Altogether, the country spans 3.8 million square miles (9.8 million km²)—making it the third largest country in the world. Even without factoring Alaska and Hawaii into the calculations, the contiguous U.S. land mass can fit up to 30 European countries within it. With this much ground to work with, it raises the natural question of how land actually gets used by America’s economy. For example, what percentage of land is taken up by urban areas, and how much farmland and forests exist in comparison? Today’s maps from the McHarg Center put America’s wide variety of land uses into perspective.
The Components of U.S. Land Use
As the U.S. prepares to add 100 million more people this century, the “2100 Project: An Atlas for the Green New Deal” provides a snapshot of U.S. land use (as of 2017), aimed at managing resources to support this future. According to this data, here is a snapshot of land use in the Lower 48 States: Let’s dive into the specifics of three types of land: urban areas, forests, and agriculture. Editor’s note: click on any map below to see a large, high-resolution version, which will open in a new window.
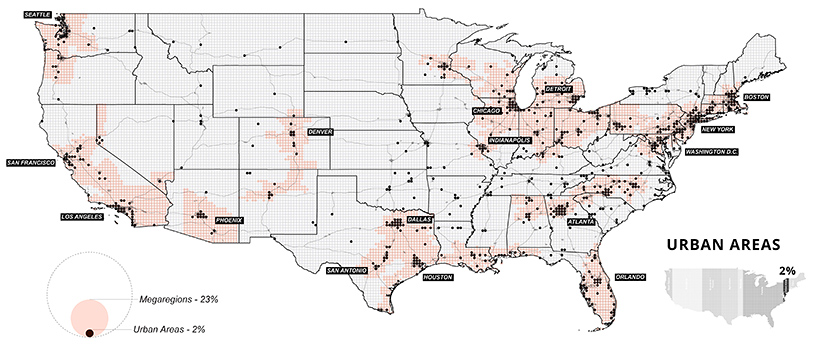
Small But Mighty: U.S. Urban Areas
It’s clear that even a little space goes a long way. Although urban areas take up only 2% of land, an overwhelming majority of Americans call cities their home. As of 2018, urbanites made up over 82% of the U.S. population. Where people go, productivity often follows. In 2018, it’s estimated that 31 county economies made up a whopping 32% of national GDP. Most of these counties were located in and around major cities, such as Los Angeles or New York.
Although urban areas are a small part of the overall land they’re built on, they’re integral to the nation’s continued growth. According to research by the McKinsey Global Institute, it’s estimated that by 2030, 60% of job growth could come from just 25 hubs.
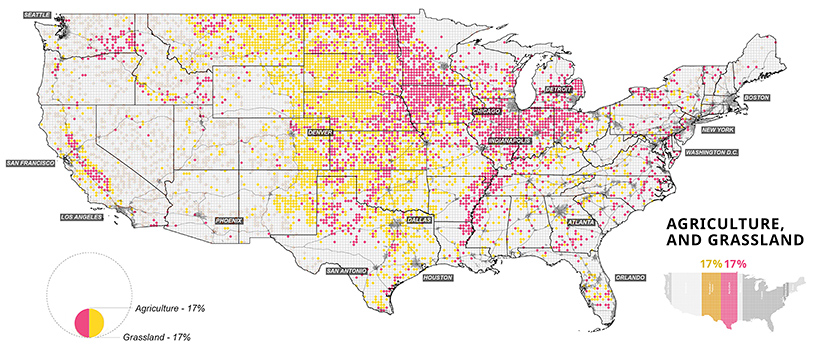
Seeing Green: America’s Vast Forests
On the flipside, forests account for over a quarter of land in the U.S., divided almost evenly between deciduous and evergreen trees. Many protected national and state parks can also be found in and around forests.
On the mainland, California and Oregon are the states with the most forested land—unfortunately, they have also been plagued by wildfires in recent, dry summer months. Wetlands are also included in the map above, particularly around the southern tip of Florida, where Everglades National Park is located. Over the years, many wetlands were drained to make way for agriculture, particularly in the Great Lakes megaregion. As a result, it’s estimated that their area today is only half of what they once used to be.
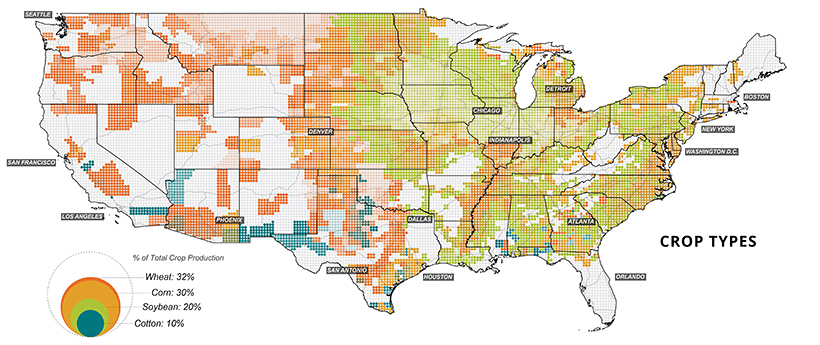
Home Grown: Agriculture in the U.S.
