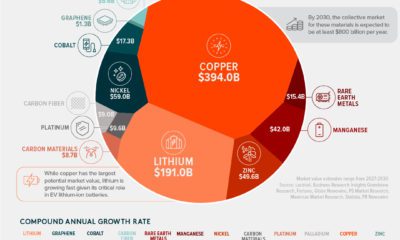
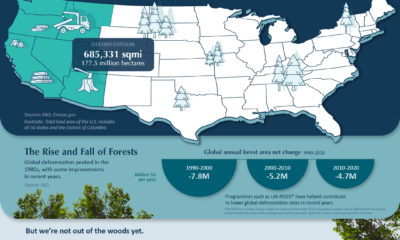
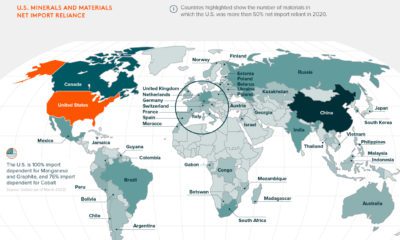
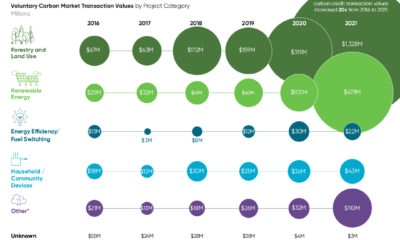
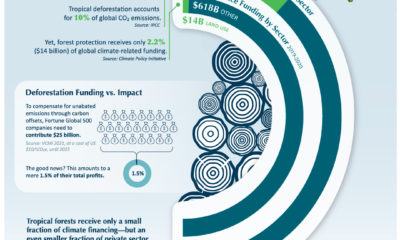
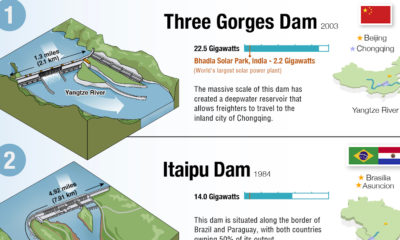
Importantly, for companies that are judged according to ESG metrics, one way to track their progress is through their alignment to the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Established in 2012, the UN SDGs are a blueprint for creating a more sustainable future by 2030 that have been adopted by 193 countries worldwide. As investors and stakeholders pay closer attention to sustainability concerns, this graphic from MSCI breaks down how companies stack up according to their alignment to the UN SDGs.
How Were Companies Measured?
To track companies net contribution to the UN SDGs, companies were scored by their positive or negative contribution to each of the 17 goals. The 17 UN SDGs are designed to achieve three primary objectives by 2030:
Protect the planet End poverty Create prosperity and peace for all
Specifically, the framework centers on a discussion paper that was developed in partnership with the OECD in 2018. Company policies, operations, products and services, and practices are analyzed according to reported and publicly available information.
Tracking the Alignment of Companies
Across a universe of 8,550 companies in the MSCI All Country World Index, constituents were measured from strongly aligned to strongly misaligned to the UN SDGs. Source: MSCI ESG Research LLC as of August 11, 2020 Broadly speaking, companies fell mostly in the middle—roughly 38% were aligned while almost 55% were misaligned or neutral. Meanwhile, just 0.2% of companies were strongly aligned to the UN SDGs. Overall, one of the most strongly aligned goals was Responsible Production and Consumption, with 115 companies meeting this criteria. Specifically, these include companies that are building sustainable infrastructure, energy efficiency, or creating green jobs. Interestingly, the worst performing goal was also Responsible Production and Consumption, with over five times as many companies (598) strongly misaligned. Along with this goal, both Climate Action and Affordable and Clean Energy each had over 500 companies strongly misaligned.
UN SDGs: A Sector Focus
Unsurprisingly, SDG-alignment varied widely according to company sectors. Educational companies, for instance, represented the highest level of alignment to Gender Equality. Meanwhile, 18% of 425 utilities companies assessed ended up aligning with Clean and Affordable Energy goals. As one would expect, the energy sector lagged behind. In 2020, fossil fuels were a key source of revenue for 91% of the companies in the energy business. In fact, just three companies derived over 50% of their revenues from green alternatives: REX American Resources, Renewable Energy Group, and Verbio.
A Call to Action?
