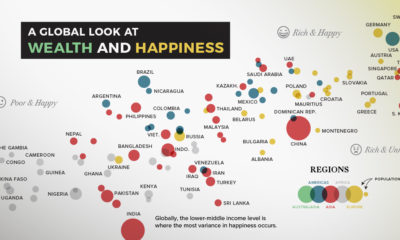
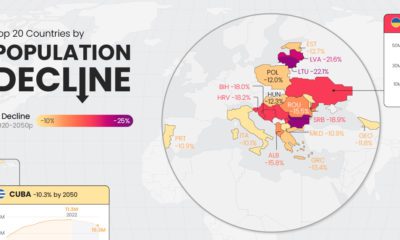
It’s generally understood that having enough money to cover your needs and wants can help you live a relatively happy, comfortable life—and recent research shows this relationship may increase linearly as income levels grow, as well. However, there’s much more to it than that. Happiness levels depend not just on financial security, but also broader perceptions of one’s social support, personal freedom, and more. This series of map pulls data from the World Happiness Report to uncover the average scores of 149 countries between 2018-2020, and which ones emerged the happiest or unhappiest. We also look at the most and least improved countries in every region.
How is Happiness Measured?
First, let’s look at the factors used to calculate world happiness levels. Some clear indicators are health and wealth, both metrics that have been steadily on the rise worldwide. The report takes these into account, weighting GDP per capita and life expectancy at birth into the scores. The report also looks at more intangible aspects, collecting survey responses around:
Social support Freedom to make life choices Generosity Perceptions of government/ business corruption Positive or negative affects (Recent experience of emotions)
