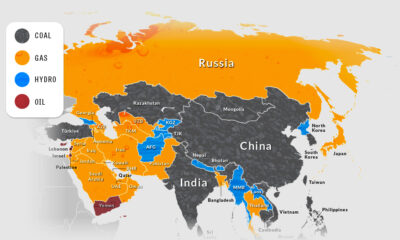
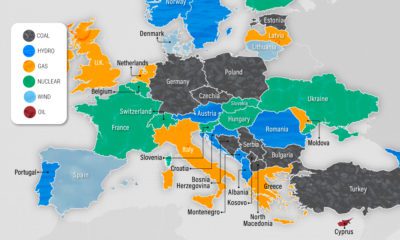
Mapped: Biggest Sources of Electricity by State and Province
On a national scale, the United States and Canada rely on a very different makeup of sources to generate their electricity. The U.S. primarily uses natural gas, coal, and nuclear power, while Canada relies on both hydro and nuclear. That said, when zooming in on the province or state level, individual primary electricity sources can differ greatly. Here’s a look at the electricity generation in the states and provinces of these two countries using data from the Nuclear Energy Institute (2021) and the Canada Energy Regulator (2019).
Natural Gas
Natural gas is widely used for electricity generation in the United States. Known as a “cleaner” fossil fuel, its abundance, coupled with an established national distribution network and relatively low cost, makes it the leading electricity source in the country. In 2021, 38% of the 4120 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity generated in the U.S. came from natural gas. Not surprisingly, more than 40% of American states have natural gas as their biggest electricity source. Here are some states that have the largest shares of natural gas-sourced electricity. In Canada, natural gas is only the third-biggest electricity source (behind hydro and nuclear), accounting for 11% of the 632 TWh of electricity produced in 2019. Alberta is the only province with natural gas as its main source of electricity.
Nuclear
Nuclear power is a carbon-free energy source that makes up a considerable share of the energy generated in both the U.S. and Canada. 19% of America’s and 15% of Canada’s electricity comes from nuclear power. While the percentages are close to one another, it’s good to note that the United States generates 6 to 7 times more electricity than Canada each year, yielding a lot more nuclear power than Canada in terms of gigawatt hours (GWh) per year. As seen in the map, many states and provinces with nuclear as their main source of electricity are concentrated in the eastern half of the two countries. In the U.S., Illinois, Pennsylvania, and South Carolina are top producers in terms of GWh/year. Illinois and South Carolina also have nuclear as their primary electricity source, whereas Pennsylvania’s electricity production from natural gas exceeds that from nuclear. The vast majority of Canada’s nuclear reactors (18 of 19) are in Ontario, with the 19th in New Brunswick. Both of these provinces rely on nuclear as their biggest source of electricity.
Renewables: Hydro, Wind and Solar
Out of the different types of renewable electricity sources, hydro is the most prevalent in North America. For example, 60% of Canada’s and 6% of the U.S.’s electricity comes from hydropower. Here are the states and provinces that have hydro as their biggest source of electricity. Wind and solar power collectively comprise a small percentage of total electricity generated in both countries. While no state or province relies on solar as its biggest source of electricity, Iowa, Kansas, Oklahoma, and South Dakota rely primarily on wind for their electricity, along with Canada’s Prince Edward Island (PEI).
Coal and Oil
Coal and oil are emission-heavy electricity sources still prevalent in North America. Currently, 22% of America’s and 7% of Canada’s electricity comes from coal, with places such as Kentucky, Missouri, West Virginia, Saskatchewan, and Nova Scotia still relying on coal as their biggest sources of electricity. Certain regions also use petroleum to generate their electricity. Although its use for this purpose is declining, it is still the biggest source of electricity in both Hawaii and Nunavut. Over the next few years, it will be interesting to observe the use of these fossil fuels for electricity generation in the U.S. and Canada. Despite the differences in climate commitments between the two countries, lowering coal and oil-related emissions may be a critical part of hitting decarbonization targets in a timely manner. on
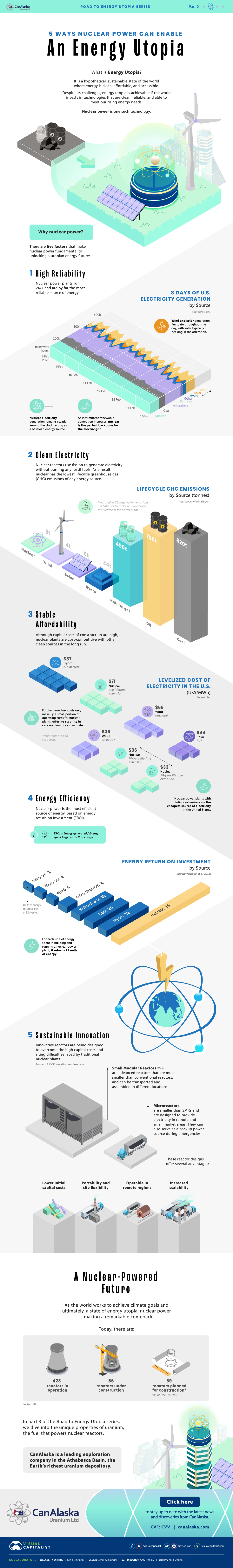
#1: High Reliability
Nuclear power plants run 24/7 and are the most reliable source of sustainable energy. Nuclear electricity generation remains steady around the clock throughout the day, week, and year. Meanwhile, daily solar generation peaks in the afternoon when electricity demand is usually lower, and wind generation depends on wind speeds.As the use of variable solar and wind power increases globally, nuclear offers a stable and reliable backbone for a clean electricity grid.
