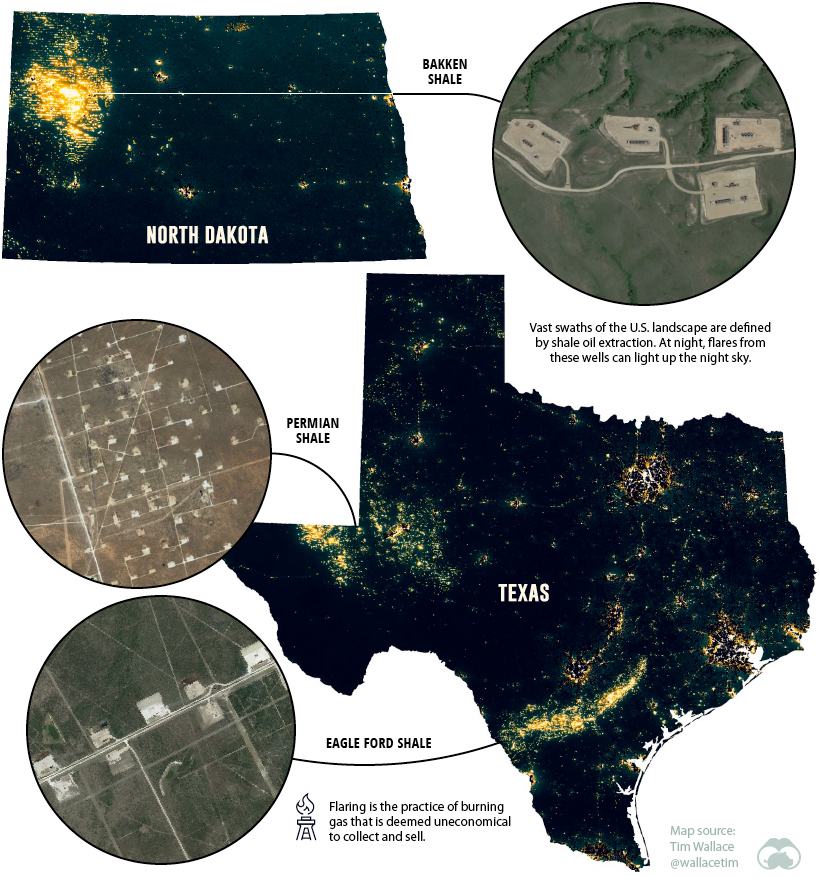
Increasingly though, economic activity in America’s rural spaces is casting a glow into the sky, and now four out of five people in North America cannot see the Milky Way at night. Today’s map, from geographer and journalist, Tim Wallace, is a different perspective on light pollution in the United States. The map was created by subtracting population from light output, which highlights areas that throw off more light than predicted given their population density. On this style of map, it isn’t the glowing metropolitan centers of New York and Los Angeles that stand out, but regions like the oil-rich corner of South Dakota or the final leg of the Mississippi River. Let’s zoom in and investigate what’s happening in these unexpected illumination zones.
Oil & Gas
Some of the most prominent patterns on the map appear in regions where shale oil is being extracted.
In a relatively short amount of time, America became the largest oil producer on the planet. One of the major factors that fueled record production for shale oil producers was the proliferation of multi-well pad drilling — when multiple wells are drilled from a single drill site. From the air, it’s easy to spot these well formations spreading across the landscape, but the effect is even more pronounced at night. At times, oil production is so strong that drillers flare the excess natural gas. In North Dakota alone, there are nearly 14,000 producing wells, and the resulting flares are what create the distinctive grid patterns on the map. One of the brightest areas per capita in the country is Loving County, Texas. The county has around 100 residents, but more than 6,000 drilled wells.
