Our vehicles and indoor spaces are climate controlled, fridges keep our food consistently chilled, and with a small twist of the tap, we get water that’s the optimal temperature. Of course, our concept of what’s hot or cold is actually very narrow in the grand scheme of things. Even the stark contrast between the wind-swept glaciers of Antarctica and the blistering sands of our deserts is a mere blip on the universe’s full temperature range. Today’s graphic, produced by the IIB Studio, looks at the hottest and coldest temperatures in our universe.
But First: What is Temperature Anyway?
Before looking at this top-to-bottom view of extreme temperatures, it helps to remember what temperature is actually measuring – kinetic energy, or the movement of atoms. Hypothetically, atoms would simply stop moving as they reach absolute zero. As matter heats up, it begins to “vibrate” more vigorously, changing states from solid to gas. Eventually, plasma forms as electrons wander away from the nuclei. With that quick primer, let’s dig into some of the hottest insights in this cool data visualization.
Highs and Lows on Planet Earth
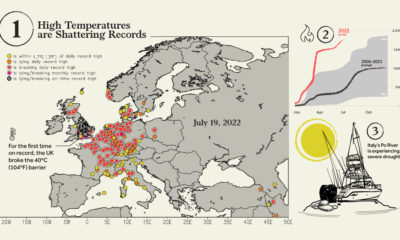
Earth’s lowest air temperature, -135ºF (-93ºC), was recorded in Antarctica in 2010. Since then, scientists have discovered that surface ice temperatures can dip as low as -144ºF (-98ºC). The conditions need to be just right: clear skies and dry air must persist for several days during the polar winter. In surroundings this cold, human lungs would actually hemorrhage within just a few breaths. On the other end of the spectrum of extreme temperatures, the hottest surface reading on Earth of 160ºF (71ºC) occurred in Iran’s Lut Desert in 2005. In fact, the Lut Desert clocked the highest surface temperature in 5 out of 7 years during a 2003-2009 study, making it the world’s hottest location. The desert’s dark pebbles, dry soil, and lack of vegetation create the perfect conditions for blistering heat. There are very few organisms that can withstand such temperatures, but one fascinating phylum makes the cut.
The Amazing Tardigrade
Commonly known as a “moss pig” or “water bear”, the one-millimeter long tardigrade is extremely resilient. While most organisms need water to survive, the tardigrade gets around this by entering a “tun” state, in which metabolism slows to just 0.01% of its normal rate. When water is scarce, the creature curls up and synthesizes molecules that lock sensitive cell components in place until re-hydration occurs. Beyond dry conditions, the tardigrade can also survive both freezing and boiling temperatures, high radiation environments, and even the vacuum of space. This video courtesy of TEDEd explains more about the hardy critter:
Testing the Limits
For better or worse, humans have pushed the limits of temperature here on Earth. At MIT, scientists cooled a sodium gas to half-a-billionth of a degree above absolute zero. In the words of the Nobel Laureate Wolfgang Ketterle, who co-led the team: “To go below one nanokelvin (one-billionth of a degree) is a little like running a mile under four minutes for the first time.” Not all experiments are conducted out of simple curiosity. Conventional bombs already explode at around 9,000ºF (5,000ºC), but nuclear explosions take things much further. For a split second, temperatures inside a nuclear fireball can reach a mind-bending 18,000,000ºF (10,000,000ºC). The highest man-made temperature ever recorded is 9,900,000,000,000ºF (5,500,000,000,000ºC), created in the Large Hadron Collider at CERN in Switzerland. It was achieved by accelerating heavy lead ions to 99% the speed of light and smashing them together.