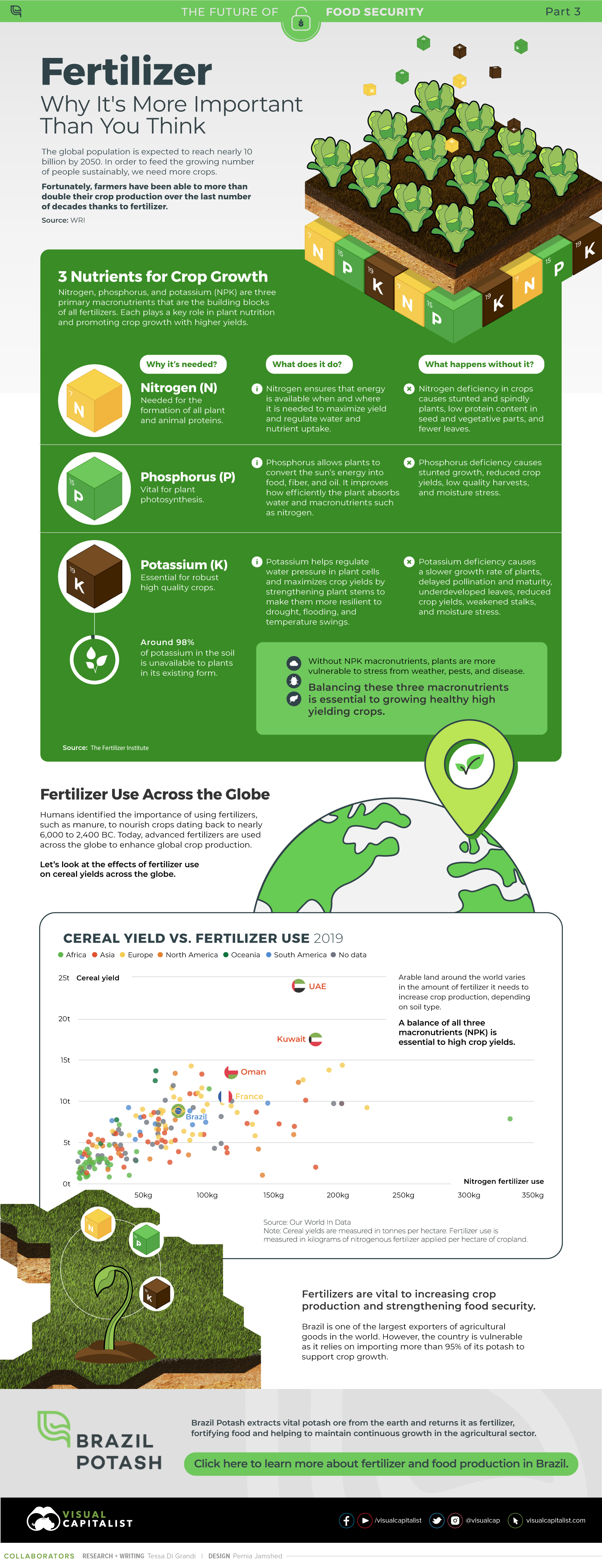
Despite the growing wave of interest in ESG investing, the reality is that progress to meet the UN SDGs has been slower going than expected. However, a greater number of individuals, stakeholders, and activists are sounding the alarm. Today, over 3,000 signatories representing trillions in assets under management have committed to the UN Principles of Responsible Investment, which has established six key actions for ESG investing. Now, many companies are required to report their ESG disclosures in Europe. Along with these key markers of progress, investors can move the dial by tracking a company’s alignment to sustainable development goals. on Over recent decades, farmers have been able to more than double their production of crops thanks to fertilizers and the vital nutrients they contain. When crops are harvested, the essential nutrients are taken away with them to the dining table, resulting in the depletion of these nutrients in the soil. To replenish these nutrients, fertilizers are needed, and the cycle continues. The above infographic by Brazil Potash shows the role that each macronutrient plays in growing healthy, high-yielding crops.
