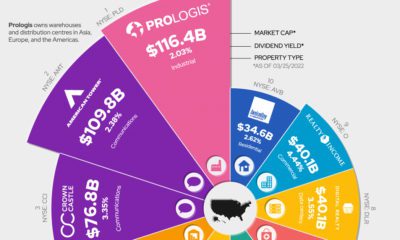
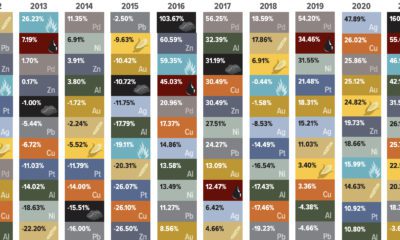
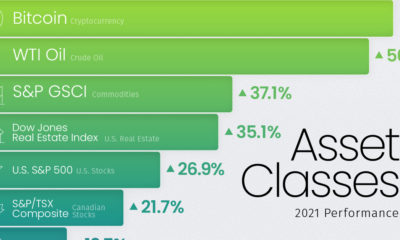
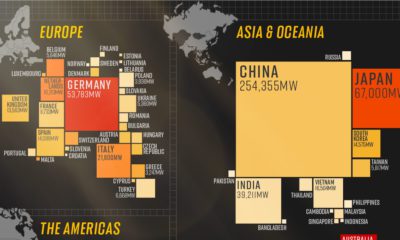
2015 Silver Series Part 4: Making The Case For Silver
In the previous parts of The Silver Series, we’ve shown that silver has a rich and multi-faceted history with applications in money, health, and technology. We’ve covered the metal’s supply and geological origins, as well as the growing demand stemming from industry, investment, and other areas. However, the real question for investors boils down to this: is it worth it to hold silver bullion or equities in a portfolio? Silver and Gold The two major precious metals are alike in many ways. They’ve both been used as money for thousands of years, and both are considered a store of wealth today. However, to understand the nuances of silver as an asset, it is important to keep in mind a couple of key differences that it holds from the yellow metal. The most obvious difference is that silver is used much more widespread in industry than gold. Approximately 50% of all demand stems from technological applications like photovoltaics, automobiles, batteries, and other such uses. This gives silver a potentially wider range of demand triggers. The other major difference is that in comparison to the gold market, silver trades thinly and with much higher volatility. In 2014, there was $20.4 billion of demand for physical silver and $159.7 billion demand for physical gold. Even more interesting, these physical markets are less than 1% the size of the total markets when factoring paper trades like derivatives, futures contracts, and options. Silver typically hits higher highs and lower lows than gold. To the savvy investor, this creates great opportunity. Why Own Silver? The reasons an investor should consider exposure to silver can be summed up with three key points.
- Diversification. Silver has little or no correlation with most asset classes such as bonds, stocks, or real estate. This is because silver prices move based on supply and demand, but also because of other factors such as the global economic environment, futures market speculators, currency markets, the level of inflation or deflation, and central bank policy decisions. Even though silver itself is more volatile than many other asset classes, it does help reduce the overall risk of a portfolio by having less correlation to other asset classes. Over the last eight years, silver’s correlation to treasuries and bonds have been basically zero (-0.07 and 0.08 respectively). It has slightly higher correlation with US equities (0.23) and real estate (0.13).
- Safe Haven When the times get tough, silver is your friend. Even in the most challenging environments it holds its value or bucks the negative global trends. How did silver do in the four years surrounding the Financial Crisis? Over a period where US equities, emerging markets, and REITs were down, silver more than doubled in value from 2007-2011.
- Fundamentals and Value The fundamental numbers around silver make it quite clear that silver could provide extreme value as an investment. Here are some key numbers:
In the earth’s crust, there is 1 gram of silver for every 12.5 tonnes of rock. For centuries since ancient times, the gold-to-silver ratio was 15 to 1. That means 1 oz of gold could buy 15 oz of silver. In the earth’s crust, there is 19x more silver than gold by mass. The “modern” gold-to-silver ratio is closer to 50 to 1. Yet, in mid-2015 the ratio is 75 to 1, which means silver could be very undervalued relative to gold. The silver price, in terms of USD, is also at its lowest point in five years. Silver miners are even cheaper, trading at their lowest valuation in years.