This year, there was a natural focus on the negative affect measure of the COVID-19 pandemic on happiness levels, such as exacerbating mental health risks. In addition, such measurements varied depending on each country’s response to the crisis.
Looking Closely at Regional Happiness Levels
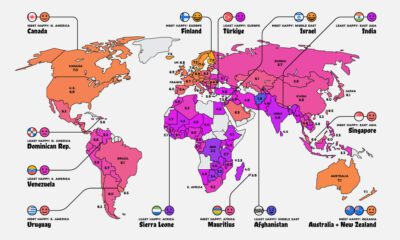
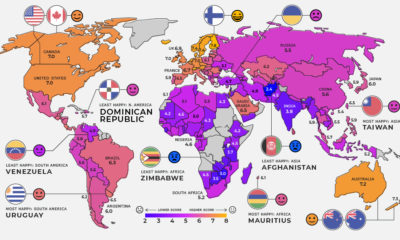
Worldwide happiness comes in at an average score of 5.5, a marginal improvement since our previous coverage of this report in 2019. Let’s dive into regional outlooks for happiness levels.
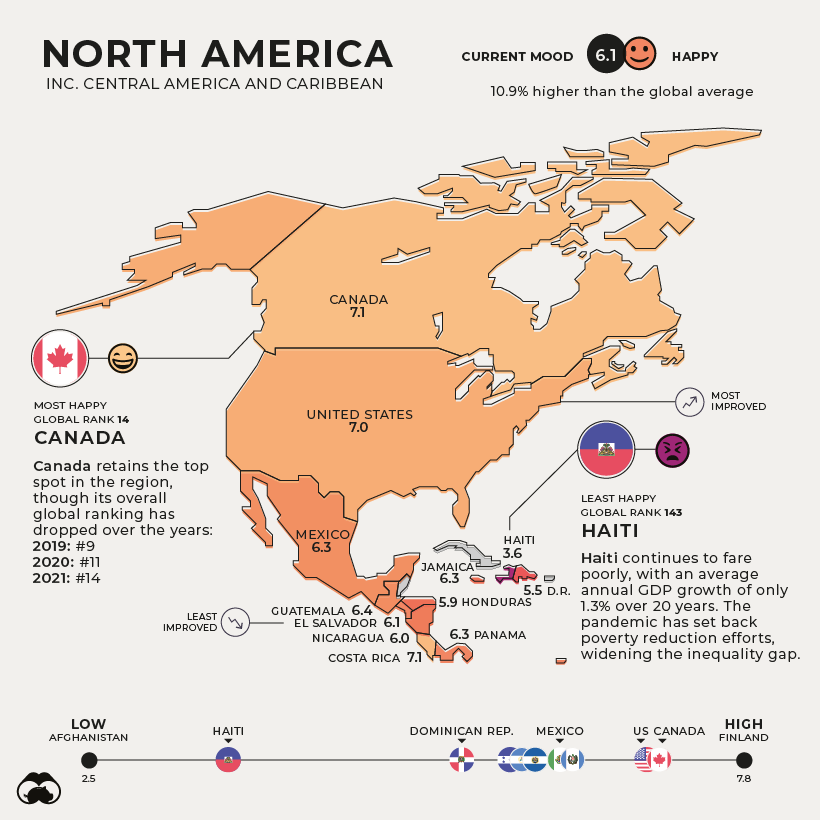
North America
Current Mood: Happy (6.1) Canada retains its spot as the happiest country in North America, although its overall global ranking has dropped over the years. In 2019, it was ranked in ninth place globally, dropping to 11th in the 2020 edition, and declining further to 14th place in this year’s report.
Haiti continues to fare poorly as the unhappiest in the region, with an average annual GDP growth of only 1.3% over 20 years. Its weak economy and political instability have been worsened by the pandemic—setting back efforts to reduce poverty and widening inequality.
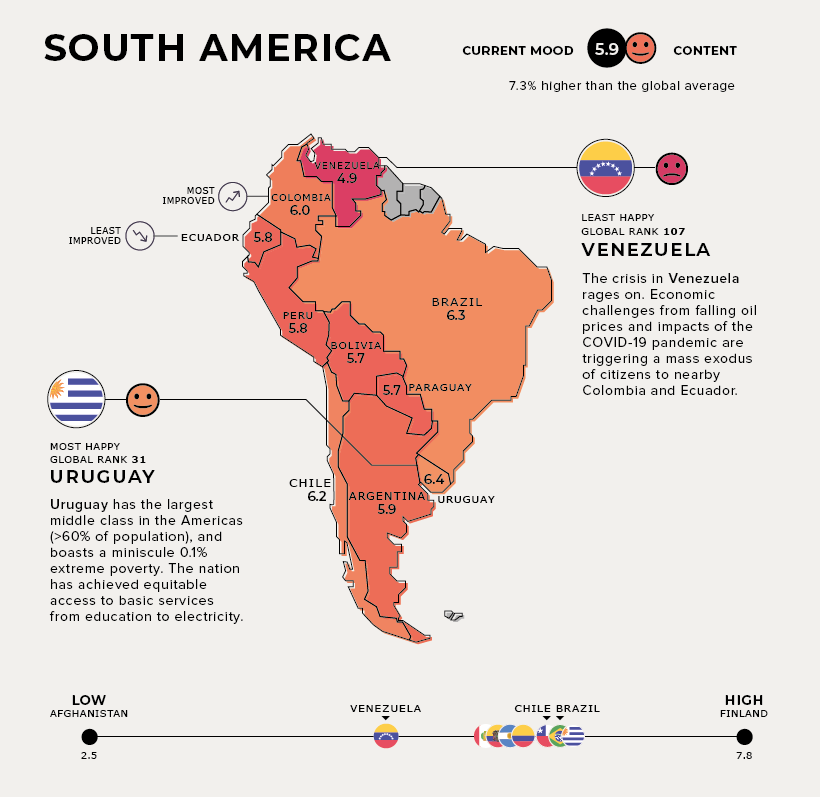
South America
Current Mood: Content (5.9) With the largest middle class in the Americas—60% of its population—and a miniscule 0.1% extreme poverty rate, Uruguay is the happiest South American country. The nation has also achieved equitable access to basic services, from education to electricity.
