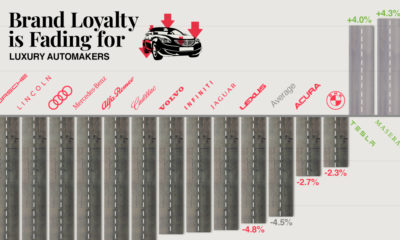
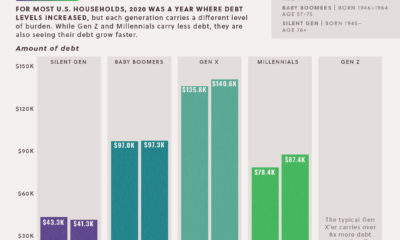
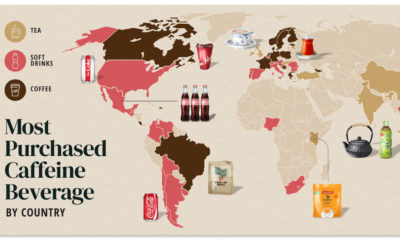
This ranking uses consumer preference data from Morning Consult to show which brands are favored considerably more by Gen Z when compared to the general public. A brand’s rank is determined by the difference in favorability between Gen Z’s survey responses and the average of all U.S. adult respondents. Note: Gen Z is the generation born between 1997-2012. Favorability in this ranking is measured using the share of a generation who said they have a “very” or “somewhat” favorable opinion of said brand.
Brands Preferred by Gen Z
Compared to Millennials, Gen X, and Boomers, who may not care as much for these 20 brands, Gen Z—currently between 9-25 years old—loves them. Let’s dive in: Note: Differences may not add up exactly due to rounding. Unsurprisingly, TikTok takes the top spot. The app that is frequently used to poke fun at older generations and that in many ways is a reflection of Gen Z culture, is 30 points more favorable with the young generation than others. Members of Gen Z are the first true “digital natives”—meaning they were raised in the age of digital technology. As a result, many of their favorite brands are either some kind of social media platform and/or digital service, like Apple Pay, Snapchat, or Spotify. In fact, eight of Gen Z’s top 10 favorites on the above list are digital brands. Another distinguishing feature of consumers in this generation is that they’re more likely to care about brand ethics and sustainable consumption than other generations. However, one brand among their top 20 that defies that sentiment is the Chinese clothing company, Shein. This fast fashion company’s model promotes a culture of mass clothing hauls and thus, clothing waste—making it far from environmentally conscious. Shein has also come under fire recently for violating labor laws in its Chinese production facilities. And yet 44% of Gen Zs have a good impression of the brand, and it particularly does well with Gen Z women. Interestingly, members of Gen Z in the U.S. are also the first cohort to have strong awareness of Chinese brands more generally.
Gen Z vs. Millennials
Two generations that are often lumped together, Gen Z and Millennials have some considerable differences when it comes to their favorite brands. Here’s a brief look at some of the brands that do better with Gen Z compared to Millennials specifically, using favorability difference:
TikTok: 14.2 Crocs: 13.4 Pixar: 8.1 Morphe: 6.1
Compared to their generational neighbors, one interesting standout is Crocs—the utilitarian, but highly-customizable foam clogs—which almost 60% of Gen Zs see as favorable compared to only 46% of Millennials.
Gen Z’s Favorite Brands Overall
While Gen Z differentiates itself from the older generations in many ways, a lot of the overall favorites still align with everyone else’s.
