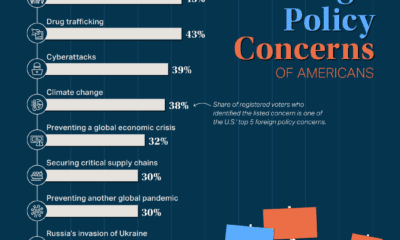
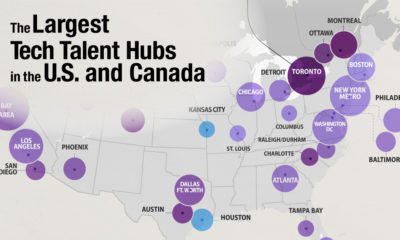
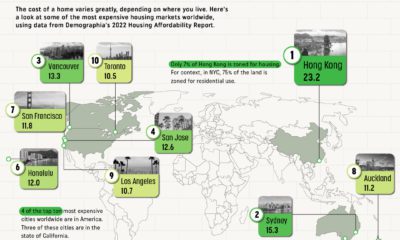
In the following charts, we feature data from a comprehensive survey conducted by UK-based startup network Founders Forum, in which hundreds of founders and their teams revealed their experiences of remote work and their plans for a post-pandemic future. While the future remains a blank page, it’s clear that hundreds of startups have no plans to hit backspace on remote work.
Who’s Talking
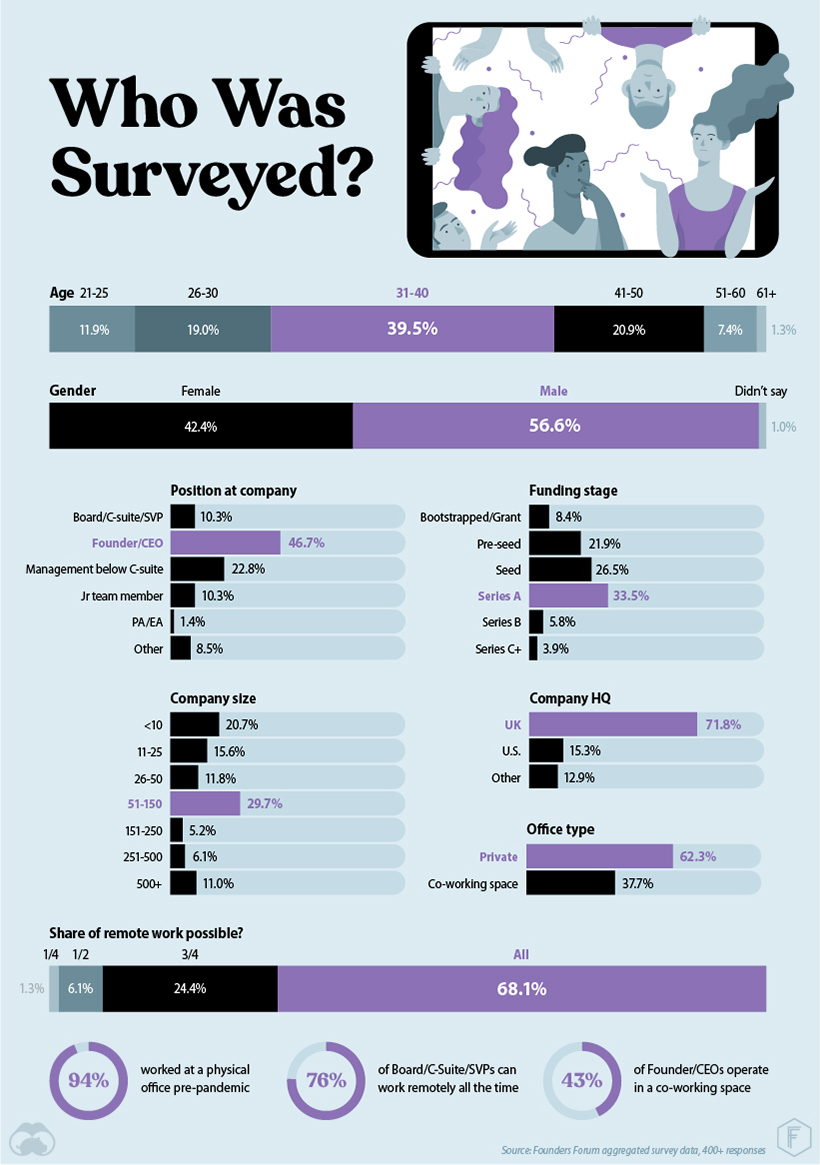
Based primarily in the UK, almost half of the survey participants were founders, and nearly a quarter were managers below the C-suite. Prior to pandemic-related lockdowns, 94% of those surveyed had worked from an external office. Despite their brick-and-mortar setup, more than 90% were able to accomplish the majority of their work remotely. Gen X and Millennials made up most of the survey contingent, with nearly 80% of respondents with ages between 26-50, and 40% in the 31-40 age bracket.