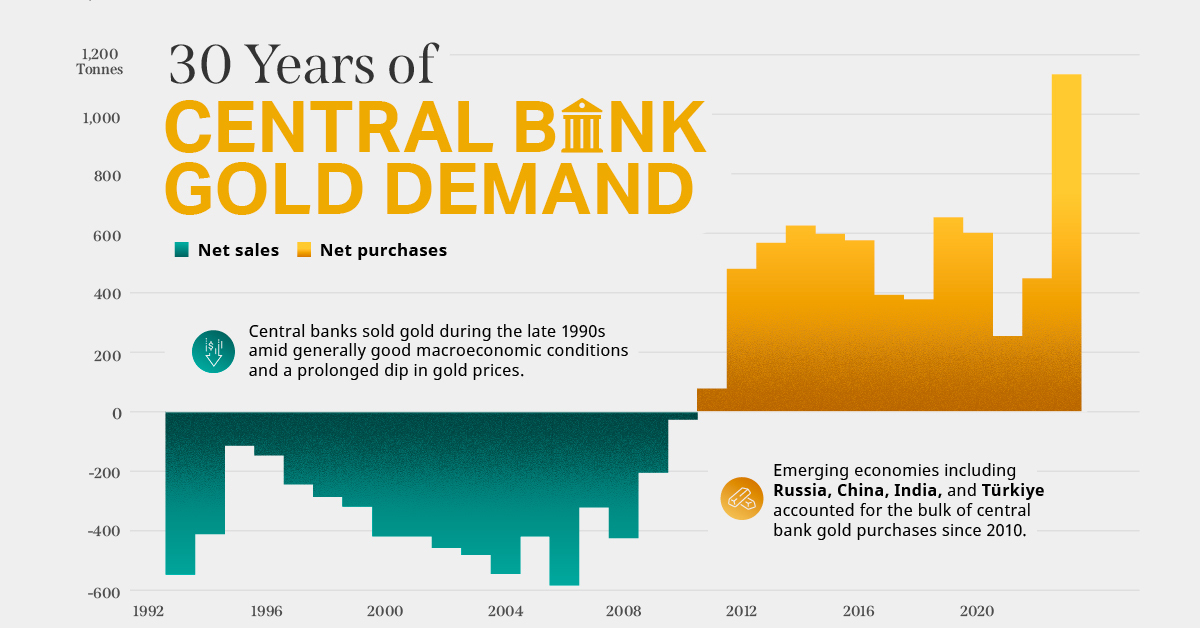
Silver, the metal itself, continues to have the same impressive properties, supply and demand fundamentals, and a rich history as money. What has changed is what people are willing to pay for it at a given time. Right now it seems that silver is being sold for half price. That’s the end of our Silver Series. Thanks for reading! on Did you know that nearly one-fifth of all the gold ever mined is held by central banks? Besides investors and jewelry consumers, central banks are a major source of gold demand. In fact, in 2022, central banks snapped up gold at the fastest pace since 1967. However, the record gold purchases of 2022 are in stark contrast to the 1990s and early 2000s, when central banks were net sellers of gold. The above infographic uses data from the World Gold Council to show 30 years of central bank gold demand, highlighting how official attitudes toward gold have changed in the last 30 years.
Why Do Central Banks Buy Gold?
