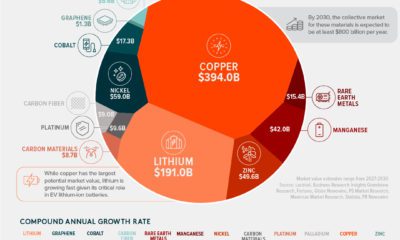
If humans were ever able to get their hands on just one asteroid, it would be a game-changer. That’s because the value of many asteroids are measured in the quintillions of dollars, which makes the market for Earth’s annual production of raw metals – about $660 billion per year – look paltry in comparison. The reality is that the Earth’s crust is saddled with uneconomic materials, while certain types of asteroids are almost pure metal. X-type asteroids, for example, are thought to be the remnants of large asteroids that were pulverized in collisions in which their dense, metallic cores got separated from the mantle. There is one such X-type asteroid near earth that is believed to hold more platinum than ever mined in human history.
Near-Earth Mining Targets
Asteroid mining companies such as Planetary Resources and Deep Space Industries are the first-movers in the sector, and they’ve already started to identify prospective targets to boldly mine where no man has mined before. Both companies are looking specifically at near-Earth asteroids in the near-term, which are the easiest ones to get to. So far, roughly 15,000 such objects have been discovered, and their orbits all come in close proximity to Earth. Planetary Resources has identified eight of these as potential targets and has listed them publicly, while Deep Space Industries has claimed to have “half a dozen very, very attractive targets”. While these will be important for verifying the feasibility of asteroid mining, the reality is that near-Earth asteroids are just tiny minnows in an ocean of big fish. Their main advantage is that they are relatively easy to access, but most targets identified so far are less than 1,000 ft (300 m) in diameter – meaning the potential economic payoff of a mission is still unclear.
Where the Money is Made
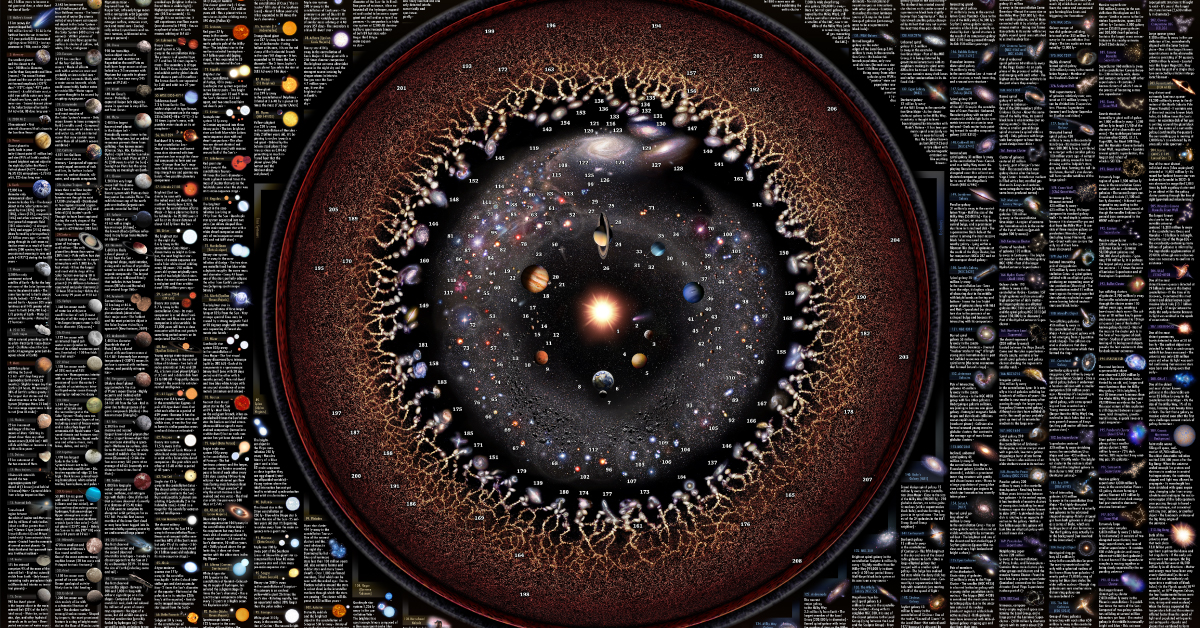
The exciting part of asteroid mining is the asteroid belt itself, which lies between Mars and Jupiter. It is there that over 1 million asteroids exist, including about 200 that are over 60 miles (100 km) in diameter. NASA estimates this belt to hold $700 quintillion of bounty. That’s about $100 billion for each person on Earth. There are obviously many technical challenges that must be overcome to make mining these possible. As it stands, NASA aims to bring back a grab sample from the surface of asteroid Bennu that is 2 and 70 ounces (about 60 to 2,000 grams) in size. The cost of the mission? Approximately $1 billion. To do anything like that on a large scale will require robots, spacecraft, and other technologies that simply do not exist yet. Further, missions like this could cost trillions of dollars – a huge risk and burden in the case that a mission is unsuccessful. Until then, the near-Earth asteroids are the fertile testing ground for aspirational asteroid