Industrial Activities
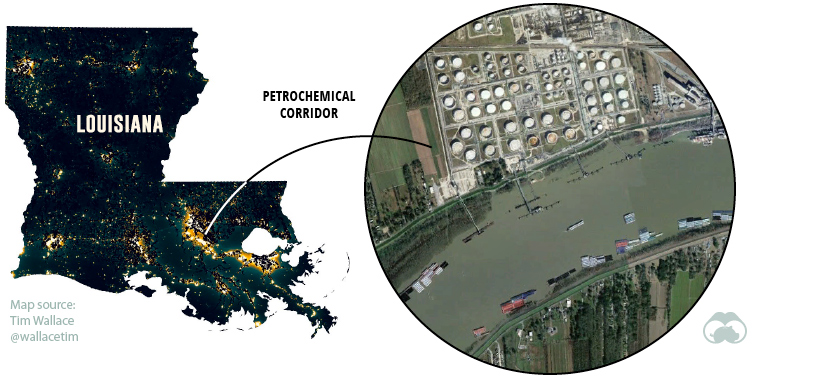
Another point of interest on the map is Louisiana’s “petrochemical corridor”, running between New Orleans and Baton Rouge. An overhead view of Southern Louisiana in the daytime will be punctuated by the “ribbon farms” flanking the Mississippi River — a nod to the region’s history of French settlement.
At night though, a different scene emerges. Over 100 sprawling petrochemical facilities run by companies like Dow Chemical and Union Carbide dot the landscape, a patchwork of highly-illuminated plots.
Commercial Sprawl
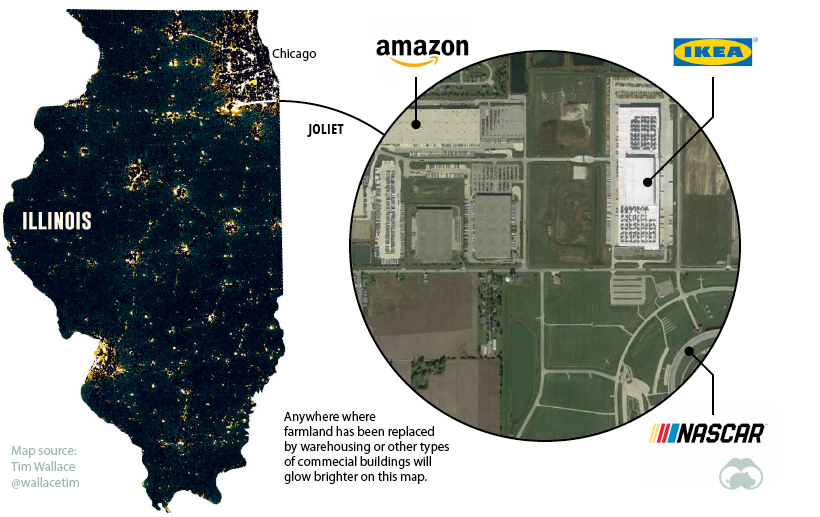
Some types of infrastructure are typically located away from the city center. Airports, power stations, and racetracks, for example, need a lot of space and aren’t the most popular neighbors. Another type of facility has been replacing farmland in recent years — logistics hubs. Many of the bright spots on the map outside cities show the warehouses and sortation centers that feed our growing demand for e-commerce.
