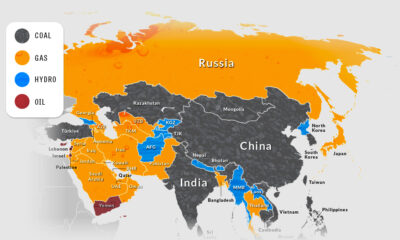
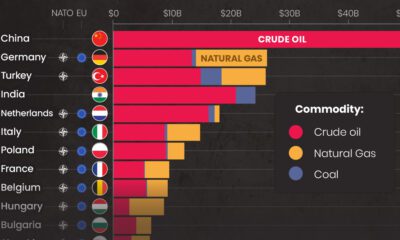
Global Firepower has released their ranking of combat tank fleet sizes for 2023, which we’ve visualized in this infographic. The ranking includes main battle tanks, like the U.S. M1A2 Abrams or the German Leopard 2, but also more lightly-armed medium and light tanks, like Thailand’s Stingray. The numbers do not include armored personnel carriers or infantry fighting vehicles.
Russia
Numbering 12,556 tanks, the Russian Federation has the largest fleet in their arsenal by far, from the workhorse T-72 series to the ultra-advanced T-14 Armata. This is more than the combined total of the number two and three spots, North Korea (6,645) and the U.S. (5,500).
But the headline number misses nuances in the composition of the Russian tank fleet. Of Russia’s nearly 13,000 active combat tanks, only a fraction are main battle tanks. A 2021 Russian source estimated that their operational main battle fleet was closer to 2,600 tanks, made up of T-72s, T-80s, and T-90s, with another 400 T-72 variants used as range tanks. On top of that, only one-quarter of those are considered modern tanks—T-72B3/B3M, T-80-BVM, and T-90A/M—that is, fitted with up-to-date fire control systems and sighting. That’s why, on top of poor morale, inadequate logistics, and inflexible tactics, Russia has struggled to perform on the Ukrainian battlefield despite having more than six times the number of tanks (12,556 vs. 1,890). According to a Pentagon official speaking in early November 2022, Russia has lost half of their tanks since their “special military operation” began on February 24, 2022. The conflict has also injured or killed thousands of civilians, displaced millions, and upended the post-Cold War security architecture.
North Korea
The world’s second-largest tank fleet belongs to North Korea, with a combat fleet of 6,645 tanks. The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea has maintained armored capabilities since the Korean War (1950-1953) when their first armored unit, the 105th Armored Brigade, participated in the invasion of South Korea armed with 120 Soviet-made T-34/85 tanks. After the war, the North Korean army rearmed with Soviet T-34/85s, and later with T-55s and Chinese-variant Type 59 tanks. Despite now being decades-old, these are likely still in service, alongside indigenous designs such as the Chonma-ho “Flying Horse” and the Pokpung-ho “Storm.” Ultimately, these tank forces are considered to be no match for modern main battle tanks despite their numbers. One military blogger called them “weak and pathetic”—especially when compared to South Korea’s fourth-generation K2 Black Panther, considered one of the most advanced tanks in the world.
China
China’s People’s Liberation Army (PLA) recently accelerated fleet modernization plans at the 20th Party Congress, in anticipation of the army’s centenary in 2027, but they still have a ways to go. Their fourth-place 4,950 combat tank fleet contains a mix of modern and obsolete tanks. China’s most modern main battle tank, the third-generation Type 99, is a domestic design. Armed with a 125mm diameter main gun—slightly larger than the NATO standard 120mm—and 1,500hp diesel engine, it is tough and maneuverable. An upgraded variant, the Type 99A, debuted in the mid-2000s.
There is some speculation that the Type 99/99A could rival the U.S. M1 Abrams. However, it still falls short of fourth-generation designs, such as Russia’s T-14 Armata, South Korea’s K2 Black Panther, or Japan’s Type 10. But thanks to a whopping $293 billion military budget, and significant industrial espionage, China’s defense industry is capable of producing military equipment at or near world-class standards, including tanks. The country even began testing unmanned tanks, including the Type 59 in 2018 and lightweight Type 15 in 2019.