From improved work-life balance and productivity levels to reduced formal teamwork, these entrepreneurs flagged some bold truths about what’s working and what’s not.
Founders With A Remote Vision
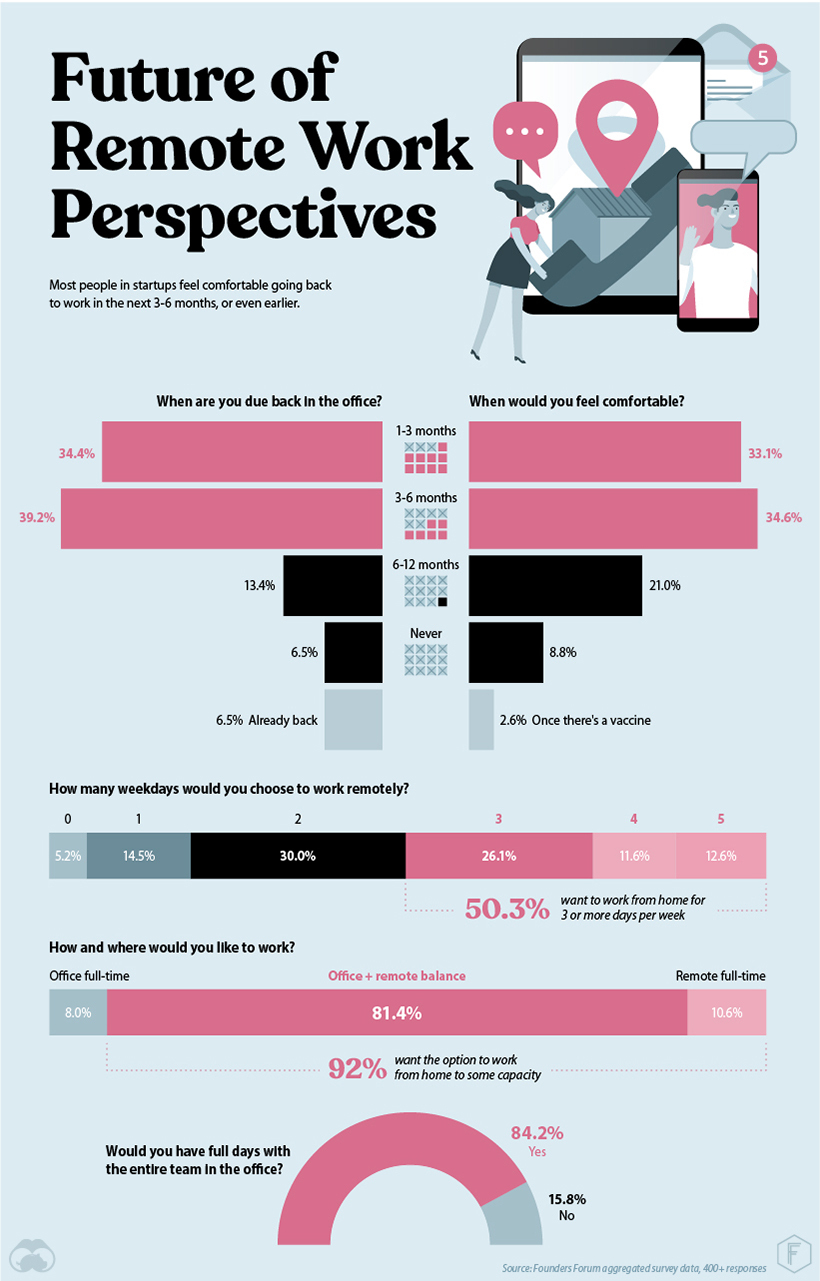
If history has taught us anything, it’s that world events have the potential to cause permanent mass change, like 9/11’s lasting impact on airport security. Although most survey respondents had plans to be back in the office within six months, those startups are rethinking their remote work policies as a direct result of COVID-19. How might that play out in a post-pandemic world? Based on the startup responses, a realistic post-pandemic work scenario could involve 3 to 5 days of remote work a week, with a couple dedicated in-office days for the entire team.