The trio of Colombia, Ecuador, and Venezuela are experiencing different stages of progress in happiness levels, but their relationship is very much interdependent. Venezuela and Ecuador face similar economic challenges and sharp declines in oil prices. Venezuela is additionally acutely affected by socio-political unrest, triggering a mass exodus of citizens to Ecuador and Colombia alike. The silver lining is that the influx of highly-educated Venezuelan migrants may provide a 2% boost to Ecuador’s GDP. Colombia, the most improved country, has halved its poverty rate in the last decade. In addition, it has welcomed almost 2 million Venezuelan migrants as of Dec 2020—and plans to provide them up to 10 years of protective status.
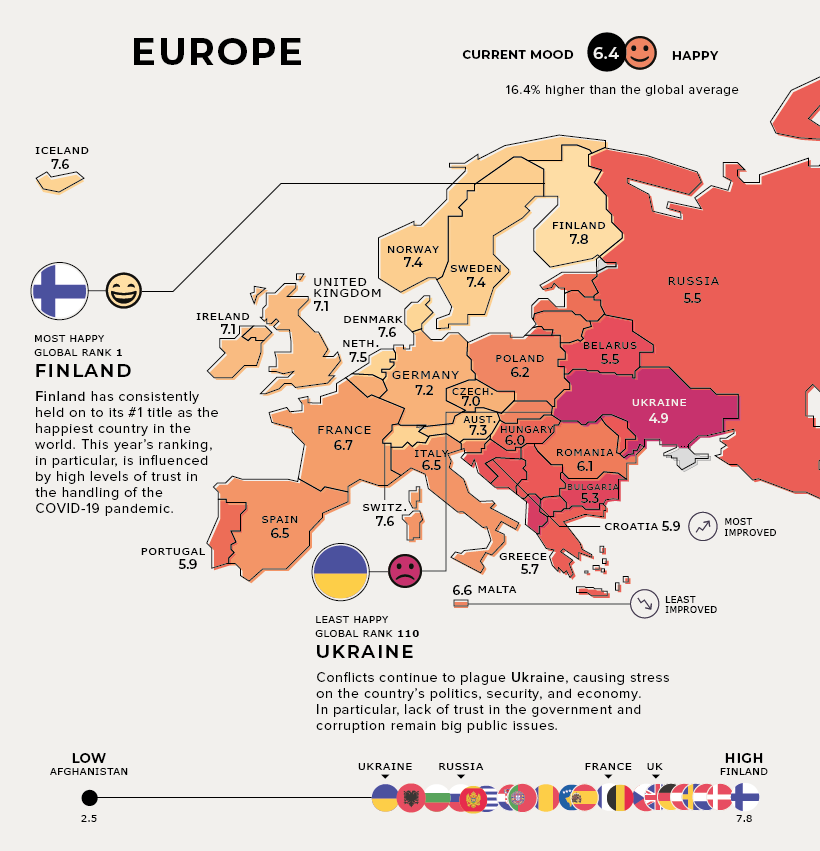
Europe
Current Mood: Happy (6.4) Finland remains at the top of the leaderboard as the world’s happiest country. This year’s ranking was also influenced by high levels of trust in the way the COVID-19 pandemic was handled. Meanwhile, the shock of the COVID-19 crisis is expected to be short-lived in Croatia, which is the most improved country. This is partly due to its steady pre-pandemic economic gains, although risks remain.
In the unhappiest country of Ukraine, conflicts continue to cause stress on its politics, security, and economy. In particular, government corruption remains a big public issue.