Gold plays an important role in the financial reserves of numerous nations. Here are three of the reasons why central banks hold gold:
Balancing foreign exchange reserves Central banks have long held gold as part of their reserves to manage risk from currency holdings and to promote stability during economic turmoil. Hedging against fiat currencies Gold offers a hedge against the eroding purchasing power of currencies (mainly the U.S. dollar) due to inflation. Diversifying portfolios Gold has an inverse correlation with the U.S. dollar. When the dollar falls in value, gold prices tend to rise, protecting central banks from volatility. The Switch from Selling to Buying In the 1990s and early 2000s, central banks were net sellers of gold. There were several reasons behind the selling, including good macroeconomic conditions and a downward trend in gold prices. Due to strong economic growth, gold’s safe-haven properties were less valuable, and low returns made it unattractive as an investment. Central bank attitudes toward gold started changing following the 1997 Asian financial crisis and then later, the 2007–08 financial crisis. Since 2010, central banks have been net buyers of gold on an annual basis. Here’s a look at the 10 largest official buyers of gold from the end of 1999 to end of 2021: Rank CountryAmount of Gold Bought (tonnes)% of All Buying #1🇷🇺 Russia 1,88828% #2🇨🇳 China 1,55223% #3🇹🇷 Türkiye 5418% #4🇮🇳 India 3956% #5🇰🇿 Kazakhstan 3455% #6🇺🇿 Uzbekistan 3115% #7🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia 1803% #8🇹🇭 Thailand 1682% #9🇵🇱 Poland1282% #10🇲🇽 Mexico 1152% Total5,62384% Source: IMF The top 10 official buyers of gold between end-1999 and end-2021 represent 84% of all the gold bought by central banks during this period. Russia and China—arguably the United States’ top geopolitical rivals—have been the largest gold buyers over the last two decades. Russia, in particular, accelerated its gold purchases after being hit by Western sanctions following its annexation of Crimea in 2014. Interestingly, the majority of nations on the above list are emerging economies. These countries have likely been stockpiling gold to hedge against financial and geopolitical risks affecting currencies, primarily the U.S. dollar. Meanwhile, European nations including Switzerland, France, Netherlands, and the UK were the largest sellers of gold between 1999 and 2021, under the Central Bank Gold Agreement (CBGA) framework. Which Central Banks Bought Gold in 2022? In 2022, central banks bought a record 1,136 tonnes of gold, worth around $70 billion. Country2022 Gold Purchases (tonnes)% of Total 🇹🇷 Türkiye14813% 🇨🇳 China 625% 🇪🇬 Egypt 474% 🇶🇦 Qatar333% 🇮🇶 Iraq 343% 🇮🇳 India 333% 🇦🇪 UAE 252% 🇰🇬 Kyrgyzstan 61% 🇹🇯 Tajikistan 40.4% 🇪🇨 Ecuador 30.3% 🌍 Unreported 74165% Total1,136100% Türkiye, experiencing 86% year-over-year inflation as of October 2022, was the largest buyer, adding 148 tonnes to its reserves. China continued its gold-buying spree with 62 tonnes added in the months of November and December, amid rising geopolitical tensions with the United States. Overall, emerging markets continued the trend that started in the 2000s, accounting for the bulk of gold purchases. Meanwhile, a significant two-thirds, or 741 tonnes of official gold purchases were unreported in 2022. According to analysts, unreported gold purchases are likely to have come from countries like China and Russia, who are looking to de-dollarize global trade to circumvent Western sanctions.
There were several reasons behind the selling, including good macroeconomic conditions and a downward trend in gold prices. Due to strong economic growth, gold’s safe-haven properties were less valuable, and low returns made it unattractive as an investment.
Central bank attitudes toward gold started changing following the 1997 Asian financial crisis and then later, the 2007–08 financial crisis. Since 2010, central banks have been net buyers of gold on an annual basis.
Here’s a look at the 10 largest official buyers of gold from the end of 1999 to end of 2021:
Source: IMF
The top 10 official buyers of gold between end-1999 and end-2021 represent 84% of all the gold bought by central banks during this period.
Russia and China—arguably the United States’ top geopolitical rivals—have been the largest gold buyers over the last two decades. Russia, in particular, accelerated its gold purchases after being hit by Western sanctions following its annexation of Crimea in 2014.
Interestingly, the majority of nations on the above list are emerging economies. These countries have likely been stockpiling gold to hedge against financial and geopolitical risks affecting currencies, primarily the U.S. dollar.
Meanwhile, European nations including Switzerland, France, Netherlands, and the UK were the largest sellers of gold between 1999 and 2021, under the Central Bank Gold Agreement (CBGA) framework.
Which Central Banks Bought Gold in 2022?
In 2022, central banks bought a record 1,136 tonnes of gold, worth around $70 billion. Türkiye, experiencing 86% year-over-year inflation as of October 2022, was the largest buyer, adding 148 tonnes to its reserves. China continued its gold-buying spree with 62 tonnes added in the months of November and December, amid rising geopolitical tensions with the United States. Overall, emerging markets continued the trend that started in the 2000s, accounting for the bulk of gold purchases. Meanwhile, a significant two-thirds, or 741 tonnes of official gold purchases were unreported in 2022. According to analysts, unreported gold purchases are likely to have come from countries like China and Russia, who are looking to de-dollarize global trade to circumvent Western sanctions.