Upwards of 92% of respondents said they wanted the option to work from home in some capacity. — Evgeny Shadchnev, CEO, Makers Academy
Productivity Scales at Home
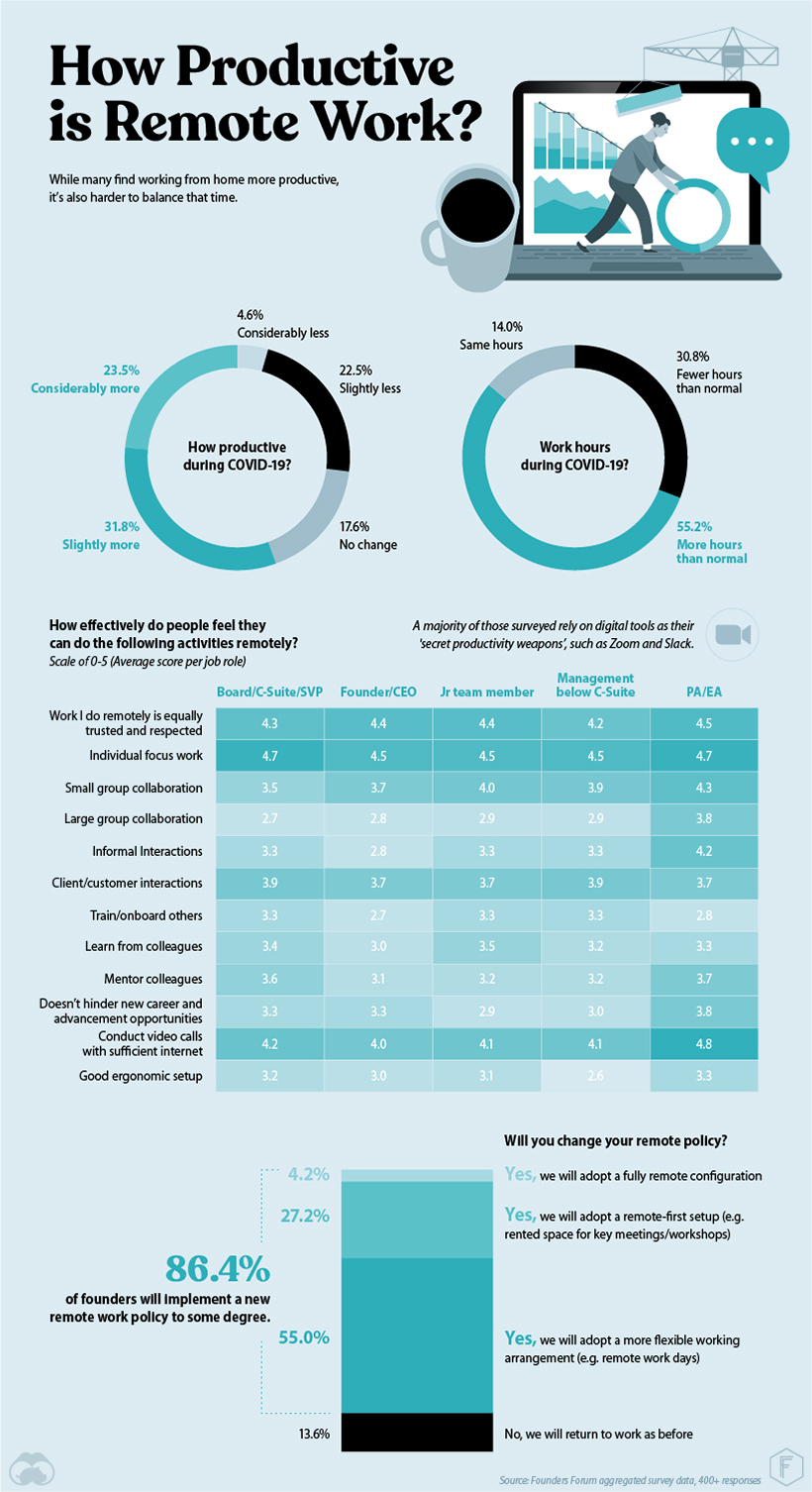
Working from home hasn’t slowed down these startups—in fact, it may have improved overall productivity in many cases. More than half of the respondents were more productive from home, and 55% also reported working longer hours.
Blurred lines, however, raised some concerns. From chores and rowdy children to extended hours, working from home often makes it difficult to compartmentalize. As a result, employers and employees may have to draw firmer lines between work and home in their remote policies, especially in the long term. Although the benefits appear to outweigh the concerns, these issues pose important questions about our increasingly remote future.
