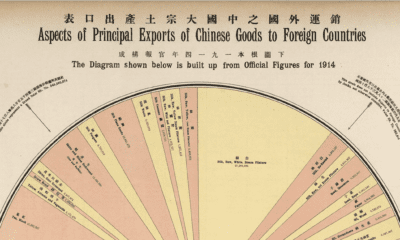
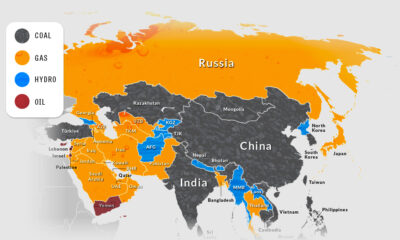
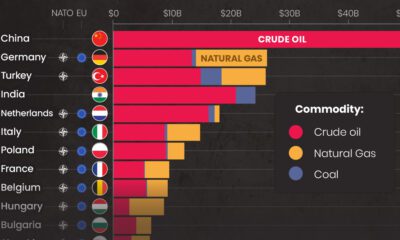
Last year, the UN revised these estimates, but the numbers it came up with were still well above 10 billion. These regular projections from the UN have been the status quo—until now. Plenty of signs have pointed to there being a population plateau, but recent research from the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME), published in The Lancet, suggests that the number of people on this planet may actually start to shrink well before the year 2100. Here’s a closer look at these complex projections.
UN vs. IHME Population Estimates
According to the UN, the world population is set to steadily rise over the years:
2030: 8.5 billion 2050: 9.7 billion 2100: 10.9 billion
In contrast, IHME paints a different picture. It projects the population to actually peak at 9.7 billion in 2064. Following this trajectory, there could be 8.8 billion people in 2100, approximately 2 billion fewer than previously thought. Various demographic factors are behind these differences—higher life expectancies, migration rates, and lower fertility rates. For this last factor, independent drivers including contraceptive access and higher educational attainment were also considered. A shifting age structure is also a key aspect of this transition. By 2100, over a quarter of the world or nearly 2.37 billion will be aged 65 years and above.
The Most Populous Countries in 2100
Amid all these demographic sea changes, which countries will come out on top? Despite an overall decline in numbers to 1.09 billion people in 2100, India moves up from second to first place on the population leaderboard. The populations of both India and China will begin to contract after the mid-century—and it’s predicted that China’s total population will drop by almost half to 732 million by 2100. Led by Nigeria, Sub-Saharan Africa is the only region that will continue to see growth by century’s end. In fact, four of the top 10 countries in the world in terms of population count will be located in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Tightly Packed Together
One final thing to consider is how population density may look in 2100, with many more people clustered in the same areas. For example, Nigeria is dealing with a land area nearly 11 times smaller than the U.S.—but it will have more than double the population. Regardless of how the future population count shakes out, it’s clear that these heavyweight countries will undergo significant transformation in the coming decades. on Even while political regimes across these countries have changed over time, they’ve largely followed a few different types of governance. Today, every country can ultimately be classified into just nine broad forms of government systems. This map by Truman Du uses information from Wikipedia to map the government systems that rule the world today.
Countries By Type of Government
It’s important to note that this map charts government systems according to each country’s legal framework. Many countries have constitutions stating their de jure or legally recognized system of government, but their de facto or realized form of governance may be quite different. Here is a list of the stated government system of UN member states and observers as of January 2023: Let’s take a closer look at some of these systems.
Monarchies
Brought back into the spotlight after the death of Queen Elizabeth II of England in September 2022, this form of government has a single ruler. They carry titles from king and queen to sultan or emperor, and their government systems can be further divided into three modern types: constitutional, semi-constitutional, and absolute. A constitutional monarchy sees the monarch act as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, giving them little to no real power. For example, King Charles III is the head of 15 Commonwealth nations including Canada and Australia. However, each has their own head of government. On the other hand, a semi-constitutional monarchy lets the monarch or ruling royal family retain substantial political powers, as is the case in Jordan and Morocco. However, their monarchs still rule the country according to a democratic constitution and in concert with other institutions. Finally, an absolute monarchy is most like the monarchies of old, where the ruler has full power over governance, with modern examples including Saudi Arabia and Vatican City.
Republics
Unlike monarchies, the people hold the power in a republic government system, directly electing representatives to form government. Again, there are multiple types of modern republic governments: presidential, semi-presidential, and parliamentary. The presidential republic could be considered a direct progression from monarchies. This system has a strong and independent chief executive with extensive powers when it comes to domestic affairs and foreign policy. An example of this is the United States, where the President is both the head of state and the head of government. In a semi-presidential republic, the president is the head of state and has some executive powers that are independent of the legislature. However, the prime minister (or chancellor or equivalent title) is the head of government, responsible to the legislature along with the cabinet. Russia is a classic example of this type of government. The last type of republic system is parliamentary. In this system, the president is a figurehead, while the head of government holds real power and is validated by and accountable to the parliament. This type of system can be seen in Germany, Italy, and India and is akin to constitutional monarchies. It’s also important to point out that some parliamentary republic systems operate slightly differently. For example in South Africa, the president is both the head of state and government, but is elected directly by the legislature. This leaves them (and their ministries) potentially subject to parliamentary confidence.
One-Party State
Many of the systems above involve multiple political parties vying to rule and govern their respective countries. In a one-party state, also called a single-party state or single-party system, only one political party has the right to form government. All other political parties are either outlawed or only allowed limited participation in elections. In this system, a country’s head of state and head of government can be executive or ceremonial but political power is constitutionally linked to a single political movement. China is the most well-known example of this government system, with the General Secretary of the Communist Party of China ruling as the de facto leader since 1989.
Provisional
The final form of government is a provisional government formed as an interim or transitional government. In this system, an emergency governmental body is created to manage political transitions after the collapse of a government, or when a new state is formed. Often these evolve into fully constitutionalized systems, but sometimes they hold power for longer than expected. Some examples of countries that are considered provisional include Libya, Burkina Faso, and Chad.