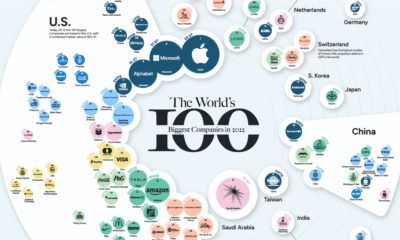
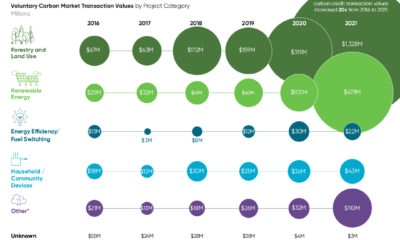
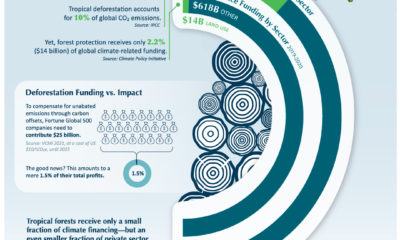
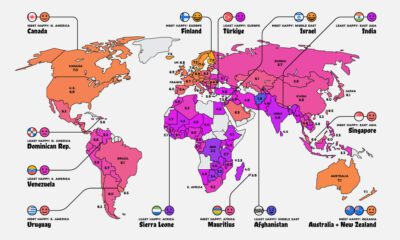
This week’s chart draws on a dataset from the Climate Accountability Institute, and highlights the companies which have been responsible for the most carbon emissions in the past half-century. Note: Carbon emissions are measured in MtCO₂e: Megatonnes of CO₂ equivalent (Millions).
The Sum of their Carbon Emissions
Between 1965-2017, the top 20 companies have contributed 480,169 MtCO₂e in total carbon emissions, or 35% of cumulative global emissions. This whopping amount is mostly from the combustion of their products—each company on this chart deals in fossil fuels. The largest contributor? Saudi Aramco, the national petroleum and natural gas company of Saudi Arabia. Saudi Aramco actually comes in first on another list as well—it’s the most profitable company, making over $304 million daily. However, this financial gain came at a significant cost: the state-owned giant’s operations have resulted in 59,262 MtCO₂e in carbon emissions since 1965. To put that into perspective, this total is more than six times China’s emissions in 2017 alone (9,838 MtCO₂e). Explore the full list of companies by location, who owns them, and their total 1965–2017 emissions count below:
A Greener Business Model?
According to the researchers, all the companies that show up in today’s chart bear some responsibility for knowingly accelerating the climate crisis even after proven scientific evidence. In fact, U.S.-based Exxon Mobil is currently on trial for misleading investors: the company downplayed the effect of climate change on its profitability, while internal calculations proved to be much larger. It also sowed public doubt on the immense impacts of rising greenhouse gas levels on the planet. Growing sustainability and environmental concerns threaten the viability of old business models for these corporations, causing many to pivot away from the fossil fuel focus. Take BP for example—originally named British Petroleum, the company embraced “Beyond Petroleum” as its new rallying cry. More recently, it launched a carbon footprint calculator and is committed to keeping its carbon emissions flat into 2025. However, the Climate Accountability Institute argues that more can still be done, with the researchers calling for these companies to reduce their fossil fuel production in the near future. Continued pressure on these “Big Oil” companies to peak their carbon emissions, and urgently increase their renewable energy investment, may help curb the climate crisis before it’s too late. Correction: A previous version of this article mistakenly reported the total cumulative value of carbon emissions in millions instead of trillions. Both the article and graphic have been updated to reflect the changes accurately. on
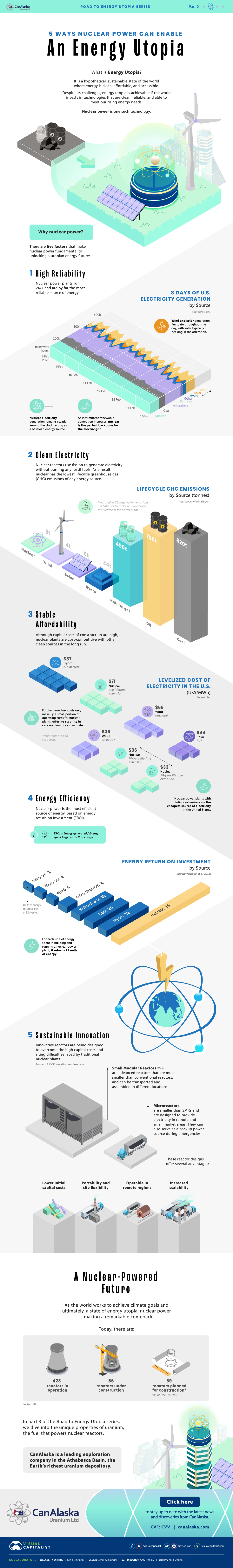
#1: High Reliability
Nuclear power plants run 24/7 and are the most reliable source of sustainable energy. Nuclear electricity generation remains steady around the clock throughout the day, week, and year. Meanwhile, daily solar generation peaks in the afternoon when electricity demand is usually lower, and wind generation depends on wind speeds.As the use of variable solar and wind power increases globally, nuclear offers a stable and reliable backbone for a clean electricity grid.