Food for Growth
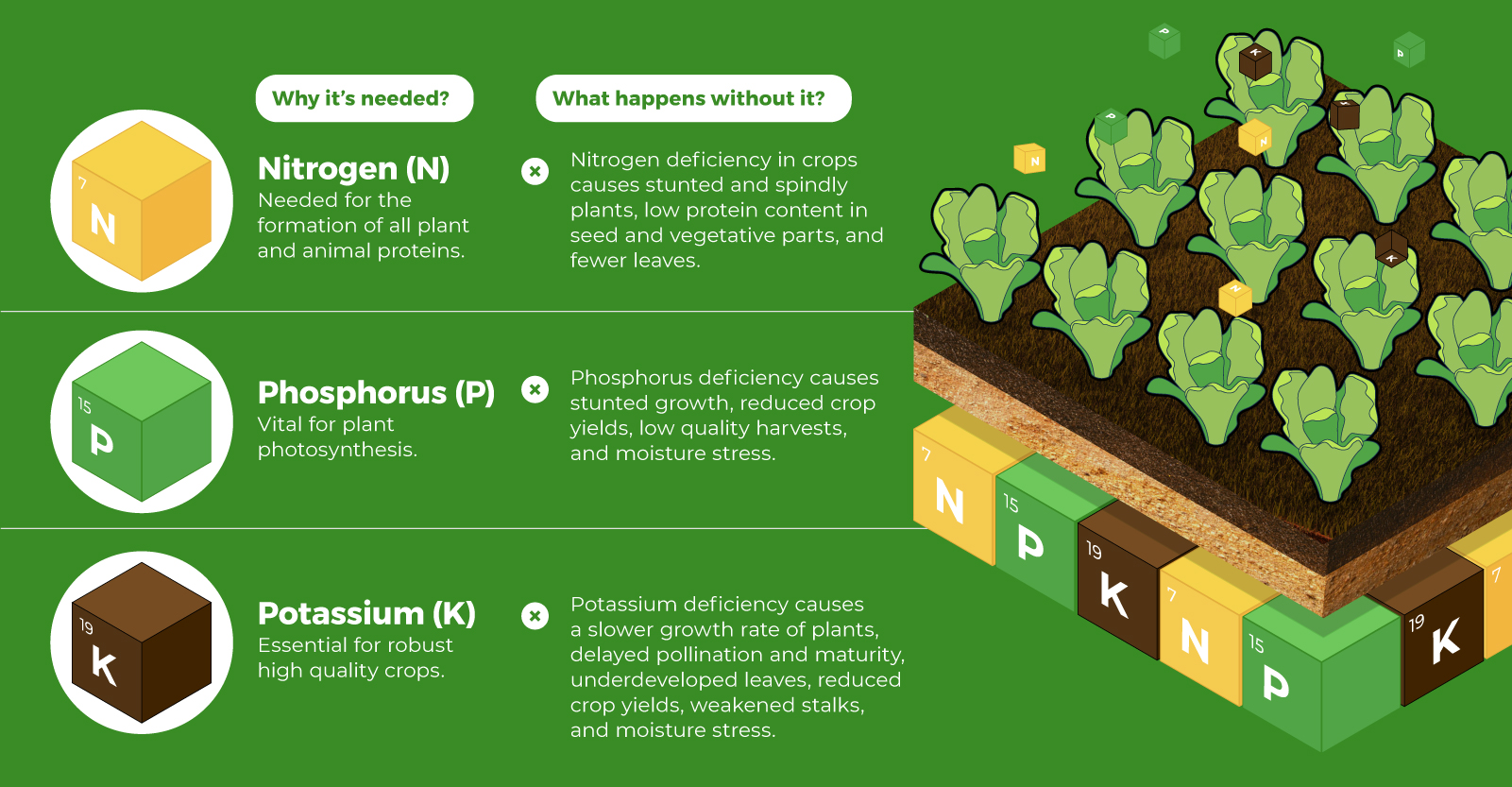
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK) are three primary macronutrients that are the building blocks of the global fertilizer industry. Each plays a key role in plant nutrition and promoting crop growth with higher yields. Let’s take a look at how each macronutrient affects plant growth. If crops lack NPK macronutrients, they become vulnerable to various stresses caused by weather conditions, pests, and diseases. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain a balance of all three macronutrients for the production of healthy, high-yielding crops.
The Importance of Fertilizers
Humans identified the importance of using fertilizers, such as manure, to nourish crops dating back to nearly 6,000 to 2,400 BC. As agriculture became more intensive and large-scale, farmers began to experiment with different types of fertilizers. Today advanced chemical fertilizers are used across the globe to enhance global crop production. There are a myriad of factors that affect soil type, and so the farmable land must have a healthy balance of all three macronutrients to support high-yielding, healthy crops. Consequently, arable land around the world varies in the amount and type of fertilizer it needs. Fertilizers play an integral role in strengthening food security, and a supply of locally available fertilizer is needed in supporting global food systems in an ever-growing world. Brazil is one of the largest exporters of agricultural goods in the world. However, the country is vulnerable as it relies on importing more than 95% of its potash to support crop growth. Brazil Potash is developing a new potash project in Brazil to ensure a stable domestic source of this nutrient-rich fertilizer critical for global food security. Click here to learn more about fertilizer and food production in Brazil.