Flipping the Switch on Light Pollution
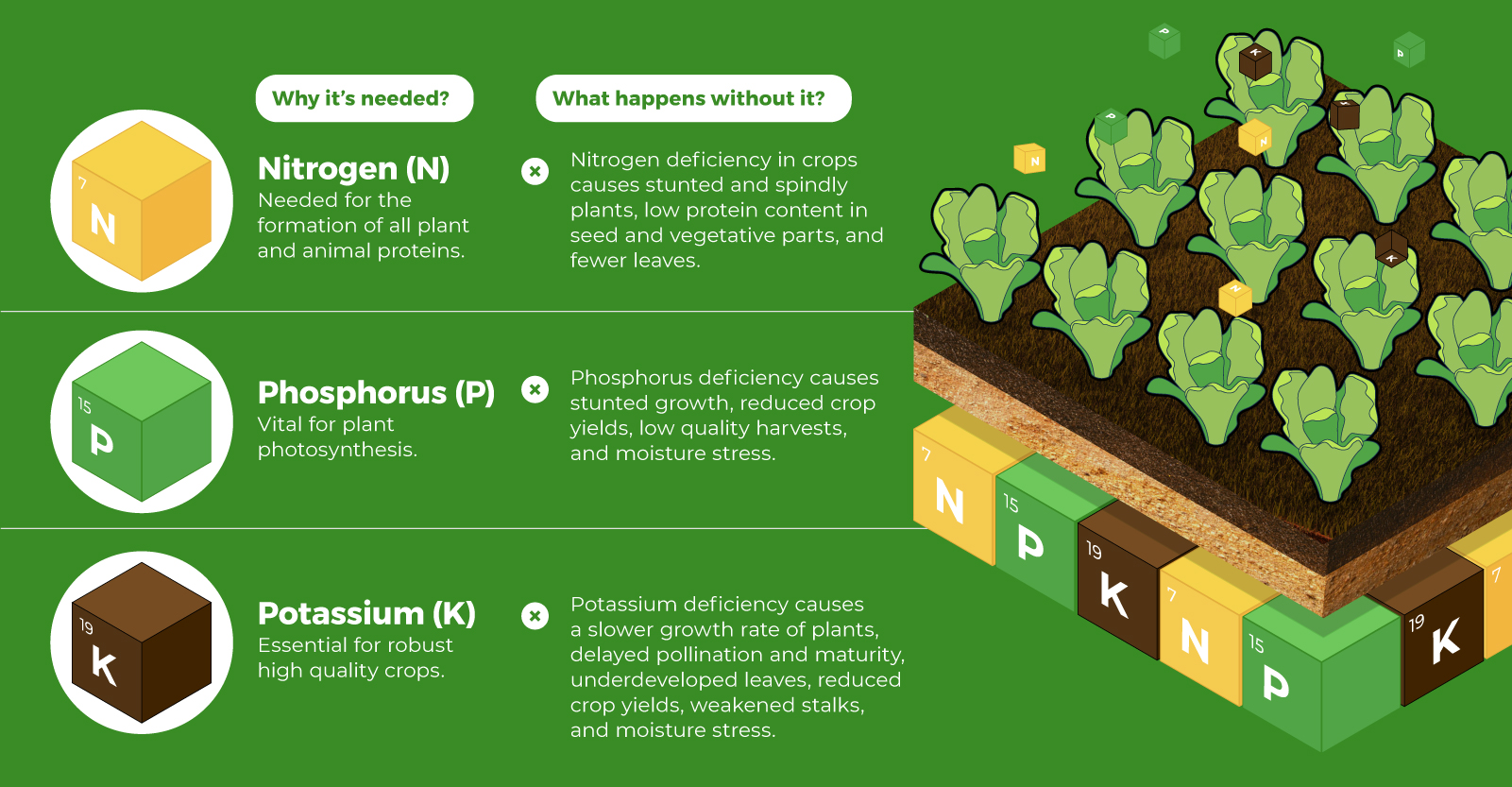
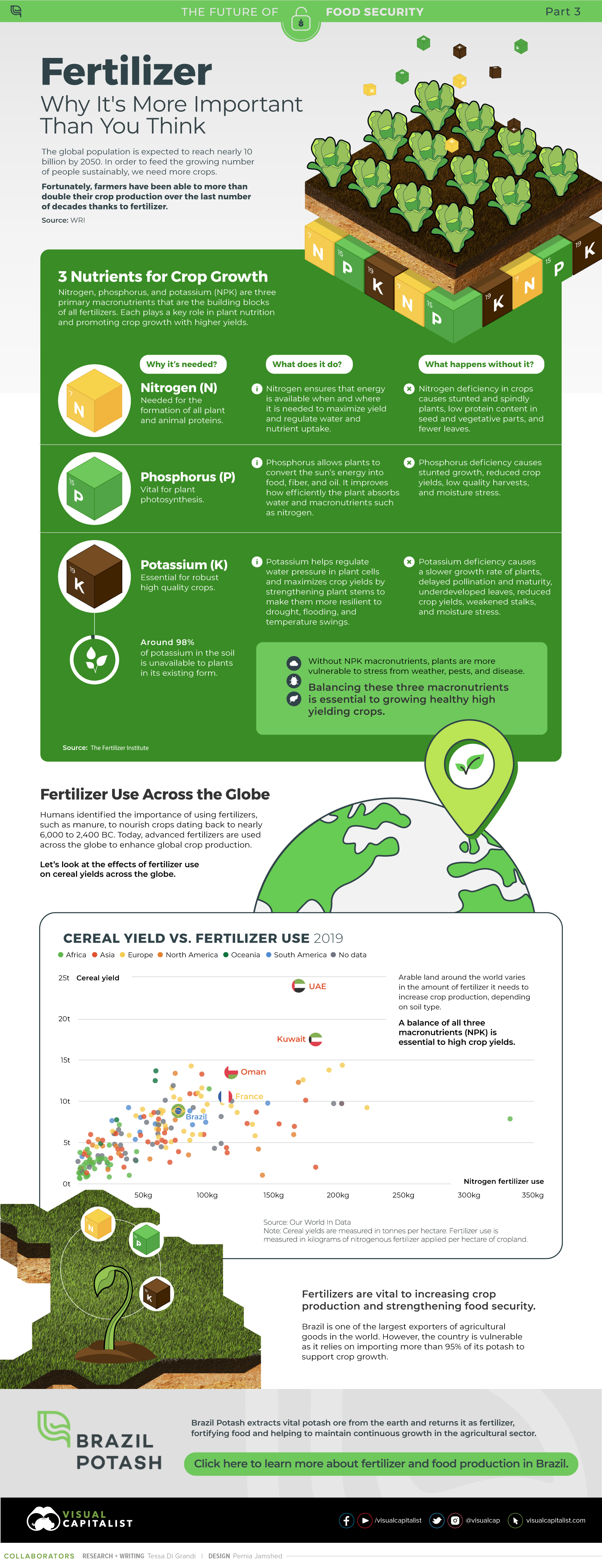
Though light isn’t toxic or overtly damaging to the natural landscape, it can still have a serious impact on wildlife, as well as blunting the beauty of the night sky. The good news is that light is one of the easiest forms of pollution to prevent. New technologies and lighting techniques aren’t just good for our night skies, they’re generally more energy efficient as well. Just as economic incentive lured buildings and infrastructure to America’s natural spaces, it may be energy efficiency that helps us return more of the night sky to its natural state. on Over recent decades, farmers have been able to more than double their production of crops thanks to fertilizers and the vital nutrients they contain. When crops are harvested, the essential nutrients are taken away with them to the dining table, resulting in the depletion of these nutrients in the soil. To replenish these nutrients, fertilizers are needed, and the cycle continues. The above infographic by Brazil Potash shows the role that each macronutrient plays in growing healthy, high-yielding crops.
Food for Growth
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK) are three primary macronutrients that are the building blocks of the global fertilizer industry. Each plays a key role in plant nutrition and promoting crop growth with higher yields. Let’s take a look at how each macronutrient affects plant growth. If crops lack NPK macronutrients, they become vulnerable to various stresses caused by weather conditions, pests, and diseases. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain a balance of all three macronutrients for the production of healthy, high-yielding crops.
The Importance of Fertilizers
Humans identified the importance of using fertilizers, such as manure, to nourish crops dating back to nearly 6,000 to 2,400 BC. As agriculture became more intensive and large-scale, farmers began to experiment with different types of fertilizers. Today advanced chemical fertilizers are used across the globe to enhance global crop production. There are a myriad of factors that affect soil type, and so the farmable land must have a healthy balance of all three macronutrients to support high-yielding, healthy crops. Consequently, arable land around the world varies in the amount and type of fertilizer it needs. Fertilizers play an integral role in strengthening food security, and a supply of locally available fertilizer is needed in supporting global food systems in an ever-growing world. Brazil is one of the largest exporters of agricultural goods in the world. However, the country is vulnerable as it relies on importing more than 95% of its potash to support crop growth. Brazil Potash is developing a new potash project in Brazil to ensure a stable domestic source of this nutrient-rich fertilizer critical for global food security. Click here to learn more about fertilizer and food production in Brazil.