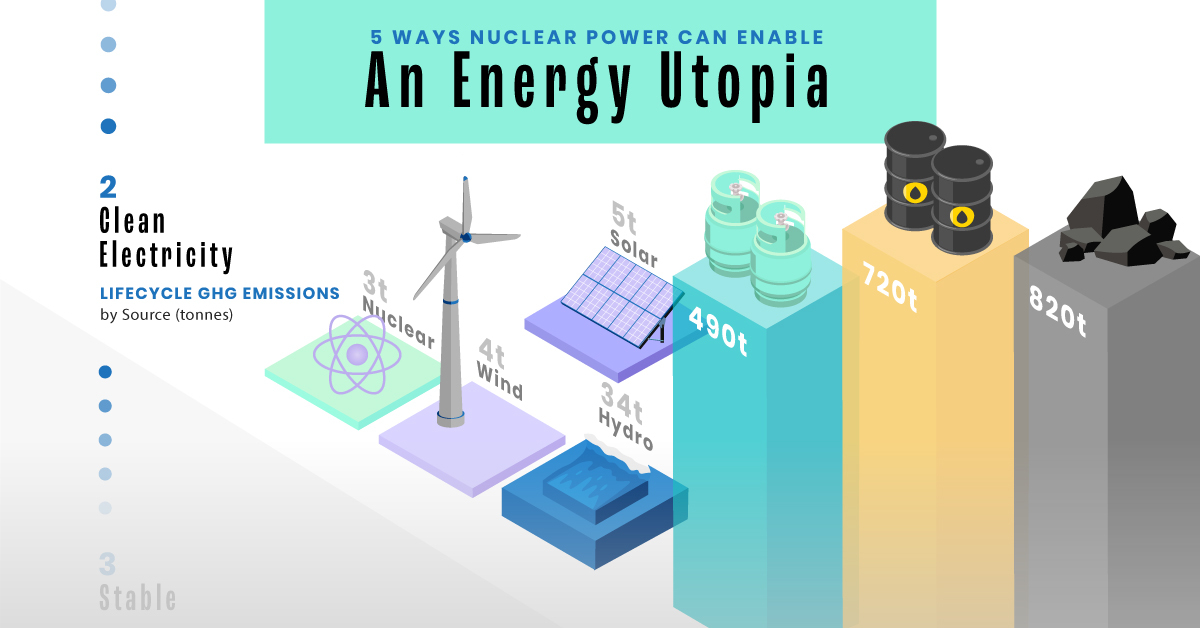
#2: Clean Electricity
Nuclear reactors use fission to generate electricity without any greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.Consequently, nuclear power is the cleanest energy source on a lifecycle basis, measured in CO2-equivalent emissions per gigawatt-hour (GWh) of electricity produced by a power plant over its lifetime. The lifecycle emissions from a typical nuclear power plant are 273 times lower than coal and 163 times lower than natural gas. Furthermore, nuclear is relatively less resource-intensive, allowing for lower supply chain emissions than wind and solar plants.
#3: Stable Affordability
Although nuclear plants can be expensive to build, they are cost-competitive in the long run. Most nuclear plants have an initial lifetime of around 40 years, after which they can continue operating with approved lifetime extensions. Nuclear plants with lifetime extensions are the cheapest sources of electricity in the United States, and 88 of the country’s 92 reactors have received approvals for 20-year extensions. Additionally, according to the World Nuclear Association, nuclear plants are relatively less susceptible to fuel price volatility than natural gas plants, allowing for stable costs of electricity generation.
#4: Energy Efficiency
Nuclear’s high energy return on investment (EROI) exemplifies its exceptional efficiency. EROI measures how many units of energy are returned for every unit invested in building and running a power plant, over its lifetime. According to a 2018 study by Weissbach et al., nuclear’s EROI is 75 units, making it the most efficient energy source by some distance, with hydropower ranking second at 35 units.
#5: Sustainable Innovation
New, advanced reactor designs are bypassing many of the difficulties faced by traditional nuclear plants, making nuclear power more accessible.
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are much smaller than conventional reactors and are modular—meaning that their components can be transported and assembled in different locations. Microreactors are smaller than SMRs and are designed to provide electricity in remote and small market areas. They can also serve as backup power sources during emergencies.
These reactor designs offer several advantages, including lower initial capital costs, portability, and increased scalability.
A Nuclear-Powered Future
Nuclear power is making a remarkable comeback as countries work to achieve climate goals and ultimately, a state of energy utopia. Besides the 423 reactors in operation worldwide, another 56 reactors are under construction, and at least 69 more are planned for construction. Some nations, like Japan, have also reversed their attitudes toward nuclear power, embracing it as a clean and reliable energy source for the future. CanAlaska is a leading exploration company in the Athabasca Basin, the Earth’s richest uranium depository. Click here to learn more now. In part 3 of the Road to Energy Utopia series, we explore the unique properties of uranium, the fuel that powers nuclear reactors.