The global electric vehicle (EV) battery market is expected to grow from $17 billion to more than $95 billion between 2019 and 2028. With increasing demand to decarbonize the transportation sector, companies producing the batteries that power EVs have seen substantial momentum. Here we update our previous graphic of the top 10 EV battery manufacturers, bringing you the world’s biggest battery manufacturers in 2022.
Chinese Dominance
Despite efforts from the United States and Europe to increase the domestic production of batteries, the market is still dominated by Asian suppliers. The top 10 producers are all Asian companies. Currently, Chinese companies make up 56% of the EV battery market, followed by Korean companies (26%) and Japanese manufacturers (10%). The leading battery supplier, CATL, expanded its market share from 32% in 2021 to 34% in 2022. One-third of the world’s EV batteries come from the Chinese company. CATL provides lithium-ion batteries to Tesla, Peugeot, Hyundai, Honda, BMW, Toyota, Volkswagen, and Volvo. Despite facing strict scrutiny after EV battery-fire recalls in the United States, LG Energy Solution remains the second-biggest battery manufacturer. In 2021, the South Korean supplier agreed to reimburse General Motors $1.9 billion to cover the 143,000 Chevy Bolt EVs recalled due to fire risks from faulty batteries. BYD took the third spot from Panasonic as it nearly doubled its market share over the last year. The Warren Buffett-backed company is the world’s third-largest automaker by market cap, but it also produces batteries sold in markets around the world. Recent sales figures point to BYD overtaking LG Energy Solution in market share the coming months or years.
The Age of Battery Power
Electric vehicles are here to stay, while internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles are set to fade away in the coming decades. Recently, General Motors announced that it aims to stop selling ICE vehicles by 2035, while Audi plans to stop producing such models by 2033. Besides EVs, battery technology is essential for the energy transition, providing storage capacity for intermittent solar and wind generation. As battery makers work to supply the EV transition’s increasing demand and improve energy density in their products, we can expect more interesting developments within this industry. on
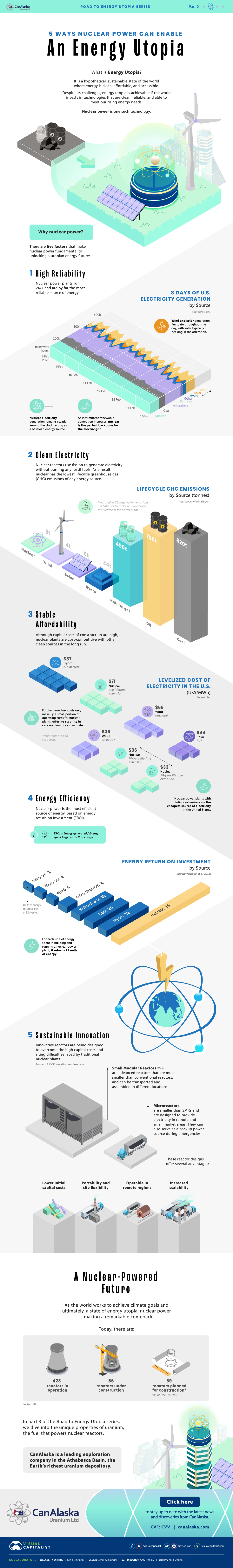
#1: High Reliability
Nuclear power plants run 24/7 and are the most reliable source of sustainable energy. Nuclear electricity generation remains steady around the clock throughout the day, week, and year. Meanwhile, daily solar generation peaks in the afternoon when electricity demand is usually lower, and wind generation depends on wind speeds.As the use of variable solar and wind power increases globally, nuclear offers a stable and reliable backbone for a clean electricity grid.