Highs and Lows of the Universe
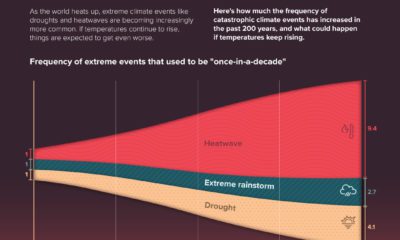
While humans have been able to manufacture extremely hot and cold temperatures, the universe has created these extremes naturally. Undoubtedly, the creation of the universe is made of the hottest stuff of all. The temperature of the universe at 10⁻³⁵ seconds old was a whopping 1 octillion ºC. Moments later, it “cooled down” to 1,800,000,000ºF (1 billion ºC) when the universe was less than two minutes old. On the other end of the spectrum, the coolest natural place currently known in the universe is the Boomerang Nebula at -457.6ºF (-272ºC). It’s found 5,000 light years away from us in the constellation Centaurus, and it is currently in a transitional phase as a dying star. As space exploration goes further than ever, these extreme temperatures may one day reach even hotter or colder heights than we can imagine. on Even while political regimes across these countries have changed over time, they’ve largely followed a few different types of governance. Today, every country can ultimately be classified into just nine broad forms of government systems. This map by Truman Du uses information from Wikipedia to map the government systems that rule the world today.
Countries By Type of Government
It’s important to note that this map charts government systems according to each country’s legal framework. Many countries have constitutions stating their de jure or legally recognized system of government, but their de facto or realized form of governance may be quite different. Here is a list of the stated government system of UN member states and observers as of January 2023: Let’s take a closer look at some of these systems.
Monarchies
Brought back into the spotlight after the death of Queen Elizabeth II of England in September 2022, this form of government has a single ruler. They carry titles from king and queen to sultan or emperor, and their government systems can be further divided into three modern types: constitutional, semi-constitutional, and absolute. A constitutional monarchy sees the monarch act as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, giving them little to no real power. For example, King Charles III is the head of 15 Commonwealth nations including Canada and Australia. However, each has their own head of government. On the other hand, a semi-constitutional monarchy lets the monarch or ruling royal family retain substantial political powers, as is the case in Jordan and Morocco. However, their monarchs still rule the country according to a democratic constitution and in concert with other institutions. Finally, an absolute monarchy is most like the monarchies of old, where the ruler has full power over governance, with modern examples including Saudi Arabia and Vatican City.
Republics
Unlike monarchies, the people hold the power in a republic government system, directly electing representatives to form government. Again, there are multiple types of modern republic governments: presidential, semi-presidential, and parliamentary. The presidential republic could be considered a direct progression from monarchies. This system has a strong and independent chief executive with extensive powers when it comes to domestic affairs and foreign policy. An example of this is the United States, where the President is both the head of state and the head of government. In a semi-presidential republic, the president is the head of state and has some executive powers that are independent of the legislature. However, the prime minister (or chancellor or equivalent title) is the head of government, responsible to the legislature along with the cabinet. Russia is a classic example of this type of government. The last type of republic system is parliamentary. In this system, the president is a figurehead, while the head of government holds real power and is validated by and accountable to the parliament. This type of system can be seen in Germany, Italy, and India and is akin to constitutional monarchies. It’s also important to point out that some parliamentary republic systems operate slightly differently. For example in South Africa, the president is both the head of state and government, but is elected directly by the legislature. This leaves them (and their ministries) potentially subject to parliamentary confidence.
One-Party State
Many of the systems above involve multiple political parties vying to rule and govern their respective countries. In a one-party state, also called a single-party state or single-party system, only one political party has the right to form government. All other political parties are either outlawed or only allowed limited participation in elections. In this system, a country’s head of state and head of government can be executive or ceremonial but political power is constitutionally linked to a single political movement. China is the most well-known example of this government system, with the General Secretary of the Communist Party of China ruling as the de facto leader since 1989.
Provisional
The final form of government is a provisional government formed as an interim or transitional government. In this system, an emergency governmental body is created to manage political transitions after the collapse of a government, or when a new state is formed. Often these evolve into fully constitutionalized systems, but sometimes they hold power for longer than expected. Some examples of countries that are considered provisional include Libya, Burkina Faso, and Chad.