Teams Reveal Some Intel
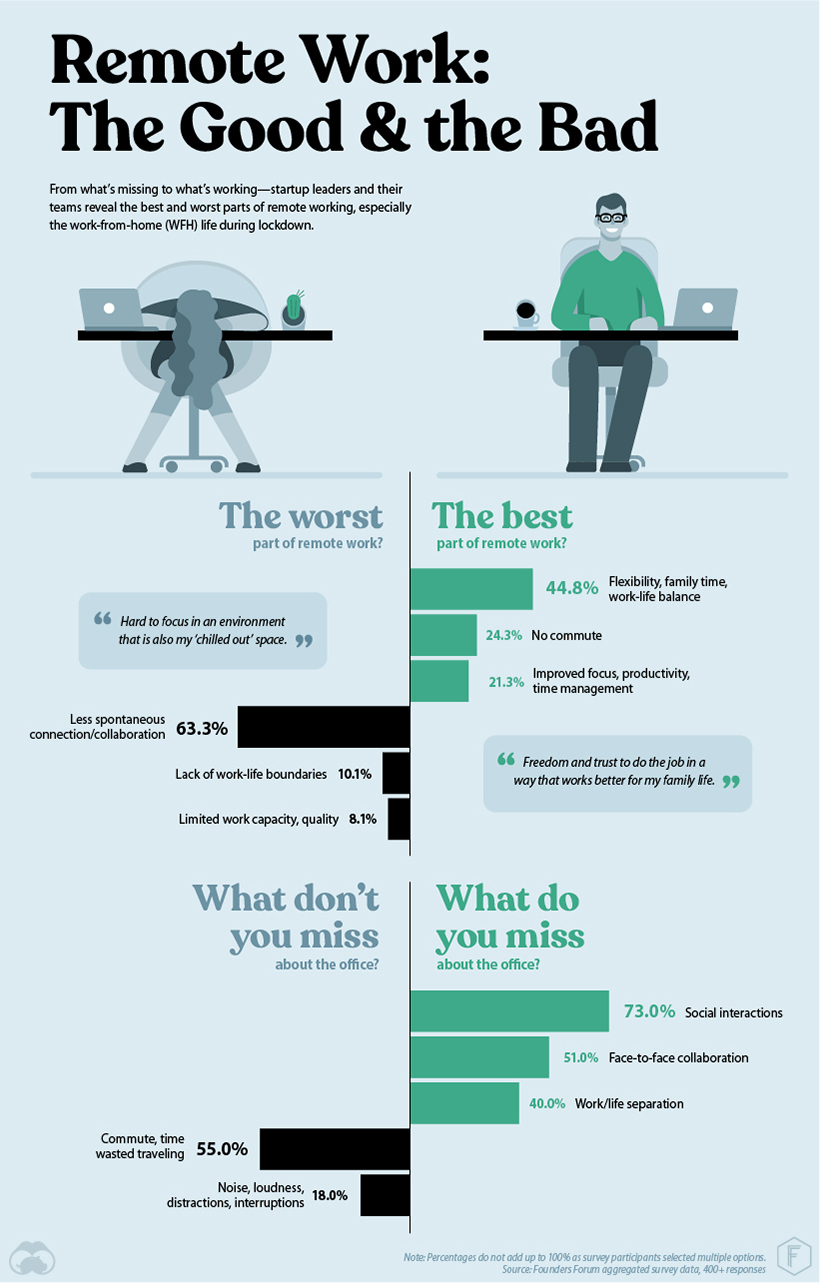
To uncover some work-from-home easter eggs (“Better for exercise. MUCH more pleasant environment”), we grouped nearly 400 open-ended questions according to sentiment and revealed some interesting patterns. From serendipitous encounters and beers with colleagues to more formal teamwork, an overwhelming number of the respondents missed the camaraderie of team interactions.
It was clear startups did not miss the hours spent commuting every day. During the pandemic, those hours have been replaced by family time, work, or other activities like cooking healthy meals and working out. — Rohan Silva, CEO, Second Home
The Future Looks Remote
This pandemic has delivered a new normal that’s simultaneously challenging and revealing. For now, it looks like a new way of working is being coded into our collective software. What becomes of the beloved open-office plan in a pandemic-prepped world remains to be seen, but if these startups are any indication, work-life may have changed for good. on But fast forward to the end of last week, and SVB was shuttered by regulators after a panic-induced bank run. So, how exactly did this happen? We dig in below.