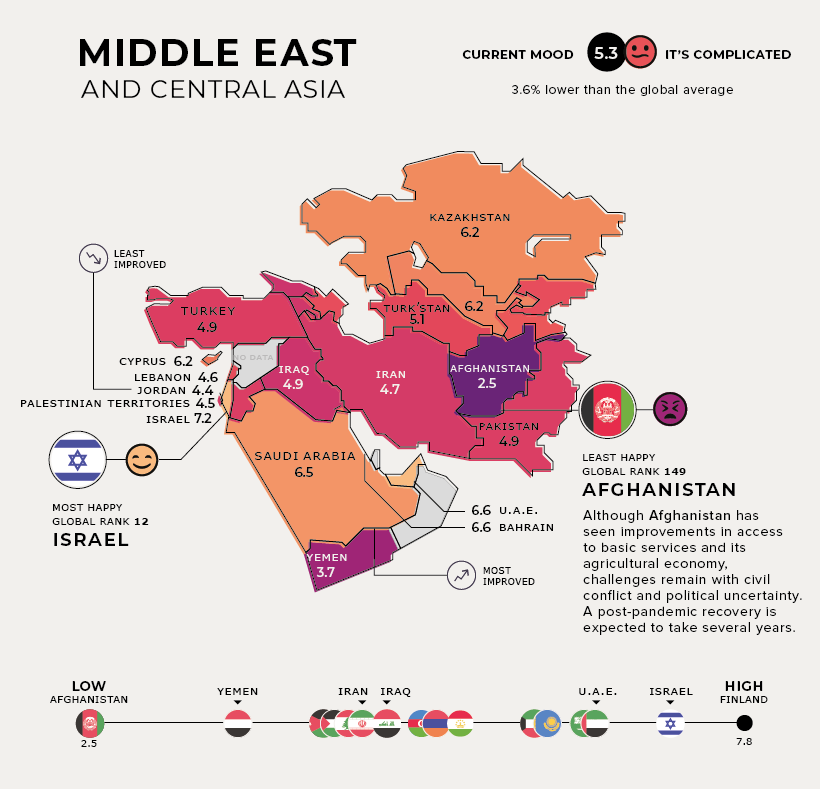
Middle East and Central Asia
Current Mood: It’s Complicated (5.3) Saudi Arabia is the most improved country in the region, as it continues to reduce its oil dependence, diversify its economy, and bolster its public services. It has also been making some progress towards gender equality.
The tourism and hospitality industries contribute nearly 20% of Jordan’s GDP—and COVID-19 has caused a prolonged economic decline in the country along with the headwinds of these industries. Although Afghanistan has seen improvements in access to basic services and its agricultural economy, challenges remain with prolonged conflict and violence. A post-pandemic recovery in the world’s unhappiest country might take several years.
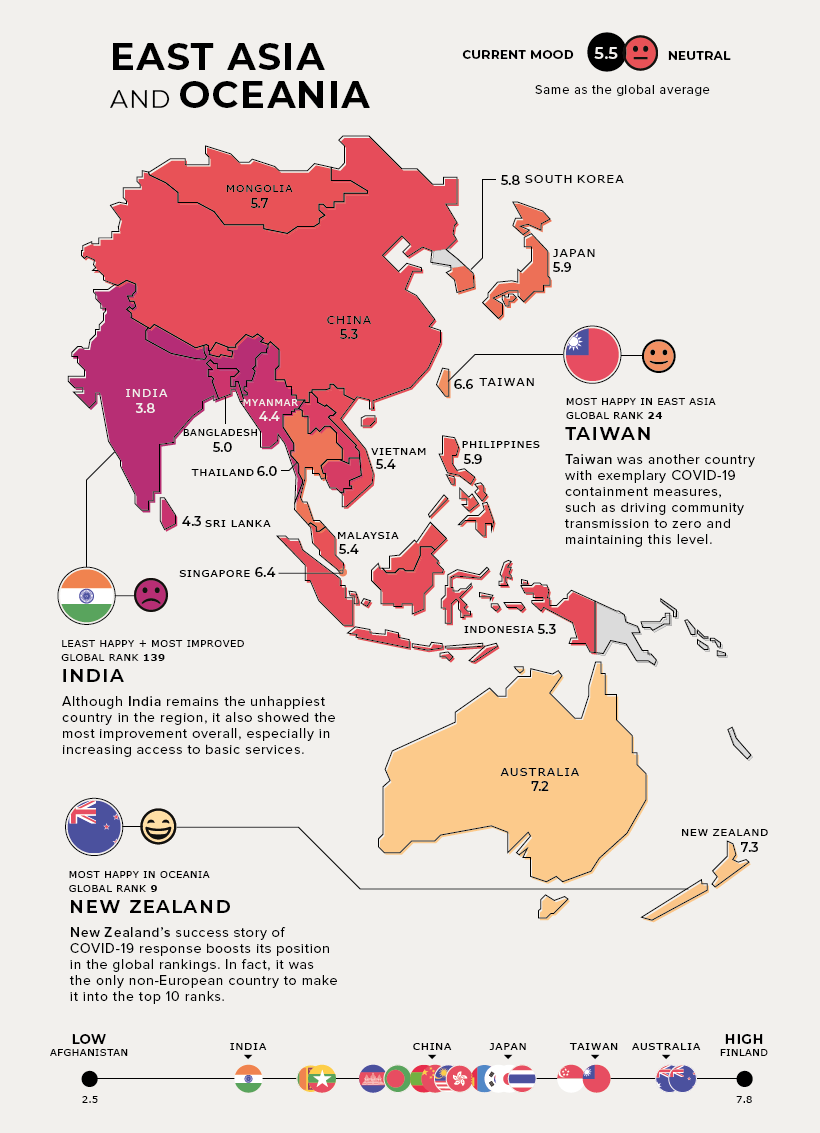
East Asia and Oceania
