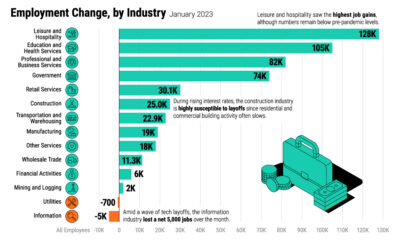
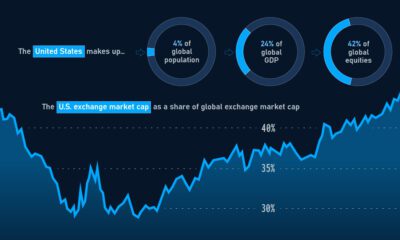
The country’s main exports are exactly what one would expect, with categories like aircraft, refined petroleum, vehicles, vehicle parts, and computer chips constituting the biggest chunk of overall goods. However, today’s infographic from HowMuch.net zooms down to the state level, where things get much more interesting. Some states tow the line by exporting one of the major U.S. goods, while others specialize in categories that you probably couldn’t ever guess.
Towing the Line
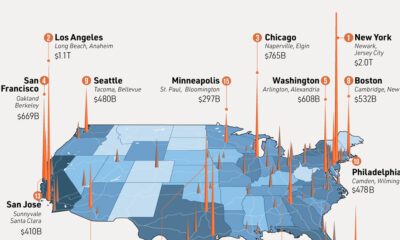
We’ll start by looking at dollar values for the states that have the single largest exports. Here are the top 10 states: Not surprisingly, some of the top national exports are represented here. Airplanes dominate the list, and Boeing’s presence in particular is clearly felt. The company’s major factory in Everett, WA – the largest building in the world by volume – helps the state of Washington generate $41.8 billion in export sales from the aerospace sector. That said, airplanes are also the top export good for five other states in the above list. The Gulf Coast is also well-represented with Texas and Louisiana as major refined oil exporters. New York (Diamonds) and Nevada (Gold) round out the list.
Keeping Exports Weird
The smaller the state, the better chance it has of specializing in a type of good that is outside of the norm. Possibly the title of “Most Unusual Top State Export” can go to South Dakota, which sent $91 million of distillery dregs outside of the country in 2017. In case you were wondering, the U.S. Census Bureau’s full category title for this is as follows: BREWING OR DISTILLING DREGS AND WASTE, W/NT PELLET. This spent grain is a byproduct of brewing or distilling processes, and is primarily sold for use in making animal feeds. Other strange top exports? The biggest state export of Wyoming is soda ash, which is used to manufacture of glass, paper, rayon, soaps, and detergents. In 2017, the state exported $842 million of soda ash, which is 10x larger than its second-biggest export category, which is also an uncommon one: rare gases. Other interesting states include Rhode Island, which exported $187 million of iron and steel waste, as well as Maine – a state that shipped away $326 million of its famous lobsters. on Last year, stock and bond returns tumbled after the Federal Reserve hiked interest rates at the fastest speed in 40 years. It was the first time in decades that both asset classes posted negative annual investment returns in tandem. Over four decades, this has happened 2.4% of the time across any 12-month rolling period. To look at how various stock and bond asset allocations have performed over history—and their broader correlations—the above graphic charts their best, worst, and average returns, using data from Vanguard.
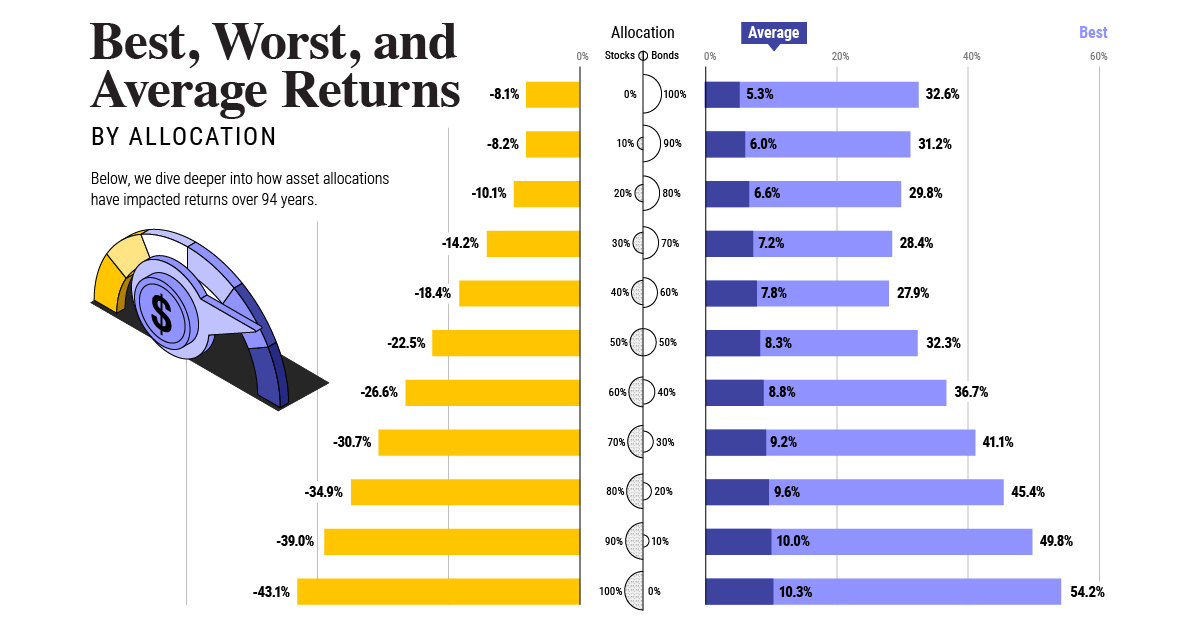
How Has Asset Allocation Impacted Returns?
Based on data between 1926 and 2019, the table below looks at the spectrum of market returns of different asset allocations:
We can see that a portfolio made entirely of stocks returned 10.3% on average, the highest across all asset allocations. Of course, this came with wider return variance, hitting an annual low of -43% and a high of 54%.
A traditional 60/40 portfolio—which has lost its luster in recent years as low interest rates have led to lower bond returns—saw an average historical return of 8.8%. As interest rates have climbed in recent years, this may widen its appeal once again as bond returns may rise.
Meanwhile, a 100% bond portfolio averaged 5.3% in annual returns over the period. Bonds typically serve as a hedge against portfolio losses thanks to their typically negative historical correlation to stocks.
A Closer Look at Historical Correlations
To understand how 2022 was an outlier in terms of asset correlations we can look at the graphic below:
The last time stocks and bonds moved together in a negative direction was in 1969. At the time, inflation was accelerating and the Fed was hiking interest rates to cool rising costs. In fact, historically, when inflation surges, stocks and bonds have often moved in similar directions. Underscoring this divergence is real interest rate volatility. When real interest rates are a driving force in the market, as we have seen in the last year, it hurts both stock and bond returns. This is because higher interest rates can reduce the future cash flows of these investments. Adding another layer is the level of risk appetite among investors. When the economic outlook is uncertain and interest rate volatility is high, investors are more likely to take risk off their portfolios and demand higher returns for taking on higher risk. This can push down equity and bond prices. On the other hand, if the economic outlook is positive, investors may be willing to take on more risk, in turn potentially boosting equity prices.
Current Investment Returns in Context
Today, financial markets are seeing sharp swings as the ripple effects of higher interest rates are sinking in. For investors, historical data provides insight on long-term asset allocation trends. Over the last century, cycles of high interest rates have come and gone. Both equity and bond investment returns have been resilient for investors who stay the course.