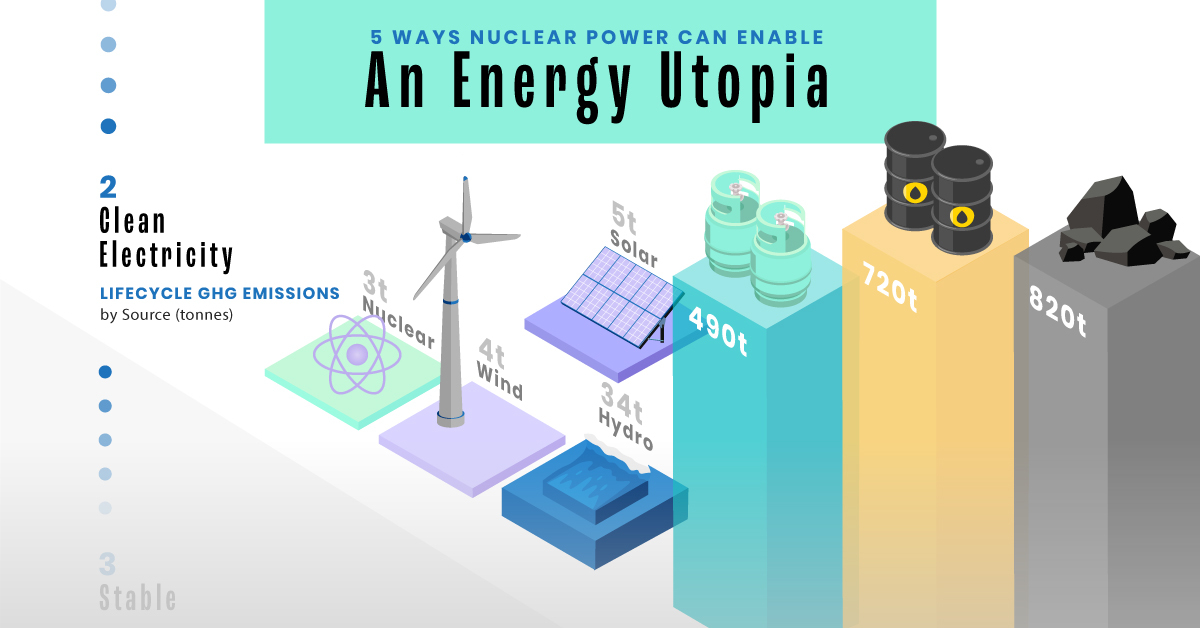
#2: Clean Electricity
Nuclear reactors use fission to generate electricity without any greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.Consequently, nuclear power is the cleanest energy source on a lifecycle basis, measured in CO2-equivalent emissions per gigawatt-hour (GWh) of electricity produced by a power plant over its lifetime. The lifecycle emissions from a typical nuclear power plant are 273 times lower than coal and 163 times lower than natural gas. Furthermore, nuclear is relatively less resource-intensive, allowing for lower supply chain emissions than wind and solar plants.
#3: Stable Affordability
Although nuclear plants can be expensive to build, they are cost-competitive in the long run. Most nuclear plants have an initial lifetime of around 40 years, after which they can continue operating with approved lifetime extensions. Nuclear plants with lifetime extensions are the cheapest sources of electricity in the United States, and 88 of the country’s 92 reactors have received approvals for 20-year extensions. Additionally, according to the World Nuclear Association, nuclear plants are relatively less susceptible to fuel price volatility than natural gas plants, allowing for stable costs of electricity generation.
#4: Energy Efficiency
Nuclear’s high energy return on investment (EROI) exemplifies its exceptional efficiency. EROI measures how many units of energy are returned for every unit invested in building and running a power plant, over its lifetime. According to a 2018 study by Weissbach et al., nuclear’s EROI is 75 units, making it the most efficient energy source by some distance, with hydropower ranking second at 35 units.
#5: Sustainable Innovation
New, advanced reactor designs are bypassing many of the difficulties faced by traditional nuclear plants, making nuclear power more accessible.
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are much smaller than conventional reactors and are modular—meaning that their components can be transported and assembled in different locations. Microreactors are smaller than SMRs and are designed to provide electricity in remote and small market areas. They can also serve as backup power sources during emergencies.
These reactor designs offer several advantages, including lower initial capital costs, portability, and increased scalability.
A Nuclear-Powered Future
Nuclear power is making a remarkable comeback as countries work to achieve climate goals and ultimately, a state of energy utopia. Besides the 423 reactors in operation worldwide, another 56 reactors are under construction, and at least 69 more are planned for construction. Some nations, like Japan, have also reversed their attitudes toward nuclear power, embracing it as a clean and reliable energy source for the future. CanAlaska is a leading exploration company in the Athabasca Basin, the Earth’s richest uranium depository. Click here to learn more now. In part 3 of the Road to Energy Utopia series, we explore the unique properties of uranium, the fuel that powers nuclear reactors.