Current Mood: Neutral (5.5) Both New Zealand and Taiwan saw a successful COVID-19 response and recovery boosting their positions in the global happiness rankings. In fact, New Zealand was the only non-European country to make it into the top 10 on the global happiness list.
Note: As the report only covers 149 countries, “Oceania” only refers to Australia and New Zealand in this instance. Although India remains the unhappiest country in the region, it also showed the most improvement overall, possibly due to its increased access to basic services. Notably though, the pandemic caused a sharp economic contraction in real GDP by 23.9% year-over-year in Q1’2021.
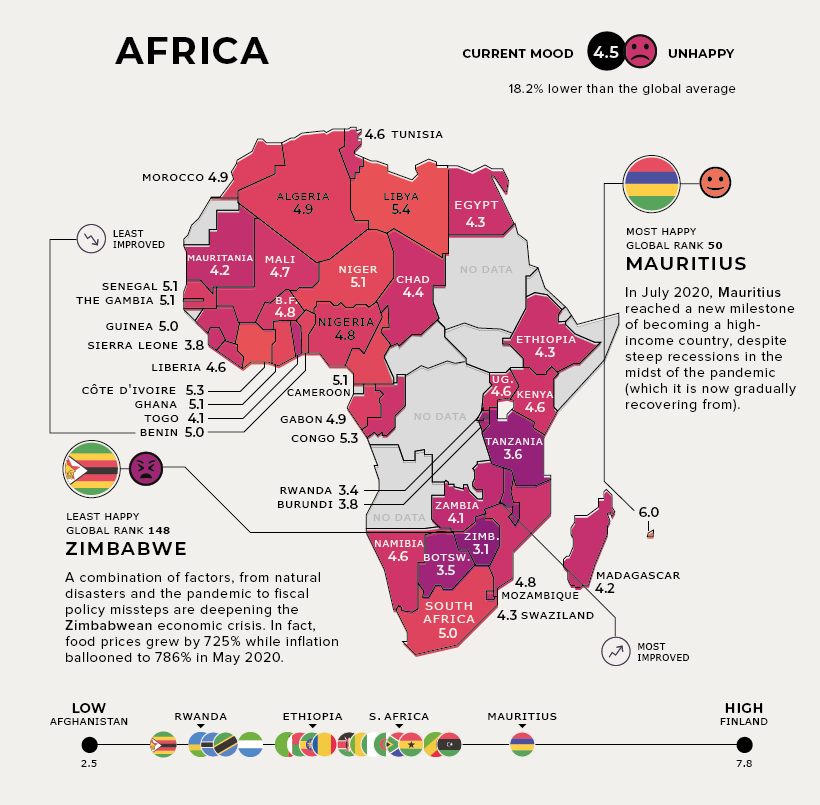
Africa
Current Mood: Unhappy (4.5) In July 2020, the island nation of Mauritius joined Seychelles to become the second high-income country in Africa, helping cement its status as the happiest in the region. Zambia, the most improved African country, has one of the world’s youngest populations by median age—which presents long-term opportunities for labor force participation.