miners – and we look forward to seeing what is possible in the future. on And while we haven’t figured out all the answers quite yet, we’ve made some remarkable discoveries when it comes to learning about outer space. What are some of the most notable observations that scientists have discovered so far? This map of outer space by Pablo Carlos Budassi highlights more than 200 celestial objects in our universe and provides details and facts about each one.
The Types of Celestial Objects Mapped
To create this graphic, Budassi used a combination of logarithmic astronomical maps from Princeton University, as well as images from NASA. The visualization highlights 216 different celestial objects that are color-coded and organized into five overarching categories:
Moons and Asteroids Planets Galaxies Star System Great Scales/Superclusters
At the center of the map is the Sun, which is the largest object in our Solar System. According to NASA, the Sun’s volume is equivalent to 1.3 million Earths. The Sun is the powerhouse of life here on Earth—its energy provides our planet with a mild, warm climate that keeps us alive, keeping the Earth from becoming a frozen rock. While the Sun is the only star in the Solar System, there is a neighboring star system called Alpha Centauri that’s approximately 4.37 light-years away. It’s made up of three stars—Proxima Centauri, Alpha Centauri A, and Alpha Centauri B. Proxima Centauri, as the Latin name indicates, is the closest of the three to Earth and has an Earth-sized planet in its habitable zone.
The Life of a Star
In a star’s early stages, it’s powered by hydrogen. However, when its hydrogen stores are depleted, some stars are able to fuse helium or even heavier elements. Stars similar to the size of the Sun will grow, cool down, and eventually transform into a red giant. The Sun has about 5,000 million more years before it reaches its red giant stage, but when that happens, it will likely expand to the point where it swallows up the Earth. While stars emit energy for years, it’s important to note that they don’t shine for eternity. Their exact life span depends on their size, with bigger stars burning out faster than their smaller counterparts. But as light from distant objects millions of light-years away takes a long time to reach us here on Earth, the largest of stars shine for hundreds of millions of years after they die.
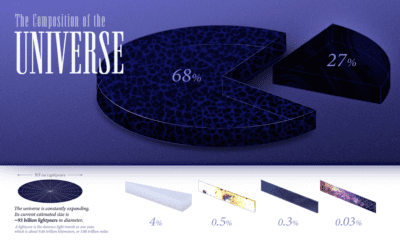
Just How Big is Our Universe?
Some experts believe that the universe is infinite, while others argue that we can’t yet know for certain because current measurements aren’t accurate enough. However, scientists believe that our observable universe extends about 46 billion light-years in every direction, giving it a diameter of roughly 93 billion light-years. But just how much of the universe extends beyond what we can see? We may never find out.