Last but not least, the final set of maps show where America grows its food. Agricultural, food, and related industries contributed $1.05 trillion (5.4%) to U.S. GDP in 2017.
Wheat, corn, and soybeans are the major crops grown in the U.S.—and cotton also makes the cut as a profitable non-food crop. Much of these crops feed not only Americans, but other parts of the world too. Soybeans, corn, and wheat are exported across the Pacific mainly to China and Japan.
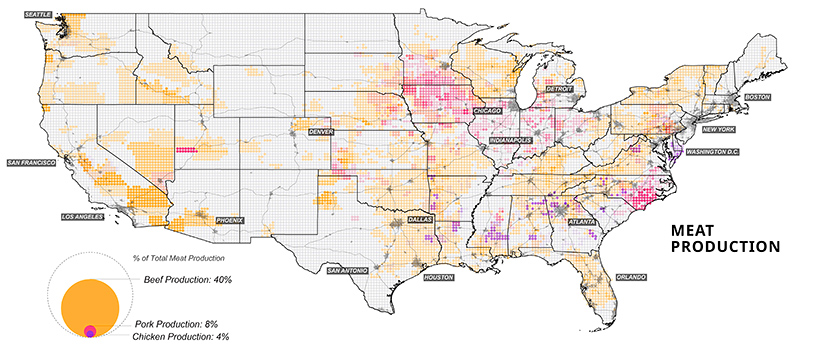
Corn, in particular, is a unique crop with a myriad of uses, from food to fuels. Up to 40% of U.S. corn is turned into livestock feed, with cows consuming over half (56%) of this amount. At present, the U.S. is the world’s largest beef producer, followed by Brazil. In fact, beef production takes up 40% of total livestock-related land use domestically.
Although fewer American consumers are opting for meat in their diets, production has remained at high rates. Further, as incomes continues to increase worldwide, the global appetite for meat is set to rise along with it.
Future Land Use
The U.S. population is set to grow by 100 million more people over the coming decades, raising the pressure on limited U.S. land and natural resources. This pressure will be felt everywhere, from dense urban land to agricultural farmland. How the land gets utilized will shape the country’s future for years to come. on Even while political regimes across these countries have changed over time, they’ve largely followed a few different types of governance. Today, every country can ultimately be classified into just nine broad forms of government systems. This map by Truman Du uses information from Wikipedia to map the government systems that rule the world today.
Countries By Type of Government
It’s important to note that this map charts government systems according to each country’s legal framework. Many countries have constitutions stating their de jure or legally recognized system of government, but their de facto or realized form of governance may be quite different. Here is a list of the stated government system of UN member states and observers as of January 2023: Let’s take a closer look at some of these systems.
Monarchies
Brought back into the spotlight after the death of Queen Elizabeth II of England in September 2022, this form of government has a single ruler. They carry titles from king and queen to sultan or emperor, and their government systems can be further divided into three modern types: constitutional, semi-constitutional, and absolute. A constitutional monarchy sees the monarch act as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, giving them little to no real power. For example, King Charles III is the head of 15 Commonwealth nations including Canada and Australia. However, each has their own head of government. On the other hand, a semi-constitutional monarchy lets the monarch or ruling royal family retain substantial political powers, as is the case in Jordan and Morocco. However, their monarchs still rule the country according to a democratic constitution and in concert with other institutions. Finally, an absolute monarchy is most like the monarchies of old, where the ruler has full power over governance, with modern examples including Saudi Arabia and Vatican City.
Republics
Unlike monarchies, the people hold the power in a republic government system, directly electing representatives to form government. Again, there are multiple types of modern republic governments: presidential, semi-presidential, and parliamentary. The presidential republic could be considered a direct progression from monarchies. This system has a strong and independent chief executive with extensive powers when it comes to domestic affairs and foreign policy. An example of this is the United States, where the President is both the head of state and the head of government. In a semi-presidential republic, the president is the head of state and has some executive powers that are independent of the legislature. However, the prime minister (or chancellor or equivalent title) is the head of government, responsible to the legislature along with the cabinet. Russia is a classic example of this type of government. The last type of republic system is parliamentary. In this system, the president is a figurehead, while the head of government holds real power and is validated by and accountable to the parliament. This type of system can be seen in Germany, Italy, and India and is akin to constitutional monarchies. It’s also important to point out that some parliamentary republic systems operate slightly differently. For example in South Africa, the president is both the head of state and government, but is elected directly by the legislature. This leaves them (and their ministries) potentially subject to parliamentary confidence.
One-Party State
Many of the systems above involve multiple political parties vying to rule and govern their respective countries. In a one-party state, also called a single-party state or single-party system, only one political party has the right to form government. All other political parties are either outlawed or only allowed limited participation in elections. In this system, a country’s head of state and head of government can be executive or ceremonial but political power is constitutionally linked to a single political movement. China is the most well-known example of this government system, with the General Secretary of the Communist Party of China ruling as the de facto leader since 1989.
Provisional
The final form of government is a provisional government formed as an interim or transitional government. In this system, an emergency governmental body is created to manage political transitions after the collapse of a government, or when a new state is formed. Often these evolve into fully constitutionalized systems, but sometimes they hold power for longer than expected. Some examples of countries that are considered provisional include Libya, Burkina Faso, and Chad.