Ukraine
Despite coming in at #13 with 1,890 tanks and initial predictions of a quick victory for Russian invaders, Ukrainian forces have successfully halted and then turned back their numerically superior foes. Originally armed with upgraded Soviet-era T-64s, as well as donations of T-72s from Poland and Czechia, Ukraine’s tank forces have swelled thanks to captured military equipment left behind by fleeing Russian soldiers. Oryx, a Dutch defense analysis website that has been tracking battlefield progress in Ukraine using open-source intelligence, estimates that 533 tanks, including several top-of-the-line T-90s, have been captured as of early 2023. According to a U.S. defense official, Ukraine may now have “more tanks in the battlefield than the Russians do.”
Arsenal of Democracy?
Looking ahead, Ukraine is asking for advanced Western main battle tanks, as it seeks to liberate the rest of its territory from Russia, including the Donbas and Crimea. NATO nations had been reluctant to take that step, as they were wary of further antagonizing Russia, but resistance seems to be diminishing. On January 4, 2023, France agreed to deliver AMX-10 RC light tanks to Ukraine, the first Western country to do so. On January 6, the U.S. and Germany each agreed to deliver armored vehicles of their own, the Bradley and Marder, respectively. And as another possible sign that sentiment has shifted, the UK has also said that it plans to donate a small number of Challenger 2 main battle tanks, while Poland has signaled their intention to donate Leopard 2 tanks (though the latter will need Germany’s permission to export). As the spring campaign season approaches, we will see how these new weapons affect the balance of tank fleets both on and off the battlefield. on Even while political regimes across these countries have changed over time, they’ve largely followed a few different types of governance. Today, every country can ultimately be classified into just nine broad forms of government systems. This map by Truman Du uses information from Wikipedia to map the government systems that rule the world today.
Countries By Type of Government
It’s important to note that this map charts government systems according to each country’s legal framework. Many countries have constitutions stating their de jure or legally recognized system of government, but their de facto or realized form of governance may be quite different. Here is a list of the stated government system of UN member states and observers as of January 2023: Let’s take a closer look at some of these systems.
Monarchies
Brought back into the spotlight after the death of Queen Elizabeth II of England in September 2022, this form of government has a single ruler. They carry titles from king and queen to sultan or emperor, and their government systems can be further divided into three modern types: constitutional, semi-constitutional, and absolute. A constitutional monarchy sees the monarch act as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, giving them little to no real power. For example, King Charles III is the head of 15 Commonwealth nations including Canada and Australia. However, each has their own head of government. On the other hand, a semi-constitutional monarchy lets the monarch or ruling royal family retain substantial political powers, as is the case in Jordan and Morocco. However, their monarchs still rule the country according to a democratic constitution and in concert with other institutions. Finally, an absolute monarchy is most like the monarchies of old, where the ruler has full power over governance, with modern examples including Saudi Arabia and Vatican City.
Republics
Unlike monarchies, the people hold the power in a republic government system, directly electing representatives to form government. Again, there are multiple types of modern republic governments: presidential, semi-presidential, and parliamentary. The presidential republic could be considered a direct progression from monarchies. This system has a strong and independent chief executive with extensive powers when it comes to domestic affairs and foreign policy. An example of this is the United States, where the President is both the head of state and the head of government. In a semi-presidential republic, the president is the head of state and has some executive powers that are independent of the legislature. However, the prime minister (or chancellor or equivalent title) is the head of government, responsible to the legislature along with the cabinet. Russia is a classic example of this type of government. The last type of republic system is parliamentary. In this system, the president is a figurehead, while the head of government holds real power and is validated by and accountable to the parliament. This type of system can be seen in Germany, Italy, and India and is akin to constitutional monarchies. It’s also important to point out that some parliamentary republic systems operate slightly differently. For example in South Africa, the president is both the head of state and government, but is elected directly by the legislature. This leaves them (and their ministries) potentially subject to parliamentary confidence.
One-Party State
Many of the systems above involve multiple political parties vying to rule and govern their respective countries. In a one-party state, also called a single-party state or single-party system, only one political party has the right to form government. All other political parties are either outlawed or only allowed limited participation in elections. In this system, a country’s head of state and head of government can be executive or ceremonial but political power is constitutionally linked to a single political movement. China is the most well-known example of this government system, with the General Secretary of the Communist Party of China ruling as the de facto leader since 1989.
Provisional
The final form of government is a provisional government formed as an interim or transitional government. In this system, an emergency governmental body is created to manage political transitions after the collapse of a government, or when a new state is formed. Often these evolve into fully constitutionalized systems, but sometimes they hold power for longer than expected. Some examples of countries that are considered provisional include Libya, Burkina Faso, and Chad.