On the flip side, agriculturally-reliant Benin struggles with high poverty, with close to 40% of the population living below $1.90 per day. Zimbabwe, the unhappiest country, has been through not just natural disasters but financial disasters too. It experienced hyperinflation of 786% in May 2020, accompanied by an equally sharp rise in food prices. Although each country has been uniquely impacted by the pandemic, it’s clear that on the whole, happiness levels take into account so much more. How will future rankings look like in a post-pandemic world? on Even while political regimes across these countries have changed over time, they’ve largely followed a few different types of governance. Today, every country can ultimately be classified into just nine broad forms of government systems. This map by Truman Du uses information from Wikipedia to map the government systems that rule the world today.
Countries By Type of Government
It’s important to note that this map charts government systems according to each country’s legal framework. Many countries have constitutions stating their de jure or legally recognized system of government, but their de facto or realized form of governance may be quite different. Here is a list of the stated government system of UN member states and observers as of January 2023: Let’s take a closer look at some of these systems.
Monarchies
Brought back into the spotlight after the death of Queen Elizabeth II of England in September 2022, this form of government has a single ruler. They carry titles from king and queen to sultan or emperor, and their government systems can be further divided into three modern types: constitutional, semi-constitutional, and absolute. A constitutional monarchy sees the monarch act as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, giving them little to no real power. For example, King Charles III is the head of 15 Commonwealth nations including Canada and Australia. However, each has their own head of government. On the other hand, a semi-constitutional monarchy lets the monarch or ruling royal family retain substantial political powers, as is the case in Jordan and Morocco. However, their monarchs still rule the country according to a democratic constitution and in concert with other institutions. Finally, an absolute monarchy is most like the monarchies of old, where the ruler has full power over governance, with modern examples including Saudi Arabia and Vatican City.
Republics
Unlike monarchies, the people hold the power in a republic government system, directly electing representatives to form government. Again, there are multiple types of modern republic governments: presidential, semi-presidential, and parliamentary. The presidential republic could be considered a direct progression from monarchies. This system has a strong and independent chief executive with extensive powers when it comes to domestic affairs and foreign policy. An example of this is the United States, where the President is both the head of state and the head of government. In a semi-presidential republic, the president is the head of state and has some executive powers that are independent of the legislature. However, the prime minister (or chancellor or equivalent title) is the head of government, responsible to the legislature along with the cabinet. Russia is a classic example of this type of government. The last type of republic system is parliamentary. In this system, the president is a figurehead, while the head of government holds real power and is validated by and accountable to the parliament. This type of system can be seen in Germany, Italy, and India and is akin to constitutional monarchies. It’s also important to point out that some parliamentary republic systems operate slightly differently. For example in South Africa, the president is both the head of state and government, but is elected directly by the legislature. This leaves them (and their ministries) potentially subject to parliamentary confidence.
One-Party State
Many of the systems above involve multiple political parties vying to rule and govern their respective countries. In a one-party state, also called a single-party state or single-party system, only one political party has the right to form government. All other political parties are either outlawed or only allowed limited participation in elections. In this system, a country’s head of state and head of government can be executive or ceremonial but political power is constitutionally linked to a single political movement. China is the most well-known example of this government system, with the General Secretary of the Communist Party of China ruling as the de facto leader since 1989.
Provisional
The final form of government is a provisional government formed as an interim or transitional government. In this system, an emergency governmental body is created to manage political transitions after the collapse of a government, or when a new state is formed. Often these evolve into fully constitutionalized systems, but sometimes they hold power for longer than expected. Some examples of countries that are considered provisional include Libya, Burkina Faso, and Chad.