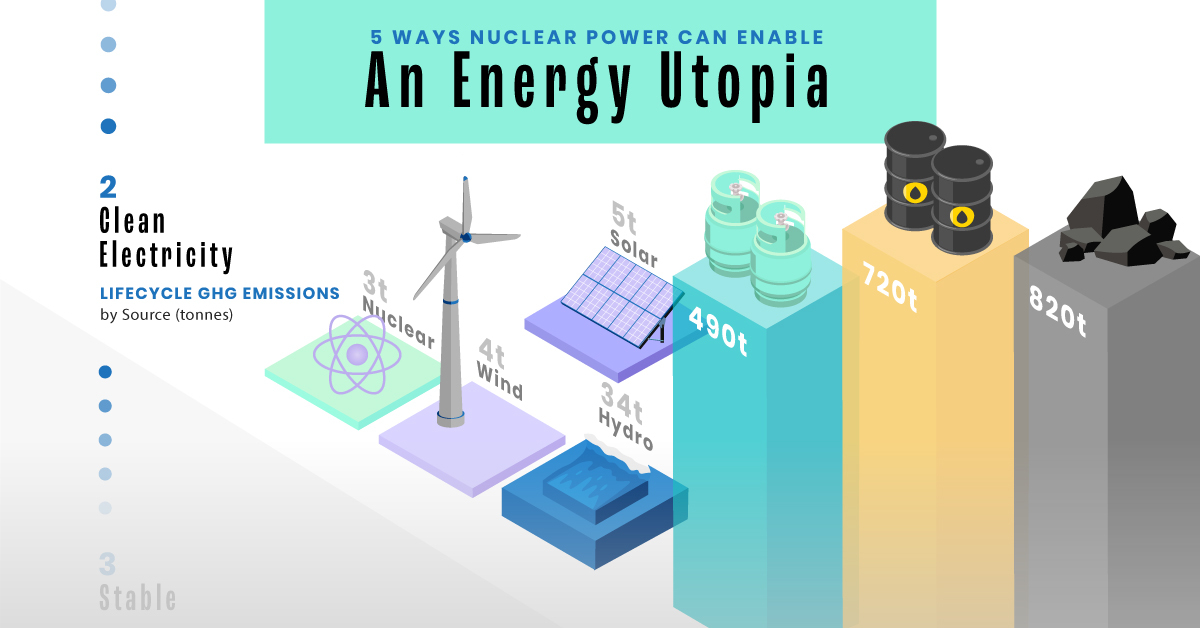
#2: Clean Electricity
Nuclear reactors use fission to generate electricity without any greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.Consequently, nuclear power is the cleanest energy source on a lifecycle basis, measured in CO2-equivalent emissions per gigawatt-hour (GWh) of electricity produced by a power plant over its lifetime. The lifecycle emissions from a typical nuclear power plant are 273 times lower than coal and 163 times lower than natural gas. Furthermore, nuclear is relatively less resource-intensive, allowing for lower supply chain emissions than wind and solar plants.
#3: Stable Affordability
Although nuclear plants can be expensive to build, they are cost-competitive in the long run. Most nuclear plants have an initial lifetime of around 40 years, after which they can continue operating with approved lifetime extensions. Nuclear plants with lifetime extensions are the cheapest sources of electricity in the United States, and 88 of the country’s 92 reactors have received approvals for 20-year extensions. Additionally, according to the World Nuclear Association, nuclear plants are relatively less susceptible to fuel price volatility than natural gas plants, allowing for stable costs of electricity generation.
#4: Energy Efficiency
Nuclear’s high energy return on investment (EROI) exemplifies its exceptional efficiency. EROI measures how many units of energy are returned for every unit invested in building and running a power plant, over its lifetime. According to a 2018 study by Weissbach et al., nuclear’s EROI is 75 units, making it the most efficient energy source by some distance, with hydropower ranking second at 35 units.
#5: Sustainable Innovation
New, advanced reactor designs are bypassing many of the difficulties faced by traditional nuclear plants, making nuclear power more accessible.
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are much smaller than conventional reactors and are modular—meaning that their components can be transported and assembled in different locations. Microreactors are smaller than SMRs and are designed to provide electricity in remote and small market areas. They can also serve as backup power sources during emergencies.
These reactor designs offer several advantages, including lower initial capital costs, portability, and increased scalability.
A Nuclear-Powered Future
Nuclear power is making a remarkable comeback as countries work to achieve climate goals and ultimately, a state of energy utopia. Besides the 423 reactors in operation worldwide, another 56 reactors are under construction, and at least 69 more are planned for construction. Some nations, like Japan, have also reversed their attitudes toward nuclear power, embracing it as a clean and reliable energy source for the future. CanAlaska is a leading exploration company in the Athabasca Basin, the Earth’s richest uranium depository. Click here to learn more now. In part 3 of the Road to Energy Utopia series, we explore the unique properties of uranium, the fuel that powers nuclear reactors.