Road to a Bank Run
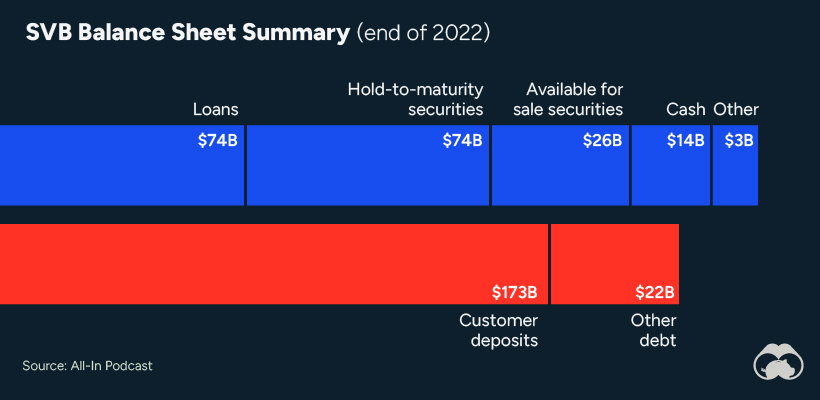
SVB and its customers generally thrived during the low interest rate era, but as rates rose, SVB found itself more exposed to risk than a typical bank. Even so, at the end of 2022, the bank’s balance sheet showed no cause for alarm.
As well, the bank was viewed positively in a number of places. Most Wall Street analyst ratings were overwhelmingly positive on the bank’s stock, and Forbes had just added the bank to its Financial All-Stars list. Outward signs of trouble emerged on Wednesday, March 8th, when SVB surprised investors with news that the bank needed to raise more than $2 billion to shore up its balance sheet. The reaction from prominent venture capitalists was not positive, with Coatue Management, Union Square Ventures, and Peter Thiel’s Founders Fund moving to limit exposure to the 40-year-old bank. The influence of these firms is believed to have added fuel to the fire, and a bank run ensued. Also influencing decision making was the fact that SVB had the highest percentage of uninsured domestic deposits of all big banks. These totaled nearly $152 billion, or about 97% of all deposits. By the end of the day, customers had tried to withdraw $42 billion in deposits.
What Triggered the SVB Collapse?
While the collapse of SVB took place over the course of 44 hours, its roots trace back to the early pandemic years. In 2021, U.S. venture capital-backed companies raised a record $330 billion—double the amount seen in 2020. At the time, interest rates were at rock-bottom levels to help buoy the economy. Matt Levine sums up the situation well: “When interest rates are low everywhere, a dollar in 20 years is about as good as a dollar today, so a startup whose business model is “we will lose money for a decade building artificial intelligence, and then rake in lots of money in the far future” sounds pretty good. When interest rates are higher, a dollar today is better than a dollar tomorrow, so investors want cash flows. When interest rates were low for a long time, and suddenly become high, all the money that was rushing to your customers is suddenly cut off.” Source: Pitchbook Why is this important? During this time, SVB received billions of dollars from these venture-backed clients. In one year alone, their deposits increased 100%. They took these funds and invested them in longer-term bonds. As a result, this created a dangerous trap as the company expected rates would remain low. During this time, SVB invested in bonds at the top of the market. As interest rates rose higher and bond prices declined, SVB started taking major losses on their long-term bond holdings.
Losses Fueling a Liquidity Crunch
When SVB reported its fourth quarter results in early 2023, Moody’s Investor Service, a credit rating agency took notice. In early March, it said that SVB was at high risk for a downgrade due to its significant unrealized losses. In response, SVB looked to sell $2 billion of its investments at a loss to help boost liquidity for its struggling balance sheet. Soon, more hedge funds and venture investors realized SVB could be on thin ice. Depositors withdrew funds in droves, spurring a liquidity squeeze and prompting California regulators and the FDIC to step in and shut down the bank.
What Happens Now?
While much of SVB’s activity was focused on the tech sector, the bank’s shocking collapse has rattled a financial sector that is already on edge.
The four biggest U.S. banks lost a combined $52 billion the day before the SVB collapse. On Friday, other banking stocks saw double-digit drops, including Signature Bank (-23%), First Republic (-15%), and Silvergate Capital (-11%).
Source: Morningstar Direct. *Represents March 9 data, trading halted on March 10.
When the dust settles, it’s hard to predict the ripple effects that will emerge from this dramatic event. For investors, the Secretary of the Treasury Janet Yellen announced confidence in the banking system remaining resilient, noting that regulators have the proper tools in response to the issue.
But others have seen trouble brewing as far back as 2020 (or earlier) when commercial banking assets were skyrocketing and banks were buying bonds when rates were low.