Gen Z Trends
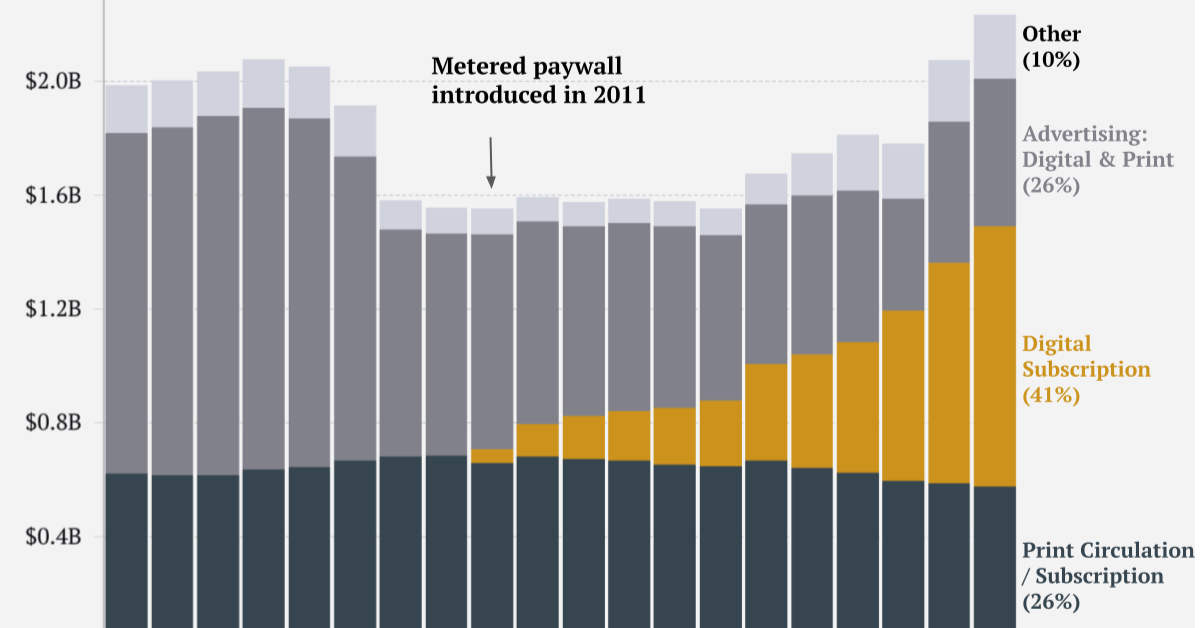
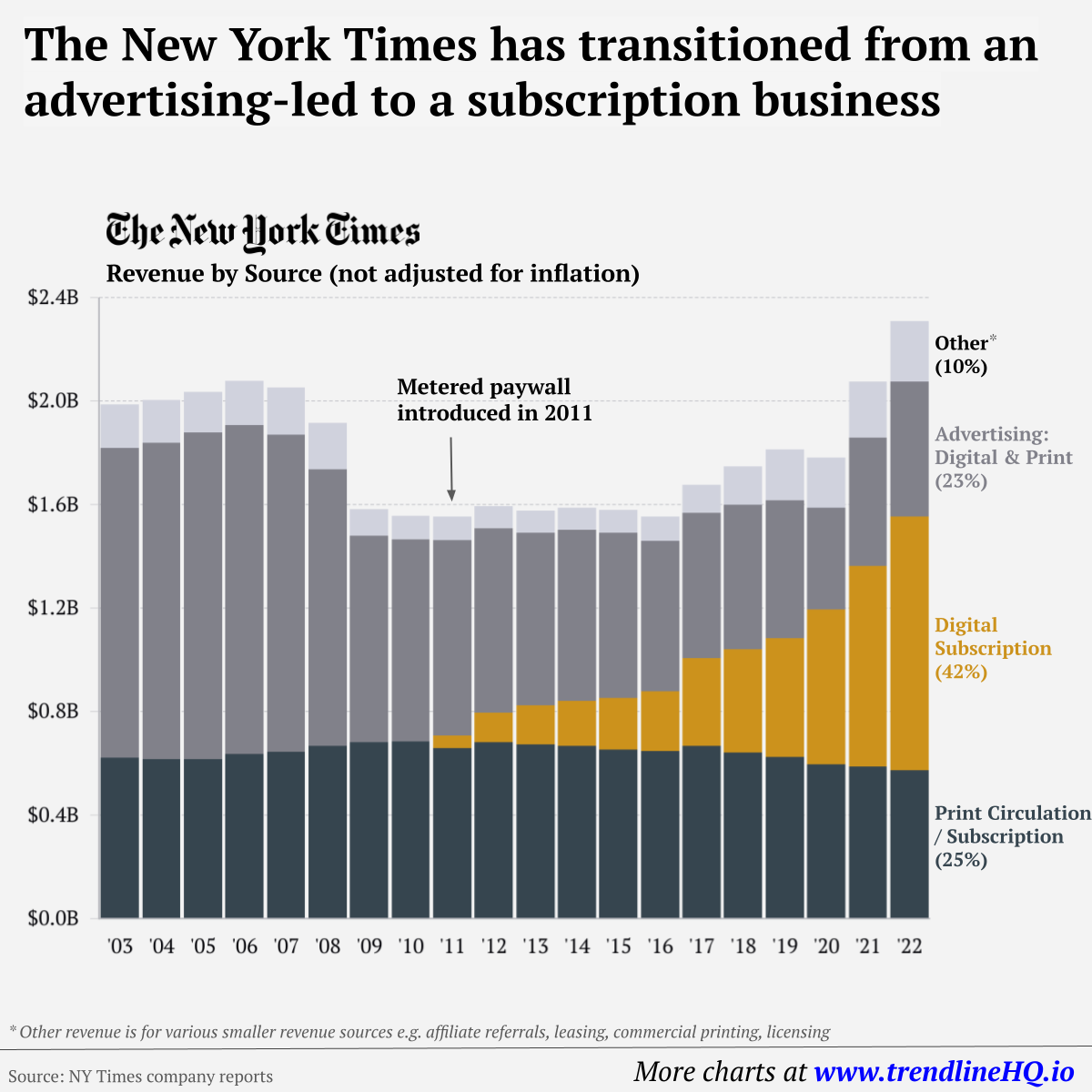
Overall, the report found that it’s hard for brands to win with Gen Z. Across all brands that were scored, 33% of the general American public rated them as favorable, but for Gen Z respondents the number dropped to 27%. In general, Gen Z tends to value conscious consumption and subsequently, brands that can meet those expectations. Digital services and products also do well with this generation that has never known a world without internet. As more and more Gen Zers enter the labor market and grow their consumer power, they will be an important generation to watch. on Similar to the the precedent set by the music industry, many news outlets have also been figuring out how to transition into a paid digital monetization model. Over the past decade or so, The New York Times (NY Times)—one of the world’s most iconic and widely read news organizations—has been transforming its revenue model to fit this trend. This chart from creator Trendline uses annual reports from the The New York Times Company to visualize how this seemingly simple transition helped the organization adapt to the digital era.
The New York Times’ Revenue Transition
The NY Times has always been one of the world’s most-widely circulated papers. Before the launch of its digital subscription model, it earned half its revenue from print and online advertisements. The rest of its income came in through circulation and other avenues including licensing, referrals, commercial printing, events, and so on. But after annual revenues dropped by more than $500 million from 2006 to 2010, something had to change. In 2011, the NY Times launched its new digital subscription model and put some of its online articles behind a paywall. It bet that consumers would be willing to pay for quality content. And while it faced a rocky start, with revenue through print circulation and advertising slowly dwindling and some consumers frustrated that once-available content was now paywalled, its income through digital subscriptions began to climb. After digital subscription revenues first launched in 2011, they totaled to $47 million of revenue in their first year. By 2022 they had climbed to $979 million and accounted for 42% of total revenue.
Why Are Readers Paying for News?
More than half of U.S. adults subscribe to the news in some format. That (perhaps surprisingly) includes around four out of 10 adults under the age of 35. One of the main reasons cited for this was the consistency of publications in covering a variety of news topics. And given the NY Times’ popularity, it’s no surprise that it recently ranked as the most popular news subscription.